(Press-News.org) Brain-wide association studies, which use magnetic resonance imaging to identify relationships between brain structure or function and human behavior or health, have faced criticism for producing results that often cannot be replicated by other researchers.
A new study published in Nature demonstrates that careful attention to study design can substantially improve the reliability of this type of research. For the study, Kaidi Kang, a biostatistics PhD student, Simon Vandekar, PhD, associate professor of Biostatistics, and colleagues analyzed data from more than 77,000 brain scans across 63 studies.
The investigators found that studies can achieve more dependable results by strategically selecting study participants to ensure a wider range of the characteristics being measured. For example, when studying age-related brain changes, including more participants at both younger and older age ranges produces more reliable findings than random sampling or concentrating on middle-aged participants.
The research also revealed that collecting multiple brain scans from the same person over time can improve reliability for some brain measurements but may actually reduce reliability for others, depending on what is being studied.
Based on their findings the authors offer practical guidance for scientists designing future brain imaging studies, potentially helping them obtain reliable results with fewer participants.
Kang and Vandekar were joined by investigators from six institutions in the U.S. and the United Kingdom. Others on the study from Vanderbilt are Jiangmei Xiong, MS, Megan Jones, Ran Tao, PhD, and Jonathan Schildcrout, PhD. The study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grants R01MH123563, R01MH132934, R01MH133843, K23DA057486, R01MH120482, R01MH112847, R01MH113550, R01EB022573, R37MH125829).
END
New research points way to more reliable brain studies
Study in Nature identifies research strategies for tying brain function and structure to behavior and health
2024-11-27
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
‘Alzheimer’s in dish’ model shows promise for accelerating drug discovery
2024-11-27
A decade ago, researchers introduced a new model for studying Alzheimer’s disease. Known as “Alzheimer’s in a dish,” the model uses cultures of mature brain cells suspended in a gel to recapitulate what takes place in the human brain over 10 to 13 years in just six weeks. But does the model truly produce the same changes that take place in patients? In a new study, researchers from Mass General Brigham, in collaboration with colleagues at Beth Israel Deaconess Medical Center (BIDMC), created an algorithm to assess, in an unbiased manner, how well models of Alzheimer’s disease ...
Ultraprocessed food intake and psoriasis
2024-11-27
About The Study: The results of this study showed an association between high ultraprocessed food intake and active psoriasis status. After adjustments for age, body mass index (BMI), alcohol intake, and comorbidities, the results remained significant, suggesting that ultraprocessed food intake has a proinflammatory action separate from high BMI.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Emilie Sbidian, MD, PhD, email emilie.sbidian@aphp.fr.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Race and ethnicity, gender, and promotion of physicians in academic medicine
2024-11-27
About The Study: The findings of this study indicate that preferential promotion of white men within academic medicine continues to persist in the new millennium, with racially and ethnically diverse women experiencing greater underpromotion. To achieve a workforce that reflects the diversity of the U.S. population, this study suggests that academic medicine needs to transform its culture and practices surrounding faculty appointments and promotions.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lauren Clark, MS, email lclark5@kumc.edu.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Testing and masking policies and hospital-onset respiratory viral infections
2024-11-27
About The Study: In this study, stopping universal masking and SARS-CoV-2 testing was associated with a significant increase in hospital-onset respiratory viral infections relative to community infections. Restarting the masking of health care workers was associated with a significant decrease.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Theodore R. Pak, MD, PhD, email tpak@mgh.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.48063)
Editor’s ...
A matter of life and death
2024-11-27
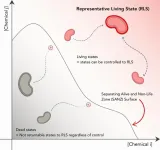
Cellular death is a fundamental concept in the biological sciences. Given its significance though, its definition depends on the context in which it takes place, and lacks a general mathematical definition. Researchers from the University of Tokyo propose a new mathematical definition of death based on whether a potentially dead cell can return to a predefined “representative state of living,” which are the states of being that we can confidently call “alive.” The researchers’ work could be useful for biological researchers and future medical research.
While it’s ...
Huge cost savings from more efficient use of CDK4/6 inhibitors in metastatic breast cancer reported in SONIA study
2024-11-27
On November 27, the prestigious journal Nature will publish the results of an innovative breast cancer research project from the Netherlands. This study, the SONIA trial, showed that delaying and shortening the duration of a specific anti-cancer therapy (CDK4/6 inhibitors) in patients with hormone receptor-positive advanced breast cancer leads to similar survival outcomes, while reducing toxicity and achieving substantial cost reductions: over 45 million euros per year in the Netherlands and over 5 billion dollars in the United States. This is the first time an efficiency study like this has been conducted in collaboration with Dutch health ...
What a gut fungus reveals about symbiosis and allergy
2024-11-27
A fungus discovered in the mouse stomach may hold a key to fungal evolution within the gastrointestinal tract, according to new research led by Weill Cornell Medicine investigators. The finding suggests that preclinical studies until now have overlooked a major influencer of mouse physiology.
Scientists recently have come to appreciate the importance, for human health and disease, of microbes—often called “commensals”—that naturally dwell in the gut. Bacterial commensals, for example, are known to have ...
Insilico Medicine recognized by Endeavor Venture Group & Mount Sinai Health System with Showcase AI and Biotech Innovation Award
2024-11-27
Insilico Medicine (“Insilico”), a clinical-stage generative artificial intelligence (AI)-driven drug discovery company, is proud to be recognized for the impact on the future of drug discovery and development, as a distinguished honoree of the Showcase AI and Biotech Innovation Award on November 13, 2024, at the Fifth Endeavor Venture Group & Mount Sinai Health System Healthcare AI and Technology Investor Summit. Michelle Chen, Ph.D., Chief Business Officer of Insilico Medicine, received the award on behalf of the company.
Delivered ...
ESMO Asia Congress 2024: Event Announcement
2024-11-27
Lugano, Switzerland, 27 November 2024 – The ESMO Asia Congress 2024 is the annual event dedicated to multidisciplinary oncology in the Asian region. It will feature a broad spectrum of topics in cancer research, including novel treatment modalities, in-depth discussions on the management of specific cancer types, pan-Asian trials and subgroup analyses of cutting-edge studies relevant for the patients in the area. Data will be presented and discussed by leading experts from across Asia and beyond. The congress will be held onsite in Singapore from 6-8 December, with no virtual option available.
Programme highlights
Subgroup ...
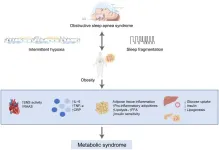
The pathophysiological relationship and treatment progress of obstructive sleep apnea syndrome, obesity, and metabolic syndrome
2024-11-27
Cardiovascular diseases remain a leading cause of mortality globally, particularly among individuals with both obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) and metabolic syndrome (MetS). These two conditions exacerbate each other, creating a vicious cycle that increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Understanding the pathophysiological relationship between OSA and MetS is crucial for developing effective prevention and treatment strategies. This review explores current knowledge on the connection between OSA and MetS and discusses the progress in treatment ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Major discovery sparks chain reactions in medicine, recyclable plastics - and more
Microbial clues uncover how wild songbirds respond to stress
Researchers develop AI tools for early detection of intimate partner violence
Researchers develop AI tool to predict patients at risk of intimate partner violence
New research outlines pathway to achieve high well-being and a safe climate without economic growth
How an alga makes the most of dim light
Race against time to save Alpine ice cores recording medieval mining, fires, and volcanoes
Inside the light: How invisible electric fields drive device luminescence
A folding magnetic soft sheet robot: Enabling precise targeted drug delivery via real-time reconfigurable magnetization
Sylvester Cancer Tip Sheet for March 2026
New tools and techniques accelerate gallium oxide as next-generation power semiconductor
Researchers discover seven different types of tension
Report calls for AI toy safety standards to protect young children
VR could reduce anxiety for people undergoing medical procedures
Scan that makes prostate cancer cells glow could cut need for biopsies
Mechanochemically modified biochar creates sustainable water repellent coating and powerful oil adsorbent
New study reveals hidden role of larger pores in biochar carbon capture
Specialist resource centres linked to stronger sense of belonging and attainment for autistic pupils – but relationships matter most
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
[Press-News.org] New research points way to more reliable brain studiesStudy in Nature identifies research strategies for tying brain function and structure to behavior and health