(Press-News.org) A group of young students became bonafide biomedical scientists before they even started high school. Through a partnership with a nearby university, the middle schoolers collected and analyzed environmental samples to find new antibiotic candidates. One unique sample, goose poop collected at a local park, had a bacterium that showed antibiotic activity and contained a novel compound that slowed the growth of human melanoma and ovarian cancer cells in lab tests.
Inequities in educational resources, especially those in science, engineering, technology and math (STEM), where experiments are expensive, have kept some students underrepresented in these fields. By engaging a group of these students early in real, high-quality research, a team from the University of Illinois at Chicago led by Brian Murphy is providing young learners a chance to see themselves as scientists and explore careers in science with hands-on experience. The team partnered with a Boys and Girls Club in Chicago to bring interested middle schoolers into a 14-week applied science program.
Murphy’s lab is focused on discovering antibiotics from natural sources, and the cohort of young scientists participated by supplying environmental samples from their local communities. And the students’ contributions to the research group didn’t end there. They stayed actively involved throughout the scientific discovery process by programming a specialized robot to scoop up bacterial colonies from growth plates and test them for antibiotic activity.
One of the 14 samples collected — goose poop from the Garfield Park Lagoon — contained a strain of bacteria called Pseudomonas idahoensis. The students interpreted the bacterium’s bioassay data and concluded it had antibiotic activity and produced a never-before-seen compound. Then, the university researchers determined the compound’s molecular structure using nuclear magnetic resonance and mass spectrometry, named it orfamide N after the family of molecules it belongs to, and investigated its biological activity. Although orfamide N was not responsible for the antibiotic activity that the team initially observed from P. idahoensis, the compound inhibited the growth of human melanoma and ovarian cancer cells in culture tests. Further studies could reveal other advantageous properties of this newly characterized molecule.
The researchers say that this work proves that it’s possible to combine educational outreach with natural product discovery research, and it emphasizes the importance of a strong relationship between universities and their local communities.
The authors acknowledge funding from the University of Illinois at Chicago Graduate College, Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant, an Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant Faculty Scholar Award, the Illinois-Indiana Sea Grant Graduate Student Scholar Award, and the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases of the National Institutes of Health. They extend special thanks to the volunteer outreach mentors at the Boys and Girls Clubs of Chicago.
###
The American Chemical Society (ACS) is a nonprofit organization chartered by the U.S. Congress. ACS’ mission is to advance the broader chemistry enterprise and its practitioners for the benefit of Earth and all its people. The Society is a global leader in promoting excellence in science education and providing access to chemistry-related information and research through its multiple research solutions, peer-reviewed journals, scientific conferences, e-books and weekly news periodical Chemical & Engineering News. ACS journals are among the most cited, most trusted and most read within the scientific literature; however, ACS itself does not conduct chemical research. As a leader in scientific information solutions, its CAS division partners with global innovators to accelerate breakthroughs by curating, connecting and analyzing the world’s scientific knowledge. ACS’ main offices are in Washington, D.C., and Columbus, Ohio.
Registered journalists can subscribe to the ACS journalist news portal on EurekAlert! to access embargoed and public science press releases. For media inquiries, contact newsroom@acs.org.
Note: ACS does not conduct research but publishes and publicizes peer-reviewed scientific studies.
Follow us: X, formerly Twitter | Facebook | LinkedIn | Instagram
END
In a first-of-its-kind breakthrough, a team of UBC Okanagan researchers has developed an artificial adhesion system that closely mimics natural biological interactions.
Dr. Isaac Li and his team in the Irving K. Barber Faculty of Science study biophysics at the single-molecule and single-cell levels. Their research focuses on understanding how cells physically interact with each other and their environment, with the ultimate goal of developing innovative tools for disease diagnosis and therapy.
Two of Dr. Li’s doctoral students, Micah Yang and David Bakker, have engineered a new molecule that could transform how cells adhere to and communicate with one another.
Micah Yang, ...
Seaweed is once again showing promise for making cattle farming more sustainable. A new study by researchers at the University of California, Davis, found that feeding grazing beef cattle a seaweed supplement in pellet form reduced their methane emissions by almost 40% without affecting their health or weight. The study was published today (Dec. 2) in Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
This is the first study to test seaweed on grazing beef cattle in the world. It follows previous studies that showed seaweed cut methane emissions 82% in feedlot cattle ...
The consumption of milk products, eggs and fish has a positive effect on childhood development in Africa. This has been demonstrated in a recent study by the CABI's regional centre for Africa in Nairobi, Kenya and the University of Bonn. The researchers used representative data from five African countries with over 32,000 child observations. If the children had a diet containing animal products, they suffered less from malnutrition and related developmental deficiencies. The study has now been published in the journal PNAS.
Almost 150 million children under the age of five around the world suffer from serious growth and developmental ...
Fukuoka and Tsukuba, Japan—Researchers have uncovered key insights about how liquid crystals, materials capable of forming complex ordered structures, transform between different phases. Published in PNAS, the study provides a clearer understanding of how these materials change their structures at the microscopic level. This research could provide a means to give a deeper insight into the transformation between different structures in a wider variety of materials.
Liquid crystals are materials that exhibit properties of both liquids and solids. They flow like liquids but can also ...
New research published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences sheds light on the pathways that drive organ damage and death in severe COVID-19 and helps explain why survivors of the disease can experience long-term complications.
“Our study resolves some of the long-standing unanswered questions about how the SARS-CoV-2 virus impacts the body,” said co-senior author Afshin Beheshti, Ph.D., professor of surgery and computational and systems biology at the University of Pittsburgh School of Medicine and associate director of the McGowan Institute for Regenerative Medicine. “The findings point ...
A new collection of published papers offers the most detailed and comprehensive breakdown yet of how water injected into the Permian Basin during oil and gas operations is changing subsurface pressures and causing earthquakes.
The Permian Basin in West Texas is the country’s most prolific energy-producing region, accounting for more than 40% of the nation’s oil production and about 15% of gas production. However, energy production has caused earthquakes and other challenges in recent years as oil and gas operators now manage roughly 15 million barrels of produced wastewater each day. This briny water comes to the surface ...
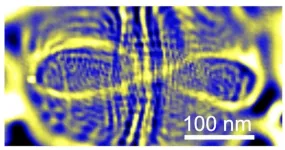
Where do you see patterns in chaos? It has been proven, in the incredibly tiny quantum realm, by an international team co-led by UC Santa Cruz physicist Jairo Velasco, Jr. In a new paper published on November 27 in Nature, the researchers detail an experiment that confirms a theory first put forth 40 years ago stating that electrons confined in quantum space would move along common paths rather than producing a chaotic jumble of trajectories.
Electrons exhibit both particle and wave-like properties—they ...
Brazilian scientists have determined that ancient specimens of partially domesticated maize (Zea mays, also known as corn) originally from Peruaçu Valley in Minas Gerais state (Brazil) were the farthest from Mexico, the plant’s historic center of origin, of any finds made so far. An article describing their research is published in the journal Science Advances. The study was led by researchers affiliated with the University of São Paulo (USP) and EMBRAPA, the Brazilian Agricultural Research Corporation.
The findings reinforce the theory, based on genetic evidence from plants alive now, that domestication ...
With support from the University of Houston's Andy & Barbara Gessner College of Nursing, two universities in India - MGM Institute of Health Sciences in Mumbai and Krishna Institute of Medical Sciences - have introduced the Doctor of Nursing Practice degree, expanding advanced nursing education in the country. It is the first time any university in India has offered the degree.
The Gessner College graduated its first class of DNP professionals in May 2024.
The DNP doctorate degree ...
What can exploding stars teach us about how blood flows through an artery? Or swimming bacteria about how the ocean’s layers mix? A collaboration of researchers from universities, science philanthropies and national laboratories has reached an important milestone toward training artificial intelligence models to find and exploit transferable knowledge between seemingly disparate fields to drive scientific discovery.
This initiative, called Polymathic AI, uses technology similar to that powering large language models such as OpenAI’s ChatGPT ...