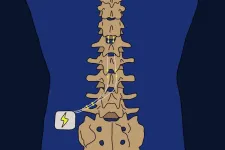
(Press-News.org) A 10-minute brain scan can predict the effectiveness of a risky spinal surgery to alleviate intractable pain. The Kobe University result gives doctors a much-needed biomarker to discuss with patients considering spinal cord stimulation.
For patients with chronic pain that cannot be cured in any other way, a surgical procedure called “spinal cord stimulation” is seen as a method of last resort. The treatment works by implanting leads into the spine of patients and electrically stimulating the spinal cord. Because the spinal cord transmits sensations to the brain from all over the body, the position of the leads is adjusted so that the patients feel the stimulation at the site of the pain. The Kobe University anesthesiologist UENO Kyohei says: “A big issue is that the procedure is effective for some but not for other patients, and which is the case is usually evaluated in a short trial of a few days to two weeks prior to permanent implantation. Although this trial is short, it is still an invasive and risky procedure. Therefore, clinicians have long been interested in the possibility of predicting a patient’s responsiveness to the procedure through non-invasive means.”
Functional magnetic resonance imaging, or fMRI, has become a standard tool to visualize how the brain processes information. More precisely, it can show which parts of the brain are active in response to a stimulus, and which regions are thus functionally connected with each other. “In an earlier study, we reported that for the analgesic ketamine, pain relief correlates negatively with how strongly connected two regions of the default mode network are before the drug’s administration,” explains Ueno. The default mode network, which plays an important role in self-related thought, has previously been implicated in chronic pain. Another relevant factor is how the default mode network connects with the salience network, which is involved in regulating attention and the response to stimuli. Ueno says, “Therefore, we wanted to examine whether the correlation of the activities within and between these networks could be used to predict responsiveness to spinal cord stimulation.”
He and his team published their results in the British Journal of Anaesthesia. They found that the better patients responded to spinal cord stimulation therapy, the weaker a specific region of the default mode network was connected to one in the salience network. Ueno comments, “Not only does this offer an attractive biomarker for a prognosis for treatment effectiveness, it also strengthens the idea that an aberrant connection between these networks is responsible for the development of intractable chronic pain in the first place.”
Undergoing an fMRI scan is not the only option. Combining pain questionnaires with various clinical indices has been reported as another similarly reliable predictor for a patient’s responsiveness to spinal cord stimulation. However, the researchers write that “Although the cost of an MRI scan is controversial, the burden on both patients and providers will be reduced if the responsiveness to spinal cord stimulation can be predicted by one 10-minute resting state fMRI scan.”
In total, 29 patients with diverse forms of intractable chronic pain participated in this Kobe University study. On the one hand, this diversity is likely the reason why the overall responsiveness to the treatment was lower compared to similar studies in the past and also made it more difficult to accurately assess the relationship between brain function and the responsiveness. On the other hand, the researchers also say that, “From a clinical perspective, the ability to predict outcomes for patients with various conditions may provide significant utility.” Ueno adds: “We believe that more accurate evaluation will become possible with more cases and more research in the future. We are also currently conducting research on which brain regions are strongly affected by various patterns of spinal cord stimulation. At this point, we are just at the beginning of this research, but our main goal is to use functional brain imaging as a biomarker for spinal cord stimulation therapy to identify the optimal treatment for each patient in the future.”
This research was funded by the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (grant 21K08993). It was conducted in collaboration with a researcher from Ritsumeikan University.
Kobe University is a national university with roots dating back to the Kobe Higher Commercial School founded in 1902. It is now one of Japan’s leading comprehensive research universities with nearly 16,000 students and nearly 1,700 faculty in 10 faculties and schools and 15 graduate schools. Combining the social and natural sciences to cultivate leaders with an interdisciplinary perspective, Kobe University creates knowledge and fosters innovation to address society’s challenges.
END
Brain scan predicts effectiveness of spinal cord surgery
2024-12-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Cognitive ability and physical health predict dementia later in life
2024-12-03
The risk of developing dementia later in life is strongly predicted by a person’s cognitive ability, functional limitations and physical health as many as 20 years before onset of the illness, according to a new RAND report.
Related new research found that early detection of cognitive impairment helps people to take mitigating actions to prepare for future loss of financial and physical independence.
While older adults’ take-up of cognitive testing currently is low, additional research found that use of cognitive tests would increase if it was free and readily accessible, ...
New survey finds 56% say ‘alone time’ is vital to their mental health
2024-12-03
COLUMBUS, Ohio – Some say the holidays are the most wonderful time of the year. But for others, the hectic holiday season may be the most stressful.
A new national survey of 1,000 Americans commissioned by The Ohio State University Wexner Medical Center and College of Medicine shows that 46% of Americans say they don’t get the alone time they need during the holidays.
In addition, 56% of survey respondents say that it’s very important to their mental health to have adequate alone time.
Sophie Lazarus, PhD, a clinical psychologist in the Department of Psychiatry and Behavioral Health at Ohio State, says in ...
How did human brains get so big? The answer could be in our gut
2024-12-03
How did human brains get so big? The answer could be in our gut
Microbes supporting the production of more metabolic energy could be key to the evolution of large brains
First study to show gut microbes from different animal species shape variations in their biology
Offers new take on human evolution, particularly the evolution of our large brains
Mice with large-brain primate microbes eat more, but grew slower and put on less body fat
Their bodies use the excess energy to produce high levels of glucose, which is the brain’s primary ...
Evaluation of the phytochemical and medicinal value of lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus), by conversion into powders and extracts to develop a nutritional bakery product
2024-12-03
Background and objectives
Because of its extraordinary phytomedicinal potential and numerous potential health benefits, lemongrass (Cymbopogon citratus), a well-known medicinal and aromatic plant, is of paramount significance. It is typically used as a drug replacement.
Methods
The present study was comprised of drying lemongrass into powder and determining the proximate and mineral composition, and then developing ethanolic extracts of powder to determine total phenolic contents (TPC), total flavonoid contents (TFC), total carotenoids (TC), and DPPH free radical scavenging activity. Next, lemongrass powder (LGP) was replaced at 0, 2.5, 5, 7.5, and 10% levels ...
Monell Chemical Senses Center and A*STAR Singapore Institute of Food and Biotechnology Innovation sign agreement to collaborate in sensory science research and education
2024-12-03
PHILADELPHIA, PA and QUEENSTOWN, SINGAPORE (Monday, Dec 2, 2024 9:30 pm EST; Tuesday, Dec 3, 2024 9:30 am SST) The Monell Chemical Senses Center, a global leader in advancing the scientific understanding of taste, smell, and related senses, and A*STAR Singapore Institute of Food and Biotechnology Innovation (A*STAR SIFBI), a translational research institute for health and well-being focused on Asian phenotype have entered into a five-year research and education alliance.
Today, Benjamin P.C. Smith, PhD, Monell Executive Director & President, met with Sze Tan, PhD, A*STAR SIFBI Executive Director, to sign a Memorandum of Understanding ...
Five new papers highlight cancer inequities, challenges and opportunities in South Asia
2024-12-03
A series of five papers, published today in The Lancet Oncology by a University of Pittsburgh-led international team, highlights critical public health challenges related to cancer control in the eight countries that form the South Asian Association for Regional Cooperation (SAARC) and the Rohingya refugee population in Bangladesh. The series underscores barriers contributing to significant disparities in cancer outcomes and identifies actionable solutions to address these challenges in one of the most comprehensive ...
Stereotypes matter: Computer science needs better role models
2024-12-03
White, male, billionaire entrepreneurs fuel stereotypes that compound the issues surrounding diversity in technology and computer science, according to a new study.
The identities of famous people contribute a lot to stereotypes in their respective domains. Prominent public figures can easily become influential to young people. But are these role models effective for creating a diverse community of computer science students? That, at this point in time, seems unlikely.
The study, carried out by the University of Reading and published today ([INSERT DATE]) in the Oxford Review of Education, ...
Insect fossil find ‘extremely rare’
2024-12-02
Newly discovered insect fossils are so small they can barely be seen by the human eye but have been preserved in an “extraordinary” way.
Published in the journal Palaeobiodiversity and Palaeoenvironments, a new study reveals rare whitefly insect fossils have been found in Miocene age crater lake sediments at Hindon Maar, near Dunedin.
Adult whiteflies are tiny insects about 3mm in size, smaller if they are immature.
The fossils found at Hindon Maar are about 1.5mm by 1.25mm and have been preserved in the position they lived and died, attached to the underside ...
New JAMA study shows text messages can be ineffective as medication refill reminders
2024-12-02
A new study published today in JAMA reveals text message reminders for patients who delay refilling their medications didn’t help improve how regularly they refilled medications over a year.
The study enrolled over 9,000 patients in a randomized pragmatic clinical trial and included representation from a diverse population across subgroups, including females, Hispanic ethnicity and Spanish-speaking patients, all groups who can be traditionally underrepresented in clinical trials.
“There are a lot of studies that focus on using technology ...
Migrant pupils need more targeted mental health support in school, study shows
2024-12-02
School-based mental health support should be more accessible for migrant children, a new study says.
Schools are increasingly considered to be critical places for identifying and supporting mental health difficulties, but little is known about the barriers migrants face in accessing mental health support in schools.
Researchers found a lack of targeted school-based mental health interventions designed specifically for young migrants that cater to their unique strengths, resilience and needs.
The review of 38 studies shows that stigma around mental health and stressors associated with migration were among ...