(Press-News.org) Social media posts containing misinformation evoke more moral outrage than posts with trustworthy information, and that outrage facilitates the spread of misinformation, according to a new study by Killian McLoughlin and colleagues. The researchers also found that people are more likely to share outrage-evoking misinformation without reading it first. The findings suggest that attempts to mitigate the online spread of misinformation by encouraging people to check its accuracy before sharing may not be successful, the researchers note. McLoughlin et al. conducted eight studies using U.S. data from Facebook and Twitter over multiple time periods, along with two behavioral experiments, to learn more about outrage related to the spread of misinformation. In the study, outrage is defined as the mix of anger and disgust triggered by perceived moral transgressions. The researchers found that outrage-evoking posts facilitated “the spread of misinformation at least as strongly as trustworthy news.” People may share outrageous misinformation without checking its accuracy because sharing is a way to signal their moral position or membership in certain groups, note McLoughlin et al. The way that social media platforms rank content to show to users likely also plays a part in the spread of misinformation, they add: “Since outrage is associated with increased engagement online, outrage-evoking misinformation may be likely to spread farther in part because of the algorithmic amplification of engaging content,” they write. “This is important because algorithms may up-rank news articles associated with outrage, even if a user intended to express outrage toward the article for containing misinformation.”
END
Moral outrage helps misinformation spread through social media
2024-11-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
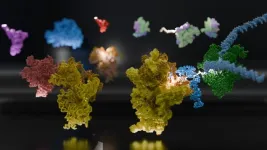
U-M, multinational team of scientists reveal structural link for initiation of protein synthesis in bacteria
2024-11-28
IMAGE
ANN ARBOR—Within a cell, DNA carries the genetic code for building proteins.
To build proteins, the cell makes a copy of DNA, called mRNA. Then, another molecule called a ribosome reads the mRNA, translating it into protein. But this step has been a visual mystery: scientists previously did not know how the ribosome attaches to and reads mRNA.
Now, a team of international scientists, including University of Michigan researchers, have used advanced microscopy to image how ribosomes recruit to mRNA while it's being transcribed by an enzyme called RNA polymerase, or RNAP. Their results, which examine the process in bacteria, are published in the journal ...
New paper calls for harnessing agrifood value chains to help farmers be climate-smart
2024-11-28
Washington DC, November 28, 2024: The global food system is uniquely vulnerable to climate impacts, making adaptation of paramount importance. While contributing roughly one-third of total anthropogenic emissions, food systems around the world fortunately also hold immense potential for mitigation through improved practices and land use. A new article published today in Science emphasizes the critical role of agrifood value chains (AVCs) in supporting both adaptation and mitigation at the farm level.
Authored by Johan Swinnen (International Food Policy Research Institute), Loraine Ronchi (World Bank Group), and Thomas Reardon (Michigan State University and IFPRI), the paper pushes back ...
Preschool education: A key to supporting allophone children
2024-11-28
Learning French while also developing language skills in one’s mother tongue is no easy task. As a result, allophone children often face learning and communication difficulties in kindergarten, which can negatively impact their educational journey. However, solutions are emerging.
According to a study led by Sylvana Côté, preschool education services significantly help bridge the gap between children whose mother tongue is French and those for whom French is a second or even a third language.
Professor Côté, from the School of Public Health at the Université de Montréal (ESPUM), is the director of the Observatory ...
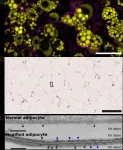
CNIC scientists discover a key mechanism in fat cells that protects the body against energetic excess
2024-11-28
A team at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC), led by Professor Miguel Ángel del Pozo Barriuso, who heads the Mechanoadaptation and Caveolae Biology group at the CNIC, has identified an essential mechanism in fat cells (adipocytes) that enables them to enlarge safely to store energy. This process avoids tissue damage and protects the body from the toxic effects of accumulating fat molecules (lipids) in inappropriate places. The results, published in Nature Communications, signify a major advance in the understanding of metabolic diseases. Moreover, this discovery ...
Chemical replacement of TNT explosive more harmful to plants, study shows
2024-11-28
The increased use of a chemical compound to replace TNT in explosive devices has a damaging and long lasting effect on plants, new research has shown.
In recent years, TNT has started to be replaced with DNAN, but until now very little was known about how this substance impacts the environment and how long it can remain in the soil.
Researchers at the University of York have been studying the environmental impact of the explosive, TNT, for more than a decade. They have shown that the chemical compound, which is used by the military around the world, remains in ...
Scientists reveal possible role of iron sulfides in creating life in terrestrial hot springs
2024-11-28
An international team of scientists recently published a study highlighting the potential role of iron sulfides in the formation of life in early Earth’s terrestrial hot springs. According to the researchers, the sulfides may have catalyzed the reduction of gaseous carbon dioxide into prebiotic organic molecules via nonenzymatic pathways.
This work, which appeared in Nature Communications, offers new insights into Earth’s early carbon cycles and prebiotic chemical reactions, underscoring the significance of iron sulfides in supporting the terrestrial hot ...
Hormone therapy affects the metabolic health of transgender individuals
2024-11-28
New research from Karolinska Institutet shows that long-term sex hormone treatment in transgender individuals can lead to significant changes in body composition and risk factors for cardiovascular disease, particularly in transgender men. The study is published in the Journal of Internal Medicine.
“We saw that transgender men treated with testosterone increased their muscle volume by an average of 21 percent over six years, but also that the amount of abdominal fat increased by 70 percent,” says Tommy Lundberg, docent at the Department of Laboratory Medicine, Karolinska Institutet. “In addition, they had more liver ...
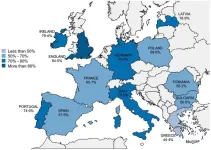
Survey of 12 European countries reveals the best and worst for smoke-free homes
2024-11-28
Seven out of ten homes in Europe are smoke-free, according to a major survey published today (Thursday) in ERJ Open Research [1]. However, some countries have come further than others in protecting children and adults from second-hand tobacco smoke in the home.
Greece came out bottom of the 12 countries in the survey, with smoking allowed in more than half of homes. In Romania, Bulgaria and Spain more than four in ten homes allow smoking to take place. England scored the highest out of the 12, with more than eight in ten homes smoke-free, with Ireland, Latvia and Italy following next.
The researchers say that the ...
First new treatment for asthma attacks in 50 years
2024-11-28
An injection given during some asthma and COPD attacks is more effective than the current treatment of steroid tablets, reducing the need for further treatment by 30%.
The findings, published today in The Lancet Respiratory Medicine, could be “game-changing” for millions of people with asthma and COPD around the world, scientists say.
Asthma attacks and COPD flare-ups (also called exacerbations) can be deadly. Every day in the UK four people with asthma and 85 people with COPD will tragically die. Both conditions are also very common, in the UK someone has an asthma attack every ...
Certain HRT tablets linked to increased heart disease and blood clot risk
2024-11-28
Certain hormone replacement therapy (HRT) tablets containing both oestrogen and progestogen are associated with a higher risk of heart disease and rare but serious blood clots known as venous thromboembolism (VTE) in women around the age of menopause, finds a study from Sweden published by The BMJ today.
Another HRT tablet called tibolone was associated with an increased risk of heart disease, heart attack and stroke, but not blood clots, “highlighting the diverse effects of different hormone combinations and administration methods on the risk of cardiovascular disease,” say the researchers.
HRT is used to relieve menopausal ...