(Press-News.org) The thirteen-lined ground squirrel doesn’t drink during its winter hibernation, even though systems throughout its body are crying out for water. Madeleine Junkins and colleagues now show that the squirrel suppresses the need to quench its thirst by reducing the activity of a set of neurons in highly vascularized brain structures called circumventricular organs, which act as a specialized connection point between brain, blood circulation and cerebrospinal fluid. The study by Junkins et al. helps explain how some hibernating animals ignore the powerful physiological drive to seek out water for months at a time. During hibernation, the squirrels cycle between periods of torpor (inactivity and suppressed metabolism) and interbout arousal (higher core temperatures and some movement in the burrow). Although squirrels in the interbout stage are deficient in fluids and are sensitive to some kidney and nervous system cues to regulate fluid homeostasis, they are less sensitive to other hormonal thirst cues. The researchers found that the baseline activity of thirst neurons in the circumventricular organs drops sharply during the months of winter hibernation, suppressing their sensitivity to physiological cues for thirst.
END
These hibernating squirrels could use a drink—but don’t feel the thirst
Summary author: Becky Ham
2024-11-28
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New footprints offer evidence of co-existing hominid species 1.5 million years ago
2024-11-28
Newly discovered footprints show that at least two hominid species were walking through the muddy submerged edge of a lake in Kenya’s Turkana Basin at the same time, about 1.5 million years ago. The find from the famous hominid fossil site of Koobi Fora described by Kevin Hatala and colleagues provides physical evidence for the co-existence of multiple hominid lineages in the region—something that has only been inferred previously from overlapping dates for scattered fossils. Based on information on gait and stance gleaned from the footprints, Hatala et al. think that the two species were Homo erectus and Paranthropus ...
Moral outrage helps misinformation spread through social media
2024-11-28
Social media posts containing misinformation evoke more moral outrage than posts with trustworthy information, and that outrage facilitates the spread of misinformation, according to a new study by Killian McLoughlin and colleagues. The researchers also found that people are more likely to share outrage-evoking misinformation without reading it first. The findings suggest that attempts to mitigate the online spread of misinformation by encouraging people to check its accuracy before sharing may not be successful, the researchers ...
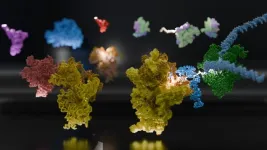
U-M, multinational team of scientists reveal structural link for initiation of protein synthesis in bacteria
2024-11-28
IMAGE
ANN ARBOR—Within a cell, DNA carries the genetic code for building proteins.
To build proteins, the cell makes a copy of DNA, called mRNA. Then, another molecule called a ribosome reads the mRNA, translating it into protein. But this step has been a visual mystery: scientists previously did not know how the ribosome attaches to and reads mRNA.
Now, a team of international scientists, including University of Michigan researchers, have used advanced microscopy to image how ribosomes recruit to mRNA while it's being transcribed by an enzyme called RNA polymerase, or RNAP. Their results, which examine the process in bacteria, are published in the journal ...
New paper calls for harnessing agrifood value chains to help farmers be climate-smart
2024-11-28
Washington DC, November 28, 2024: The global food system is uniquely vulnerable to climate impacts, making adaptation of paramount importance. While contributing roughly one-third of total anthropogenic emissions, food systems around the world fortunately also hold immense potential for mitigation through improved practices and land use. A new article published today in Science emphasizes the critical role of agrifood value chains (AVCs) in supporting both adaptation and mitigation at the farm level.
Authored by Johan Swinnen (International Food Policy Research Institute), Loraine Ronchi (World Bank Group), and Thomas Reardon (Michigan State University and IFPRI), the paper pushes back ...
Preschool education: A key to supporting allophone children
2024-11-28
Learning French while also developing language skills in one’s mother tongue is no easy task. As a result, allophone children often face learning and communication difficulties in kindergarten, which can negatively impact their educational journey. However, solutions are emerging.
According to a study led by Sylvana Côté, preschool education services significantly help bridge the gap between children whose mother tongue is French and those for whom French is a second or even a third language.
Professor Côté, from the School of Public Health at the Université de Montréal (ESPUM), is the director of the Observatory ...
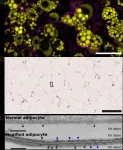
CNIC scientists discover a key mechanism in fat cells that protects the body against energetic excess
2024-11-28
A team at the Centro Nacional de Investigaciones Cardiovasculares (CNIC), led by Professor Miguel Ángel del Pozo Barriuso, who heads the Mechanoadaptation and Caveolae Biology group at the CNIC, has identified an essential mechanism in fat cells (adipocytes) that enables them to enlarge safely to store energy. This process avoids tissue damage and protects the body from the toxic effects of accumulating fat molecules (lipids) in inappropriate places. The results, published in Nature Communications, signify a major advance in the understanding of metabolic diseases. Moreover, this discovery ...
Chemical replacement of TNT explosive more harmful to plants, study shows
2024-11-28
The increased use of a chemical compound to replace TNT in explosive devices has a damaging and long lasting effect on plants, new research has shown.
In recent years, TNT has started to be replaced with DNAN, but until now very little was known about how this substance impacts the environment and how long it can remain in the soil.
Researchers at the University of York have been studying the environmental impact of the explosive, TNT, for more than a decade. They have shown that the chemical compound, which is used by the military around the world, remains in ...
Scientists reveal possible role of iron sulfides in creating life in terrestrial hot springs
2024-11-28
An international team of scientists recently published a study highlighting the potential role of iron sulfides in the formation of life in early Earth’s terrestrial hot springs. According to the researchers, the sulfides may have catalyzed the reduction of gaseous carbon dioxide into prebiotic organic molecules via nonenzymatic pathways.
This work, which appeared in Nature Communications, offers new insights into Earth’s early carbon cycles and prebiotic chemical reactions, underscoring the significance of iron sulfides in supporting the terrestrial hot ...
Hormone therapy affects the metabolic health of transgender individuals
2024-11-28
New research from Karolinska Institutet shows that long-term sex hormone treatment in transgender individuals can lead to significant changes in body composition and risk factors for cardiovascular disease, particularly in transgender men. The study is published in the Journal of Internal Medicine.
“We saw that transgender men treated with testosterone increased their muscle volume by an average of 21 percent over six years, but also that the amount of abdominal fat increased by 70 percent,” says Tommy Lundberg, docent at the Department of Laboratory Medicine, Karolinska Institutet. “In addition, they had more liver ...
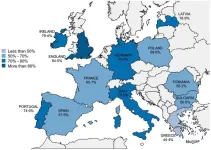
Survey of 12 European countries reveals the best and worst for smoke-free homes
2024-11-28
Seven out of ten homes in Europe are smoke-free, according to a major survey published today (Thursday) in ERJ Open Research [1]. However, some countries have come further than others in protecting children and adults from second-hand tobacco smoke in the home.
Greece came out bottom of the 12 countries in the survey, with smoking allowed in more than half of homes. In Romania, Bulgaria and Spain more than four in ten homes allow smoking to take place. England scored the highest out of the 12, with more than eight in ten homes smoke-free, with Ireland, Latvia and Italy following next.
The researchers say that the ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
How much sleep do teens get? Six-seven hours.
Patients regain weight rapidly after stopping weight loss drugs – but still keep off a quarter of weight lost
GLP-1 diabetes drugs linked to reduced risk of addiction and substance-related death
Councils face industry legal threats for campaigns warning against wood burning stoves
GLP-1 medications get at the heart of addiction: study
Global trauma study highlights shared learning as interest in whole blood resurges
Almost a third of Gen Z men agree a wife should obey her husband
Trapping light on thermal photodetectors shatters speed records
New review highlights the future of tubular solid oxide fuel cells for clean energy systems
Pig farm ammonia pollution may indirectly accelerate climate warming, new study finds
Modified biochar helps compost retain nitrogen and build richer soil organic matter
First gene regulation clinical trials for epilepsy show promising results
Life-changing drug identified for children with rare epilepsy
Husker researchers collaborate to explore fear of spiders
Mayo Clinic researchers discover hidden brain map that may improve epilepsy care
NYCST announces Round 2 Awards for space technology projects
How the Dobbs decision and abortion restrictions changed where medical students apply to residency programs
Microwave frying can help lower oil content for healthier French fries
In MS, wearable sensors may help identify people at risk of worsening disability
Study: Football associated with nearly one in five brain injuries in youth sports
Machine-learning immune-system analysis study may hold clues to personalized medicine
A promising potential therapeutic strategy for Rett syndrome
How time changes impact public sentiment in the U.S.
Analysis of charred food in pot reveals that prehistoric Europeans had surprisingly complex cuisines
As a whole, LGB+ workers in the NHS do not experience pay gaps compared to their heterosexual colleagues
How cocaine rewires the brain to drive relapse
Mosquito monitoring through sound - implications for AI species recognition
UCLA researchers engineer CAR-T cells to target hard-to-treat solid tumors
New study reveals asynchronous land–ocean responses to ancient ocean anoxia
Ctenophore research points to earlier origins of brain-like structures
[Press-News.org] These hibernating squirrels could use a drink—but don’t feel the thirstSummary author: Becky Ham