(Press-News.org) Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have demonstrated that large language models (LLMs), such as GPT-4, could help automate functional genomics research, which seeks to determine what genes do and how they interact. The most frequently-used approach in functional genomics, called gene set enrichment, aims to determine the function of experimentally-identified gene sets by comparing them to existing genomics databases. However, more interesting and novel biology is often beyond the scope of established databases. Using artificial intelligence (AI) to analyze gene sets could save scientists many hours of intensive labor and bring science one step closer to automating one of the most widely used methods for understanding how genes work together to influence biology.
Testing five different LLMs, the researchers found that GPT-4 was the most successful, achieving a 73% accuracy rate in identifying common functions of curated gene sets from a commonly used genomics database. When asked to analyze random gene sets, GPT-4 refused to provide a name in 87% of cases, demonstrating the potential of GPT-4 to analyze gene sets with minimal hallucination. GPT-4 was also capable of providing detailed narratives to support its naming process.
While further research is needed to fully explore the potential of LLMs in automating functional genomics, the study highlights the need for continued investment in the development of LLMs and their applications in genomics and precision medicine. To support this, the researchers created a web portal to help other researchers incorporate LLMs into their functional genomics workflows. More broadly, the findings also demonstrate the power of AI to revolutionize the scientific process by synthesizing complex information to generate new, testable hypotheses in a fraction of the time.
The study, published in Nature Methods, was led by Trey Ideker, Ph.D., a professor at UC San Diego School of Medicine and UC San Diego Jacobs School of Engineering, Dexter Pratt, Ph.D., a software architect in Ideker’s group, and Clara Hu, a biomedical sciences doctoral candidate in Ideker’s group. The study was funded, in part, by the National Institutes of Health.
# # #
END
Research alert: How artificial intelligence could automate genomics research
2024-12-02
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
‘I don’t feel your pain’: How alcohol increases aggression
2024-12-02
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Alcohol’s ability to increase people’s pain threshold is one reason that drinking also leads to more aggressive behavior, a new study suggests.
Researchers found that the less pain that study participants felt after drinking an alcoholic beverage, the more pain they were willing to inflict on someone else.
“We’ve all heard the idiom ‘I feel your pain,’” said study co-author Brad Bushman, professor of communication at The Ohio State University.
“But if intoxicated people can’t feel their own pain, they might be less likely to feel ...
The Microprocessor inside you
2024-12-02
It’s a big year for microRNAs. The 2024 Nobel Prize in Physiology or Medicine went to Victor Ambros and Gary Ruvkun, who discovered the first microRNA in 1993. Today, we know that humans make more than 1,000 different microRNAS. These molecules are critical for building and maintaining healthy bodies, so it’s crucial that they’re made the right way. Errors in microRNA manufacture can put us at risk for developmental disorders, cancer, or neurodegenerative disease.
To learn how cells accurately generate a mind-boggling array of microRNAs, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Professor and HHMI Investigator Leemor ...
Landmark World Drought Atlas reveals systemic nature of hazard risks, underlines need for national plans, international cooperation
2024-12-02
Riyadh, Saudi Arabia — As record-breaking droughts are becoming a new normal around the globe, the UN Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD) and the European Commission Joint Research Centre (JRC) launch the most comprehensive global publication on drought risks and solutions as an urgent wake-up call for world leaders and citizens.
The landmark new World Drought Atlas depicts the systemic nature of drought risks through dozens of maps, infographics, and case studies. It illustrates how drought risks are interconnected across sectors like energy, agriculture, river transport, and international trade and how they can trigger cascading effects, fueling inequalities and ...
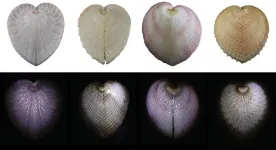
To build better fiber optic cables, ask a clam
2024-12-02
DURHAM, N.C. -- Since the first fiber optic cables rolled out in the 1970s, they’ve become a major part of everything from medical devices to high-speed internet and cable TV. But as it turns out, one group of marine mollusks was way ahead of us.
A new study reveals that clams called heart cockles -– so-named because of their heart-shaped shells -- have unique structures in their shells that act like fiber optic cables to convey specific wavelengths of light into the bivalves’ tissues.
Researchers from Duke University and Stanford University used electron and laser microscopy and computer simulations ...
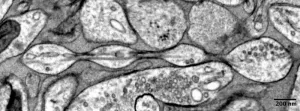
Study may reverse century-old understanding of the shape of ‘arms’ on mammals’ brain cells
2024-12-02
**EMBARGOED FOR RELEASE UNTIL MONDAY, DEC. 2, AT 5 A.M.**
Biology textbooks may need a revision, say Johns Hopkins Medicine scientists, who present new evidence that an armlike structure of mammalian brain cells may be a different shape than scientists have assumed for more than a century.
Their study on mouse brain cells shows that the cells’ axons — the armlike structures that reach out and exchange information with other brain cells — are not the cylindrical tubes often pictured in books and on websites ...
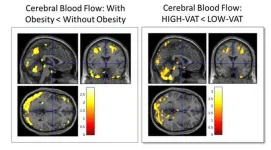
Hidden fat predicts Alzheimer’s 20 years ahead of symptoms
2024-12-02
CHICAGO – Researchers have linked a specific type of body fat to the abnormal proteins in the brain that are hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease up to 20 years before the earliest symptoms of dementia appear, according to a study being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA). The researchers emphasized that lifestyle modifications targeted at reducing this fat could influence the development of Alzheimer’s disease.
“This crucial result was discovered because we investigated Alzheimer’s disease pathology as ...
Countertop workers exposed to serious lung disease
2024-12-02
CHICAGO – Durable and attractive, engineered stone countertops are a popular feature in modern American kitchens, but the workers who build them are risking their health. A growing number of these countertop workers are developing silicosis, a serious and long-term lung disease, according to a study being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“This is a new and emerging epidemic, and we must increase awareness of this disease process so we can avoid delays in diagnosis and treatment for our patients,” ...
Higher ratio of plant protein to animal protein may improve heart health
2024-12-02
Embargoed for release: Monday, December 2, 4:00 AM ET
Key points:
In a 30-year study of American adults’ diets, those who consumed the highest ratio of plant-based protein to animal-based protein had a 19% lower risk of cardiovascular disease (CVD) and a 27% lower risk of coronary heart disease (CHD) compared to those who consumed the lowest ratio.
According to the researchers, the findings suggest that a 1:2 ratio of plant to animal protein is effective in preventing CVD—and that an even higher ratio (1:1.3) may be needed to protect against CHD.
While global dietary guidelines recommend higher intake of plant ...
Lung cancer screening CTs find coronary artery disease in 83% of cases
2024-12-02
Lung cancer screening with low-dose chest computed tomography (CT) may detect more than just lung cancer. As new research in CMAJ (Canadian Medical Association Journal) https://www.cmaj.ca/lookup/doi/10.1503/cmaj.231602 shows, these CTs can identify coronary artery calcium, a strong risk factor for coronary artery disease (CAD), in patients without cardiac symptoms.
“Lung cancer screening, although primarily geared towards reducing deaths from lung cancer, also has an opportunity to help tackle the second ...
Consumers face barriers to embracing ethical fashion, psychologist warns
2024-12-02
Consumers are likely to continue making poor fashion choices unless eco-friendly choices become more accessible, according to a leading psychologist.
Carolyn Mair says brands must do more to promote sustainable clothing by making it more accessible to all, and by doing more to educate the public about mindful consumption.
Meaningful reforms to the current model of fashion production, in which garments are made from raw materials then discarded, have lagged, says Dr Mair who is also a fashion business consultant.
Making sustainable choices
In Dr Mair’s new book The Psychology of Fashion, she says eco-labels on garments are an important influence ...