(Press-News.org) Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-Suk) developed a smart monitoring system that applies digital sensing technology to maintain and manage small- and medium-sized aging bridges. This study was conducted as an international matching joint research funded by KICT, and established a foundation for technology diffusion to ASEAN countries through joint research with University of Transport and Communications (UTC) in Vietnam.
In general, bridge maintenance monitoring technology is applied to long-span bridges such as cable-stayed bridges and suspension bridges. This monitoring system consumes a lot of resources for design and installation, and the system configuration itself is complex, so there are limits to its application for maintenance of small- and medium-sized bridges.
Currently, the most actively used bridge monitoring system is operated based on analog measurement and sensing. Due to the nature of the signal, the analog method is vulnerable to electrical noise, so there is a high possibility of data quality deterioration, and there are limitations in effectively processing various types of signals collected from sensors. Additionally, because analog sensors require 1:1 wiring between the sensor and the receiver, the configuration complexity and installation cost increase dramatically as the system grows.
The digital sensing technique adopted by KICT to overcome the limitations and problems of analog sensors has a low possibility of data quality deterioration due to noise. It also has excellent data transmission speed and processing ability, making up for the shortcomings of analog sensing.
In addition, by using the BUS communication serial connection method, multiple sensor data can be integrated and transmitted through a single wire. This method is widely used in various applications due to its simplicity and economic efficiency. Furthermore, it has the advantage of complementing and replacing analog sensing in terms of simplification of system configuration.
In the case of Vietnam, which co-participated in the study, various transportation infrastructure, including bridges, are being built along with economic growth, but effective maintenance techniques are more required. Although overseas manpower and technology are being introduced to perform facility maintenance, only a few applications are being made to long-span bridges and large structures due to a limited maintenance budget and lack of technology and professional manpower. Safety monitoring for general maintenance of small- and medium-sized bridges has not been implemented, so it is necessary to introduce efficient monitoring techniques suited to local conditions.
The research team led by Dr. Dong-woo, Seo, at the Department of Structural Engineering Research of KICT, developed a monitoring system that can be efficiently applied to small- and medium-sized aging bridges through digital sensing techniques, and verified the performance of the system by demonstrating it on site with a research team at UTC in Vietnam. The measurement performance and local applicability of the based smart monitoring system were confirmed.
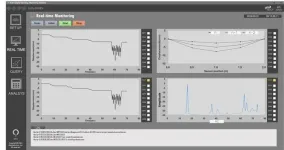
In particular, the smart monitoring technique developed by KICT can accurately calculate the vertical displacement of the target bridge with simple sensor placement and coordinate input. This is provided to the user in real time through a GUI (graphical user interface), and simple operations are required to operate the system and produce results.
As a result of local verification in Vietnam, the bridge vertical displacement and actual measured deflection results showed an accuracy of more than 95%. Also, the developed system and monitoring algorithm technology are transferred to ‘ATECH SOLUTION, Inc.’ for the commercialization.
Dr. Seo said, “The biggest advantage of the developed digital smart monitoring technique is user-friendliness,” and added, “Easy to use and economical monitoring technique through a simple system installment method using digital sensors and a GUI-based data analysis system.”
###
Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology, a government-funded research institute with 41 years of extensive research experience, is at the forefront of solving national issues that are directly related to the quality of the people’s life.
The research for this work was carried out under the KICT Research Program (project no. 20240400-001, Development of digital sensing based smart monitoring system for the maintenance of aged bridges in Vietnam) funded by the Ministry of Science and ICT.
END
Maintaining bridge safer; Digital sensing-based monitoring system
Establishing a foundation for local technology commercialization in Vietnam
2024-11-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
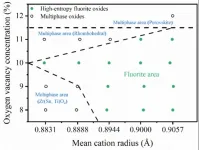
A novel approach for the composition design of high-entropy fluorite oxides with low thermal conductivity
2024-11-22
Current researches show that the standard deviation of the cationic radii, configuration entropy, or maintenance of Ce4+ have a certain impact on the formation of single-phase HEFOs, but the discovered rules are only applicable to partially synthesized material systems and have significant limitations. Furthermore, the range of elements used in the synthesized materials is relatively narrow, which restricts the potential to fully exploit the advantages of high-entropy materials and their vast compositional space.
“Inspired by the synthesized HEFOs and the stabilization mechanism ...
A groundbreaking new approach to treating chronic abdominal pain
2024-11-22
A research team at the University of Vienna, led by medicinal chemist Markus Muttenthaler, has developed a new class of oral peptide therapeutic leads for treating chronic abdominal pain. This groundbreaking innovation offers a safe, non-opioid-based solution for conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), which affect millions of people worldwide. The research results were recently published in the international edition of the renowned journal Angewandte Chemie.
An Innovative Approach to Pain Management
Current medications used to treat chronic abdominal pain often rely on opioids. ...
ECOG-ACRIN appoints seven researchers to scientific committee leadership positions
2024-11-22
The ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) announces new appointments of cancer researchers to lead committees in its expansive scientific program. ECOG-ACRIN is at the forefront of research spanning the cancer care spectrum, from early detection to management of advanced disease. These impactful appointments, which are effective immediately, underscore the group’s commitment to wide-ranging cancer research excellence and premier professional opportunities for researchers.
Angela M. DeMichele, MD, MSCE, is chair of the Breast Cancer Committee, succeeding ...
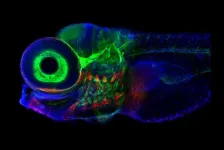
New model of neuronal circuit provides insight on eye movement
2024-11-22
Working with week-old zebrafish larva, researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and colleagues decoded how the connections formed by a network of neurons in the brainstem guide the fishes’ gaze. The study, published Nov. 22 in Nature Neuroscience, found that a simplified artificial circuit, based on the architecture of this neuronal system, can predict activity in the network. In addition to shedding light on how the brain handles short-term memory, the findings could lead to novel approaches for ...
Cooking up a breakthrough: Penn engineers refine lipid nanoparticles for better mRNA therapies
2024-11-22
Penn Engineers have cooked up a new way to improve mRNA delivery, developing an optimal “recipe” for ionizable lipids — key ingredients in lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), the molecules behind the COVID-19 vaccines and other innovative therapies. The method, described in Nature Biomedical Engineering, mirrors the iterative process of developing a culinary dish and may lead to safer, more effective mRNA vaccines and therapeutics.
Just as a chef perfects a dish by experimenting with flavors and textures, the researchers used an iterative process, testing variations to find the ideal structure ...
CD Laboratory at Graz University of Technology researches new semiconductor materials
2024-11-22
The global production of semiconductors is growing rapidly and with it the demand for primary products, especially crystalline silicon. However, its production is very energy-intensive and only half of the raw silicon used is actually utilised. This leads to large quantities of waste. In the Christian Doppler Laboratory for New Semiconductor Materials Based on Functionalized Hydrosilanes, which opened today, a team led by laboratory manager Michael Haas from the Institute of Inorganic Chemistry at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz) is carrying out research on alternatives. Funded by the Austrian Ministry of Economics and Labour, the researchers are working with ...
Animal characters can boost young children’s psychological development, study suggests
2024-11-22
Children’s books are full of animal characters whose antics capture the hearts and inspire the imaginations of their young readers.
However, a new study has shown that iconic characters such as Peter Rabbit – or Toad and Ratty from The Wind in the Willows – can also play an important role in children’s psychological development.
The research explored the extent to which different non-human characters influence children’s theory of mind skills, which include the ability to read and predict social changes in the environment through tone of voice, choice of words, or facial expression.
For ...
South Korea completes delivery of ITER vacuum vessel sectors
2024-11-22
The ITER vacuum vessel sectors, manufactured in South Korea, have been successfully delivered to the ITER construction site in Cadarache, France. South Korea was responsible for manufacturing 4 out of the 9 sectors that make up the ITER vacuum vessel. Starting with the delivery of the first sector in 2020, South Korea has now completed all four sectors, fulfilling its commitment to this significant international project.
The ITER vacuum vessel is a key component that sustains the ultra-high-temperature plasma required for nuclear fusion reactions by maintaining a high-vacuum environment. This large structure weighs 5,000 tons and consists of 9 sectors and ...
Global research team develops advanced H5N1 detection kit to tackle avian flu
2024-11-22
Singapore – The Diagnostics Development Hub (DxD Hub), a national platform hosted by the Agency for Science, Technology and Research (A*STAR), Singapore, in collaboration with the National Institute for Environmental Studies (NIES), Japan, and the A*STAR Bioinformatics Institute (A*STAR BII), has successfully developed Steadfast, an advanced diagnostic kit for detecting the highly pathogenic H5N1 Avian Influenza Virus (AIV). This development marks a significant breakthrough in avian influenza monitoring, reinforcing global efforts in pandemic preparedness.
Steadfast ...
From food crops to cancer clinics: Lessons in extermination resistance
2024-11-22
Just as crop-devouring insects evolve to resist pesticides, cancer cells can increase their lethality by developing resistance to treatment. In fact, most deaths from cancer are caused by the evolution of therapeutic resistance.
In a new review, Arizona State University researchers, working with colleagues around the world, explore how established agricultural pest management strategies could be adapted to address cancer therapy. The pioneering method opens new possibilities for controlling drug resistance and improving patient survival.
The research, which appears in the current issue of the journal Cancer Research, explores 10 pest management principles that could ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
Johns Hopkins scientists engineer nanoparticles able to seek and destroy diseased immune cells
A hidden immune circuit in the uterus revealed: Findings shed light on preeclampsia and early pregnancy failure
Google Earth’ for human organs made available online
AI assistants can sway writers’ attitudes, even when they’re watching for bias
Still standing but mostly dead: Recovery of dying coral reef in Moorea stalls
3D-printed rattlesnake reveals how the rattle is a warning signal
Despite their contrasting reputations, bonobos and chimpanzees show similar levels of aggression in zoos
Unusual tumor cells may be overlooked factors in advanced breast cancer
Plants pause, play and fast forward growth depending on types of climate stress
University of Minnesota scientists reveal how deadly Marburg virus enters human cells, identify therapeutic vulnerability
Here's why seafarers have little confidence in autonomous ships
MYC amplification in metastatic prostate cancer associated with reduced tumor immunogenicity
The gut can drive age-associated memory loss
Enhancing gut-brain communication reversed cognitive decline, improved memory formation in aging mice
Mothers exposure to microbes protect their newborn babies against infection
How one flu virus can hamper the immune response to another
Researchers uncover distinct tumor “neighborhoods”, with each cell subtype playing a specific role, in aggressive childhood brain cancer
Researchers develop new way to safely insert gene-sized DNA into the genome
Astronomers capture birth of a magnetar, confirming link to some of universe’s brightest exploding stars
New photonic device, developed by MIT researchers, efficiently beams light into free space
[Press-News.org] Maintaining bridge safer; Digital sensing-based monitoring systemEstablishing a foundation for local technology commercialization in Vietnam