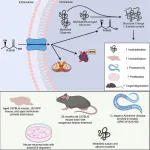
(Press-News.org) As part of the COVID-19 International Research Team, researchers at the Johns Hopkins Kimmel Cancer Center, Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia, the University of Pittsburgh and Weill Cornell Medicine discovered a novel cause of cytokine storm — the extreme inflammatory response associated with increased risk of death in COVID-19 infection.
Their findings were reported Nov. 27 in the online issue of Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
In an intensive genomic search for causes of cytokine storm, the research team used autopsy samples obtained from 40 patients who died from COVID-19. They performed genome analysis on samples taken from multiple sites, including the lung, heart, liver, kidney, lymph nodes in the chest that initially filter the virus, and the nasal cavity where the virus enters the body.
They zeroed in on some 50 upregulated immune genes in the samples obtained from nasal swabs and followed through in the genomics for the autopsy tissues.
Stephen Baylin, M.D., Virginia and D.K. Ludwig Professor for Cancer Research and co-senior author, and first author Michael Topper, Ph.D., Evelyn Grollman Glick Scholar and instructor in oncology, were
familiar with many of the genes as part of the inflammasome, a protein signaling network they helped define that is activated to rid the body of virus or bacteria-infected cells.
“Some of the same genes involved in overactivation of the inflammasome appear to be key immune gene regulators of the hyperinflammatory process that leads to a new view of how these subsequently activate the “cytokine storm syndrome” and severely damage multiple tissues, says Topper.
The genes should turn on and off, Baylin explains, but when they stay on, it results in cytokine storm, the very severe inflammation that can be lethal to patients with COVID.
Essentially, immune genes in the nasal cavity, where the virus enters, send signals downstream through a system called renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system (RAAS) to initiate cytokine storm.
RAAS, a hormone system that normally turns on and off to help regulate blood pressure, body fluids and electrolytes, is the spark that pushes the immune response into overdrive, the researchers found, compromising the infection-fighting function of lymph nodes and causing severe damage to the lungs, kidneys, heart, liver and other organs.
“Markers of this inflammatory response in patients who die from COVID-19 can be detected in the blood, making it possible to identify patients at risk for developing the most severe and deadly COVID-19 infections and pointing to possible ways to intervene with drugs,” says Baylin.
The researchers also believe their findings may have implications for long COVID, a chronic condition following COVID-19 infection that is characterized by a wide range of symptoms, including fever, fatigue, coughing, chest pain, heart palpitations, headaches, joint and muscle pain, gastrointestinal issues and more. This is a focus of ongoing research, Topper and Baylin say.
In addition to Baylin and Topper, other researchers participating in the investigation are co-first author Joseph W. Guarnieri and co-corresponding authors with Baylin: Afshin Behesti (leader of COVIRT) and Douglas C. Wallace, Simon Pollett, Deanne Taylor, Eve Syrkin Wurtele, Robert E. Schwartz, Christopher E. Mason, Jeffrey A. Haltom, Amy Chadburn, Henry Cope, Justin Frere, Julia An, Alain Borczuk, Saloni Sinha, JangKeun Kim, Jiwoon Park, Daniel Butler, Cem Meydan, Jonathan Foox, Yaron Bram, Stephanie A. Richard, Nusrat J. Epsi, Brian Agan, Josh G. Chenoweth, Mark P. Simons, David Tribble, Timothy Burgess, Clifton Dalgard, Mark T. Heise, Nathaniel J. Moorman, Victoria K. Baxter, Emily A. Madden, Sharon A. Taft-Benz, Elizabeth J. Anderson, Wes A. Sanders, Rebekah J. Dickmander, Katherine Beigel, Gabrielle A. Widjaja, Kevin A. Janssen, Timothy Lie, Deborah G. Murdock, Alessia Angelin, Yentli E. Soto Albrecht, Arnold Z. Olali, Zimu Cen, Joseph Dybas, Waldemar Priebe, Mark R. Emmett, Sonja M. Best, Maya Kelsey Johnson, Nidia S. Trovao, Kevin B. Clark, Victoria Zaksas, Robert Meller, Peter Grabham, Jonathan C. Schisler, and Pedro M. Moraes-Vieira.
This researach was supported by the Division of Intramural Research, NIAID, NIH grant to Sonja Best, and DOD W81XWH-21-1-0128 grant awarded to Douglas Wallace, the Bill & Melinda Gates Foundation Grant INV-046722 awarded to Douglas Wallace, Adelson Medical Research Foundation, Hodson Scholar Foundation, Glick scholar awards and Samuel Waxman Research Foundation awarded to Stephen Baylin from the Defense Health Program (HU00012020067 and HU00012120103), the National Institute of Allergy and Infectious Disease (HU00011920111), and the USU RESPONSE award (HU00012020070).
Robert Schwartz is on the scientific advisory board of Miromatrix, Inc. and Lime Therapeutics, and is a consultant for Alnylam, Inc. Douglas Wallace is on the scientific advisory boards of Pano Therapeutics,
Inc. and Medical Excellent Capital. Simon Pollett, Mark Simons, Timothy Burgess, and Deanne Taylor report that the Uniformed Services University (USU) Infectious Diseases Clinical Research Program (IDCRP), a U.S. Department of Defense institution, and the Henry M. Jackson Foundation for the Advancement of Military Medicine, Inc (HJF) were funded under a Cooperative Research and Development Agreement to conduct an unrelated phase III COVID-19 monoclonal antibody immunoprophylaxis trial sponsored by AstraZeneca. The HJF, in support of the USU IDCRP, was funded by the Department of Defense Joint Program Executive Office for Chemical, Biological, Radiological, and Nuclear Defense to augment the conduct of an unrelated phase III vaccine trial sponsored by AstraZeneca. Both trials were part of the U.S. Government’s COVID-19 response. Neither is related to the work presented here. All other authors declare no competing interests for this research.
END
A cause of hyperinflammatory response in lethal COVID-19 identified
2024-12-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sleep deprivation in dementia: Heart disease, diabetes, anxiety, and thyroid disorders
2024-12-02
"Sleep disturbances are a significant concern in individuals with dementia, affecting their overall health and quality of life, as well as that of their family members and caregivers.”
BUFFALO, NY- December 2, 2024 – A new review was published on the cover of Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as "Aging (Albany NY)" and "Aging-US" by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 21, titled, “Sleep deprivation in dementia comorbidities: focus on cardiovascular disease, diabetes, anxiety/depression and thyroid disorders.”
The review, authored by Upasana Mukherjee, Ujala Sehar, Malcolm Brownell, and ...
Temporary tattoo printed directly on the scalp offers easy, hair-friendly solution for measuring brainwaves
2024-12-02
For the first time, scientists have invented a liquid ink that doctors can print onto a patient’s scalp to measure brain activity. The technology, presented December 2 in the Cell Press journal Cell Biomaterials, offers a promising alternative to the cumbersome process currently used for monitoring brainwaves and diagnosing neurological conditions. It also has the potential to enhance non-invasive brain-computer interface applications.
“Our innovations in sensor design, biocompatible ink, and high-speed printing pave the way for future on-body manufacturing of electronic tattoo sensors, with broad applications both within and beyond ...
Ketone bodies: more than energy, they are powerful signaling metabolites that clean up damaged proteins
2024-12-02
Ketone bodies, produced by the body to provide fuel during fasting, have roles in regulating cellular processes and aging mechanisms beyond energy production. Research at the Buck Institute shows that ketone bodies can best be understood as powerful signaling metabolites affecting brain function in aging and Alzheimer’s disease. A new study demonstrates that ketone bodies and similar metabolites have profound effects on the proteome and protein quality control in the brain. Publishing in Cell Chemical Biology, Buck Institute scientists, ...
Implementation of electronic triggers to identify diagnostic errors in emergency departments
2024-12-02
About The Study: In this retrospective medical record review study, rules-based e-triggers were useful for post hoc detection of missed opportunities in diagnosis in emergency department visits. Interventions to target emergency department work system factors are urgently needed to support patient-clinician encounters and minimize harm from diagnostic errors.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Hardeep Singh, MD, MPH, email hardeeps@bcm.edu.
To access the embargoed study: ...
Characterizing services advertised on crisis pregnancy center websites
2024-12-02
About The Study: The findings of this study suggest the need for greater scrutiny of crisis pregnancy center practices, particularly their service provision, provider qualifications, and how these conform with regulations or best practices. A key concern is their promotion of abortion pill reversal, which lacks FDA approval or scientific support and may cause harm.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, John W. Ayers, PhD, MA, email ayers.john.w@gmail.com.
To ...
Study of crisis pregnancy centers reveals misleading and dangerous claims
2024-12-02
La Jolla, Calif. (December 2, 2024) — A new study from scientists at the University of California San Diego introduces a powerful new approach to understanding the operation of crisis pregnancy centers, non-profit organizations dedicated to an anti-abortion agenda. The study published in JAMA Internal Medicine provides the first account of the practices of crisis pregnancy centers (CPC) operating in the United States.
"While our study shows crisis pregnancy centers provide valuable community services, like parenting classes, there is a clear need for consumer safety measures to prevent the promotion and use of their ...
Researchers deal a blow to theory that Venus once had liquid water on its surface
2024-12-02
A team of astronomers has found that Venus has never been habitable, despite decades of speculation that our closest planetary neighbour was once much more like Earth than it is today.
The researchers, from the University of Cambridge, studied the chemical composition of the Venusian atmosphere and inferred that its interior is too dry today for there ever to have been enough water for oceans to exist at its surface. Instead, the planet has likely been a scorching, inhospitable world for its entire history.
The results, reported in the journal Nature Astronomy, have implications for understanding Earth’s uniqueness, and for the search for life on planets outside ...
Photonic processor could enable ultrafast AI computations with extreme energy efficiency
2024-12-02
The deep neural network models that power today’s most demanding machine-learning applications have grown so large and complex that they are pushing the limits of traditional electronic computing hardware.
Photonic hardware, which can perform machine-learning computations with light, offers a faster and more energy-efficient alternative. However, there are some types of neural network computations that a photonic device can’t perform, requiring the use of off-chip electronics or other techniques that hamper speed and efficiency.
Building on a decade of research, scientists from ...
Researchers create a new organoid with all key pancreas cells
2024-12-02
Researchers from the Organoid group (previously Clevers group) at the Hubrecht Institute have developed a new organoid that mimics the human fetal pancreas, offering a clearer view of its early development. The researchers were able to recreate a complete structure that includes the three key cell types in the pancreas, which previous organoids couldn’t fully mimic. Notably, the team identified a new stem cell that develops into the three cell types. These findings, published in Cell ...
Stimulating hypothalamus restores walking in paralyzed patients
2024-12-02
Researchers at EPFL and Lausanne University Hospital (CHUV), led by professors Grégoire Courtine and Jocelyne Bloch, have achieved a major milestone in the treatment of spinal cord injuries (SCI). By applying deep brain stimulation (DBS) to an unexpected region in the brain—the lateral hypothalamus (LH)—the team has improved the recovery of lower limb movements in two individuals with partial SCI, greatly improving their autonomy and well-being.
Wolfgang Jäger, a 54-year-old from Kappel, Austria, has been in a wheelchair ...