(Press-News.org) About The Study: This serial cross-sectional study observed a significant decrease in positive reviews for health care facilities post-COVID. These findings underscore a disparity in patient experience, particularly in rural areas and areas with the highest proportions of Black and white residents.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Neil K. R. Sehgal, ME, email neilsehgal99@gmail.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.46890)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time http://jamanetwork.com/journals/jamanetworkopen/fullarticle/10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.46890?utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_term=112224
About JAMA Network Open: JAMA Network Open is an online-only open access general medical journal from the JAMA Network. On weekdays, the journal publishes peer-reviewed clinical research and commentary in more than 40 medical and health subject areas. Every article is free online from the day of publication.
END
Disparities by race and urbanicity in online health care facility reviews
JAMA Network Open
2024-11-22
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Exploring factors affecting workers' acquisition of exercise habits using machine learning approaches
2024-11-22
Tsukuba, Japan—Physical inactivity is the fourth leading mortality risk factor, following hypertension, smoking, and hyperglycemia. Therefore, acquiring an exercise habit is crucial to maintain and improve health. In Japan, Specific Health Guidance is provided to support the improvement of lifestyle habits, including exercise habits. To develop more efficient health guidance, it is important to identify factors that influence its effectiveness (e.g., characteristics and lifestyle of the target ...
Nano-patterned copper oxide sensor for ultra-low hydrogen detection
2024-11-22
Hydrogen is becoming an increasingly popular choice as we shift towards cleaner energy. It can be burned like traditional fuels, producing only water as a byproduct, and can generate electricity when used in fuel cells. However, as hydrogen production, use, and transportation increase, so do safety concerns. Hydrogen is highly flammable at concentrations as low as 4% and is odorless and colorless, making leaks challenging to detect.
To address these concerns, researchers led by Professor Yutaka Majima from Institute of Science Tokyo (Science Tokyo) have developed a sensor that detects hydrogen at ultra-low concentrations ...
Maintaining bridge safer; Digital sensing-based monitoring system
2024-11-22
Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Kim Byung-Suk) developed a smart monitoring system that applies digital sensing technology to maintain and manage small- and medium-sized aging bridges. This study was conducted as an international matching joint research funded by KICT, and established a foundation for technology diffusion to ASEAN countries through joint research with University of Transport and Communications (UTC) in Vietnam.
In general, bridge maintenance monitoring technology is applied to long-span bridges such as cable-stayed bridges and suspension bridges. This monitoring system consumes a lot of resources for design and installation, ...
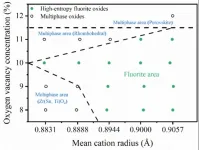
A novel approach for the composition design of high-entropy fluorite oxides with low thermal conductivity
2024-11-22
Current researches show that the standard deviation of the cationic radii, configuration entropy, or maintenance of Ce4+ have a certain impact on the formation of single-phase HEFOs, but the discovered rules are only applicable to partially synthesized material systems and have significant limitations. Furthermore, the range of elements used in the synthesized materials is relatively narrow, which restricts the potential to fully exploit the advantages of high-entropy materials and their vast compositional space.
“Inspired by the synthesized HEFOs and the stabilization mechanism ...
A groundbreaking new approach to treating chronic abdominal pain
2024-11-22
A research team at the University of Vienna, led by medicinal chemist Markus Muttenthaler, has developed a new class of oral peptide therapeutic leads for treating chronic abdominal pain. This groundbreaking innovation offers a safe, non-opioid-based solution for conditions such as irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) and inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), which affect millions of people worldwide. The research results were recently published in the international edition of the renowned journal Angewandte Chemie.
An Innovative Approach to Pain Management
Current medications used to treat chronic abdominal pain often rely on opioids. ...
ECOG-ACRIN appoints seven researchers to scientific committee leadership positions
2024-11-22
The ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) announces new appointments of cancer researchers to lead committees in its expansive scientific program. ECOG-ACRIN is at the forefront of research spanning the cancer care spectrum, from early detection to management of advanced disease. These impactful appointments, which are effective immediately, underscore the group’s commitment to wide-ranging cancer research excellence and premier professional opportunities for researchers.
Angela M. DeMichele, MD, MSCE, is chair of the Breast Cancer Committee, succeeding ...
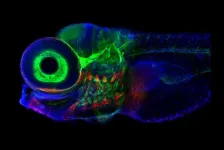
New model of neuronal circuit provides insight on eye movement
2024-11-22
Working with week-old zebrafish larva, researchers at Weill Cornell Medicine and colleagues decoded how the connections formed by a network of neurons in the brainstem guide the fishes’ gaze. The study, published Nov. 22 in Nature Neuroscience, found that a simplified artificial circuit, based on the architecture of this neuronal system, can predict activity in the network. In addition to shedding light on how the brain handles short-term memory, the findings could lead to novel approaches for ...
Cooking up a breakthrough: Penn engineers refine lipid nanoparticles for better mRNA therapies
2024-11-22
Penn Engineers have cooked up a new way to improve mRNA delivery, developing an optimal “recipe” for ionizable lipids — key ingredients in lipid nanoparticles (LNPs), the molecules behind the COVID-19 vaccines and other innovative therapies. The method, described in Nature Biomedical Engineering, mirrors the iterative process of developing a culinary dish and may lead to safer, more effective mRNA vaccines and therapeutics.
Just as a chef perfects a dish by experimenting with flavors and textures, the researchers used an iterative process, testing variations to find the ideal structure ...
CD Laboratory at Graz University of Technology researches new semiconductor materials
2024-11-22
The global production of semiconductors is growing rapidly and with it the demand for primary products, especially crystalline silicon. However, its production is very energy-intensive and only half of the raw silicon used is actually utilised. This leads to large quantities of waste. In the Christian Doppler Laboratory for New Semiconductor Materials Based on Functionalized Hydrosilanes, which opened today, a team led by laboratory manager Michael Haas from the Institute of Inorganic Chemistry at Graz University of Technology (TU Graz) is carrying out research on alternatives. Funded by the Austrian Ministry of Economics and Labour, the researchers are working with ...
Animal characters can boost young children’s psychological development, study suggests
2024-11-22
Children’s books are full of animal characters whose antics capture the hearts and inspire the imaginations of their young readers.
However, a new study has shown that iconic characters such as Peter Rabbit – or Toad and Ratty from The Wind in the Willows – can also play an important role in children’s psychological development.
The research explored the extent to which different non-human characters influence children’s theory of mind skills, which include the ability to read and predict social changes in the environment through tone of voice, choice of words, or facial expression.
For ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
Pregnancy complications impact women’s stress levels and cardiovascular risk long after delivery
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
[Press-News.org] Disparities by race and urbanicity in online health care facility reviewsJAMA Network Open