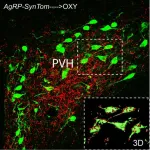
(Press-News.org) Researchers from the Vanderbilt University School of Medicine Basic Sciences have uncovered the first example of activity-dependent development of hypothalamic neural circuitry. Although previous research has shown that the hormone leptin acts directly on hunger neurons through leptin receptors to promote the development of neural circuitry, results that will be published in PNAS on Nov. 25 indicate that certain neurons that do not express leptin receptors are nonetheless sensitive to its activity.
The research, led by the lab of Richard Simerly, Louise B. McGavock Professor and professor of molecular physiology and biophysics, also supports a novel role for leptin in specifying the development of neural circuits involved in autonomic regulation and food intake. His lab found that silencing the activity of hunger neurons (called “AgRP” neurons) during the critical, postnatal period of neuronal circuitry development may exert lasting effects on the structure and function of circuits that control energy balance.
Leptin is a hormone that, in adults, regulates hunger by providing a sensation of satiety and helps maintain body weight on a long-term basis. In the weeks following birth, however, leptin also helps direct the formation of circuits that control homeostatic functions.
In their PNAS paper, the Simerly lab describes three primary results:
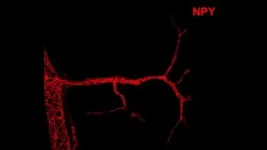
Leptin is required for the normal development of neural connections between hypothalamic oxytocin neurons, which link AgRP neurons with brainstem neurons that coordinate autonomic responses associated with feeding, even though oxytocin neurons in this pathway do not express leptin receptors.
The development of the neural circuits that link the hypothalamus and brainstem are dependent on the activity of leptin-sensing AgRP neurons during a postnatal, critical period of hypothalamic development.
Perturbing of the neural activity in hypothalamic neurons can permanently alter the functional regulation of brainstem regions that coordinate gastrointestinal processes related to feeding.
The results reported in this paper should expand our appreciation of the developmental role that hormones such as leptin play in specifying the organization of neural circuits that control essential functions related to metabolic health and expression of disease risk. Although we have known for decades that neural activity impacts the development of the visual system and other sensory systems, the role of neuronal activity in mediating actions of hormones has been largely overlooked in studies of hypothalamic development, where the focus has been on receptor-mediated control of gene expression.
“The possibility that neural circuits that control something as fundamental as energy balance are sensitive to activity alone during key periods of development suggests that there may be a wide variety of factors impacting hypothalamic development through this mechanism,” Simerly said. “Exposure of the developing brain to molecules that alter neural activity may have lasting consequences when building key neural circuits, which may have lasting effects on how the brain functions in health and disease.”
This research opens the door to the possibility of harnessing this mechanism to facilitate normal development and improve outcomes for populations who are at risk due to genetic abnormalities or harmful environmental exposure.
The work described here would not have been possible without the talent and tenacity of staff scientist and first author Jessica Biddinger. The contributions of collaborating author Julio Ayala, associate professor of molecular physiology and biophysics and director of the Vanderbilt Mouse Metabolic Phenotyping Center, were also integral to the work.
END
Vanderbilt authors find evidence that the hunger hormone leptin can direct neural development in a leptin receptor–independent manner
Researchers have uncovered the first example of activity-dependent development of hypothalamic neural circuitry. The work suggests a novel role for the hunger hormone in the development of neural circuits
2024-11-25
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
To design better water filters, MIT engineers look to manta rays
2024-11-25
Filter feeders are everywhere in the animal world, from tiny crustaceans and certain types of coral and krill, to various molluscs, barnacles, and even massive basking sharks and baleen whales. Now, MIT engineers have found that one filter feeder has evolved to sift food in ways that could improve the design of industrial water filters.
In a paper appearing this week in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, the team characterizes the filter-feeding mechanism of the mobula ray — a family of ...
Self-assembling proteins can be used for higher performance, more sustainable skincare products
2024-11-25
If you have a meticulous skincare routine, you know that personal skincare products (PSCPs) are a big business. The PSCP industry will reach $74.12 billion USD by 2027, with an annual growth rate of 8.64%. With such competition, companies are always looking to engineer themselves an edge, producing products that perform better without the downsides of current offerings.
In a new study published in ACS Applied Polymer Materials from the lab of Professor of Chemical and Biomolecular Engineering Jin Kim Montclare, researchers have created a novel protein-based gel as a potential ingredient in sustainable and high-performance PSCPs. This protein-based ...
Cannabis, maybe, for attention problems
2024-11-25
Cannabis — whether marijuana itself or various products containing cannabinoids and/or THC, the main psychoactive compound in weed – have been touted as panaceas for everything from anxiety and sleep problems to epilepsy and cancer pain.
Nursing researcher Jennie Ryan, PhD, at Thomas Jefferson University, studies the effects of cannabis on symptoms of attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD). Current medical guidelines for ADHD include medications such as Adderall and cognitive behavioral therapy. ...
Building a better path to recovery for OUD
2024-11-25
A new study led by Thomas Jefferson University researchers highlights critical healthcare gaps that hinder long-term recovery for people living with opioid use disorders (OUD) in Philadelphia.
The researchers conducted 13 focus groups with 70 participants accessing various types of OUD treatment. Participants reported several challenges, such as lengthy and restrictive assessment processes, inadequate operating hours and lack of sufficient withdrawal management. Participants also reported broader socio-economic needs, such as housing and income support, as barriers to their recovery.
Meghan Reed, PhD, MPH, senior ...
How climate change threatens this iconic Florida bird
2024-11-25
ITHACA, N.Y. – Because of warmer winters, Florida scrub-jays are now nesting one week earlier than they did in 1981. But these early birds are not always getting the worm.
A new analysis of data from a long-term study, published in Ornithological Advances, finds that warmer winters driven by climate change reduced the number of offspring raised annually by the federally threatened Florida scrub-jay by 25% since 1981.
Warmer temperatures, the scientists hypothesize, make jay nests susceptible to predation by snakes for a longer period of the Florida ...
Study reveals new factor involved in controlling calorie expenditure
2024-11-25
An international team of researchers has discovered a new component of the peripheral nervous system that acts by increasing energy metabolism in the body. The finding paves the way for the development of simpler and cheaper drugs to control obesity and weight gain, regardless of the amount of food ingested.
In an article published in the journal Nature, researchers from the University of Oxford in the United Kingdom and the Obesity and Comorbidities Research Center (OCRC) – funded by FAPESP and based at the State University of Campinas (UNICAMP) in Brazil – describe where and how this component ...
Managing forests with smart technologies
2024-11-25
Deforestation has remained a significant issue globally, with primary forests contributing to 16 per cent of the total tree cover loss in the last two decades, driven by climate change and intensive human activity. This threatens natural resources, biodiversity, and people’s quality of life. To protect forests, Lithuanian scientists, in collaboration with Swedish experts, have developed Forest 4.0, an intelligent forest data processing model integrating blockchain, Internet of Things (IoT), and Artificial Intelligence (AI) technologies. The system ...
Clinical trial finds that adding the chemotherapy pill temozolomide to radiation therapy improves survival in adult patients with a slow-growing type of brain tumor
2024-11-25
Both radiation and temozolomide, a generic chemotherapy treatment in pill form, have meaningful single-modality anti-tumor activity against slow-growing, low-grade gliomas. The randomized phase 3 trial E3F05 by the ECOG-ACRIN Cancer Research Group (ECOG-ACRIN) tested whether combined therapy using temozolomide alongside radiation therapy is more effective than radiation therapy alone in these patients. The trial followed 172 patients for more than 10 years, and its results have an immediate clinical impact by providing the first evidence from a randomized phase 3 trial that temozolomide improves long-term survival for these patients.
“We found that the 10-year ...
H.E.S.S. collaboration detects the most energetic cosmic-ray electrons and positrons ever observed
2024-11-25
The Universe teems with extreme environments, ranging from the very coldest temperatures to the highest energy sources possible. As a consequence, extreme objects such as supernova remnants, pulsars and active galactic nuclei are capable of emitting charged particles and gamma rays with incredibly high energies, so high that they exceed the energy produced by the nuclear fusion in stars by several orders of magnitude.
The gamma rays detected on Earth tell us a great deal about these sources, since they travel through space undisturbed. However, in the case of charged particles, ...
Novel supernova observations grant astronomers a peek into the cosmic past
2024-11-25
COLUMBUS, Ohio – An international team of researchers has made new observations of an unusual supernova, finding the most metal-poor stellar explosion ever observed.
This rare supernova, called 2023ufx, originated from the core collapse of a red supergiant star, exploded on the outskirts of a nearby dwarf galaxy. Results of the study showed that observations of both this supernova and the galaxy it was discovered in are of low metallicity, meaning they lack an abundance of elements heavier than hydrogen or helium.
Since the metals produced within supernovae ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Concrete sensor manufacturer Wavelogix receives $500,000 grant from National Science Foundation
California communities’ recovery time between wildfire smoke events is shrinking
Augmented reality job coaching boosts performance by 79% for people with disabilities
Medical debt associated with deferring dental, medical, and mental health care
AAI appoints Anand Balasubramani as Chief Scientific Programs Officer
Prior authorization may hinder access to lifesaving heart failure medications
Scholars propose transparency, credit and accountability as key principles in scientific authorship guidelines
Jeonbuk National University researchers develop DDINet for accurate and scalable drug-drug interaction prediction
IEEE researchers achieve 20x signal boost in cerebral blood flow monitoring with next-generation interferometric diffusing wave spectroscopy
IEEE researchers achieve low-power ultrashort mid-IR pulse compression
Deep-sea natural compound targets cancer cells through a dual mechanism
Antibiotics can affect the gut microbiome for several years
Study: Electrical stimulation can restore ability to move limbs, receive sensory feedback after spinal cord injury
Rice scientists unveil new tool to watch quantum behavior in action
Gene-based therapies poised for major upgrade thanks to Oregon State University research
Extreme heat has extreme effects r—but some like it hot
Blood marker for Alzheimer’s may also be useful in heart and kidney diseases
Climate extremes hinder early development in young birds
Climate policies: The swing voters that determine their fate
Building protection against infectious diseases with nanostructured vaccines
Oval orbit casts new light on black hole - neutron star mergers
Does online sports gambling affect substance use behaviors?
How do rapid socio-environmental transitions reshape cancer risk?
Do abortion bans affect birth rates and food-assistance costs?
Can artificial intelligence help reduce the carbon footprint of weather forecasting models?
Mangrove forests are short of breath
Low testosterone, high fructose: A recipe for liver disaster
SKKU research team unravels the origin of stochasticity, a key to next-generation data security and computing
Flexible polymer‑based electronics for human health monitoring: A safety‑level‑oriented review of materials and applications
Could ultrasound help save hedgehogs?
[Press-News.org] Vanderbilt authors find evidence that the hunger hormone leptin can direct neural development in a leptin receptor–independent mannerResearchers have uncovered the first example of activity-dependent development of hypothalamic neural circuitry. The work suggests a novel role for the hunger hormone in the development of neural circuits