(Press-News.org) A team of astronomers has found that Venus has never been habitable, despite decades of speculation that our closest planetary neighbour was once much more like Earth than it is today.
The researchers, from the University of Cambridge, studied the chemical composition of the Venusian atmosphere and inferred that its interior is too dry today for there ever to have been enough water for oceans to exist at its surface. Instead, the planet has likely been a scorching, inhospitable world for its entire history.
The results, reported in the journal Nature Astronomy, have implications for understanding Earth’s uniqueness, and for the search for life on planets outside our Solar System. While many exoplanets are Venus-like, the study suggests that astronomers should narrow their focus to exoplanets which are more like Earth.
From a distance, Venus and Earth look like siblings: it is almost identical in size and is a rocky planet like Earth. But up close, Venus is more like an evil twin: it is covered with thick clouds of sulfuric acid, and its surface has a mean temperature close to 500°C.
Despite these extreme conditions, for decades, astronomers have been investigating whether Venus once had liquid oceans capable of supporting life, or whether some mysterious form of ‘aerial’ life exists in its thick clouds now.
“We won’t know for sure whether Venus can or did support life until we send probes at the end of this decade,” said first author Tereza Constantinou, a PhD student at Cambridge’s Institute of Astronomy. “But given it likely never had oceans, it is hard to imagine Venus ever having supported Earth-like life, which requires liquid water.”
When searching for life elsewhere in our galaxy, astronomers focus on planets orbiting their host stars in the habitable zone, where temperatures are such that liquid water can exist on the planet’s surface. Venus provides a powerful limit on where this habitable zone lies around a star.
“Even though it’s the closest planet to us, Venus is important for exoplanet science, because it gives us a unique opportunity to explore a planet that evolved very differently to ours, right at the edge of the habitable zone,” said Constantinou.
There are two primary theories on how conditions on Venus may have evolved since its formation 4.6 billion years ago. The first is that conditions on the surface of Venus were once temperate enough to support liquid water, but a runaway greenhouse effect caused by widespread volcanic activity caused the planet to get hotter and hotter. The second theory is that Venus was born hot, and liquid water has never been able to condense at the surface.
“Both of those theories are based on climate models, but we wanted to take a different approach based on observations of Venus’ current atmospheric chemistry,” said Constantinou. “To keep the Venusian atmosphere stable, then any chemicals being removed from the atmosphere should also be getting restored to it, since the planet’s interior and exterior are in constant chemical communication with one another.”
The researchers calculated the present destruction rate of water, carbon dioxide and carbonyl sulphide molecules in Venus’ atmosphere, which must be restored by volcanic gases to keep the atmosphere stable.
Volcanism, through its supply of gases to the atmosphere, provides a window into the interior of rocky planets like Venus. As magma rises from the mantle to the surface, it releases gases from the deeper portions of the planet.
On Earth, volcanic eruptions are mostly steam, due to our planet’s water-rich interior. But, based on the composition of the volcanic gases necessary to sustain the Venusian atmosphere, the researchers found that volcanic gases on Venus are at most six percent water. These dry eruptions suggest that Venus’s interior, the source of the magma that releases volcanic gases, is also dehydrated.
At the end of this decade, NASA’s DAVINCI mission will be able to test and confirm whether Venus has always been a dry, inhospitable planet, with a series of flybys and a probe sent to the surface. The results could help astronomers narrow their focus when searching for planets that can support life in orbit around other stars in the galaxy.
“If Venus was habitable in the past, it would mean other planets we have already found might also be habitable,” said Constantinou. “Instruments like the James Webb Space Telescope are best at studying the atmospheres of planets close to their host star, like Venus. But if Venus was never habitable, then it makes Venus-like planets elsewhere less likely candidates for habitable conditions or life.
“We would have loved to find that Venus was once a planet much closer to our own, so it’s kind of sad in a way to find out that it wasn’t, but ultimately it’s more useful to focus the search on planets that are mostly likely to be able to support life – at least life as we know it.”
The research was supported in part by the Science and Technology Facilities Council (STFC), part of UK Research and Innovation (UKRI).
END
Researchers deal a blow to theory that Venus once had liquid water on its surface
2024-12-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Photonic processor could enable ultrafast AI computations with extreme energy efficiency
2024-12-02
The deep neural network models that power today’s most demanding machine-learning applications have grown so large and complex that they are pushing the limits of traditional electronic computing hardware.
Photonic hardware, which can perform machine-learning computations with light, offers a faster and more energy-efficient alternative. However, there are some types of neural network computations that a photonic device can’t perform, requiring the use of off-chip electronics or other techniques that hamper speed and efficiency.
Building on a decade of research, scientists from ...
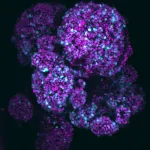
Researchers create a new organoid with all key pancreas cells
2024-12-02
Researchers from the Organoid group (previously Clevers group) at the Hubrecht Institute have developed a new organoid that mimics the human fetal pancreas, offering a clearer view of its early development. The researchers were able to recreate a complete structure that includes the three key cell types in the pancreas, which previous organoids couldn’t fully mimic. Notably, the team identified a new stem cell that develops into the three cell types. These findings, published in Cell ...
Stimulating hypothalamus restores walking in paralyzed patients
2024-12-02
Researchers at EPFL and Lausanne University Hospital (CHUV), led by professors Grégoire Courtine and Jocelyne Bloch, have achieved a major milestone in the treatment of spinal cord injuries (SCI). By applying deep brain stimulation (DBS) to an unexpected region in the brain—the lateral hypothalamus (LH)—the team has improved the recovery of lower limb movements in two individuals with partial SCI, greatly improving their autonomy and well-being.
Wolfgang Jäger, a 54-year-old from Kappel, Austria, has been in a wheelchair ...
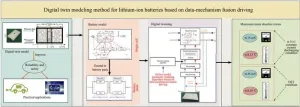
Pioneering digital twin model elevates lithium-ion battery performance and safety
2024-12-02
Source: Beijing Institute of Technology Press
Lithium-ion batteries are celebrated for their high specific energy, long service life, and low self-discharge rates. However, ensuring their reliability and safety under various operating conditions is critical for their continued success in industrial applications. Digital twin technology, which creates a virtual replica of a physical entity, offers a promising solution by enabling real-time monitoring and optimization of battery performance. This technology facilitates interactive feedback, data fusion, and iterative ...
A breakthrough in battery capacity degradation analysis and knee point prediction
2024-12-02
Analyzing capacity degradation characteristics and accurately predicting the knee point of capacity are crucial for the safety management of lithium-ion batteries (LIBs). A recent breakthrough study presented by researchers from Shandong University introduces a knee point prediction method based on neural network. This advanced method can help us clarify the degradation mechanism and predict the knee point.
The study focuses on battery life, which is the result of multiple coupling aging mechanisms affected by multiple factors. It is significantly necessary to clarify the mechanism for the capacity degradation at each stage and possess the ability to detect the knee point. It can not only ...
Newfound mechanism may explain why some cancer treatments boost risk of heart disease
2024-12-02
A cancer therapy that prompts the body’s immune defenses against viruses and bacteria to attack tumors can make patients more vulnerable to heart attack and stroke. A possible explanation for this side effect is that the treatment interferes with immune regulation in the heart’s largest blood vessels, a new study suggests.
Led by researchers at NYU Langone Health and its Perlmutter Cancer Center, the new work focused on a potent class of cancer-fighting drugs called immune checkpoint inhibitors. These medications ...
Research alert: How artificial intelligence could automate genomics research
2024-12-02
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have demonstrated that large language models (LLMs), such as GPT-4, could help automate functional genomics research, which seeks to determine what genes do and how they interact. The most frequently-used approach in functional genomics, called gene set enrichment, aims to determine the function of experimentally-identified gene sets by comparing them to existing genomics databases. However, more interesting and novel biology is often beyond the scope of established databases. Using artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze gene ...
‘I don’t feel your pain’: How alcohol increases aggression
2024-12-02
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Alcohol’s ability to increase people’s pain threshold is one reason that drinking also leads to more aggressive behavior, a new study suggests.
Researchers found that the less pain that study participants felt after drinking an alcoholic beverage, the more pain they were willing to inflict on someone else.
“We’ve all heard the idiom ‘I feel your pain,’” said study co-author Brad Bushman, professor of communication at The Ohio State University.
“But if intoxicated people can’t feel their own pain, they might be less likely to feel ...
The Microprocessor inside you
2024-12-02
It’s a big year for microRNAs. The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine went to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun, who discovered the first microRNA in 1993. Today, we know that humans make more than 1,000 different microRNAS. These molecules are critical for building and maintaining healthy bodies, so it’s crucial that they’re made the right way. Errors in microRNA manufacture can put us at risk for developmental disorders, cancer, or neurodegenerative disease.
To learn how cells accurately generate a mind-boggling array of microRNAs, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor and HHMI Investigator Leemor ...
Landmark World Drought Atlas reveals systemic nature of hazard risks, underlines need for national plans, international cooperation
2024-12-02
Riyadh, Saudi Arabia — As record-breaking droughts are becoming a new normal around the globe, the UN Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) and the European Commission Joint Research Centre (JRC) launch the most comprehensive global publication on drought risks and solutions as an urgent wake-up call for world leaders and citizens.
The landmark new World Drought Atlas depicts the systemic nature of drought risks through dozens of maps, infographics, and case studies. It illustrates how drought risks are interconnected across sectors like energy, agriculture, river transport, and international trade and how they can trigger cascading effects, fueling inequalities and ...