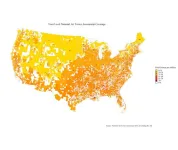
(Press-News.org) New research builds on scientific understanding of how air pollution and cancer risk are distributed throughout the U.S. Air pollution, often resulting from industrial or vehicle emissions, can travel for hundreds of miles and impact the health of communities through higher rates of asthma, respiratory infections, stroke, and lung cancer. Although previous studies have identified disparities in how public health risks vary by income and race, a new study takes a detailed look across U.S. census tracts to find patterns in who is most at risk from cancer resulting from lifetime exposure to air pollution and how this risk is changing through time.
Researchers from Desert Research Institute (DRI) and the University of Nevada, Reno (UNR) teamed up for the new study, published October in Environmental Science & Technology. Using sociodemographic data from the U.S. Census Bureau and public health and air pollution information from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency (EPA) between 2011 and 2019, the study identified higher estimated cancer risk tied to air toxics in urban communities, those with lower incomes, and those with higher proportions of racial minorities.
“I wanted to look holistically at poor health outcomes from air pollution exposure throughout the country and through time to see if things are getting better or worse, and what the main socioeconomic drivers are for where the pollution is being distributed,” says Patrick Hurbain, postdoctoral researcher and environmental epidemiologist at DRI who led the study.
Although previous studies have identified public health disparities related to specific air pollutants, this is one of the first to look at air pollution loads as a whole and changes over time. Public and environmental health data came from the EPA’s Air Toxics Screening Assessment. This publicly available tool maps concentrations of hundreds of toxic air pollutants from all sources, as well as cancer risk estimates tied to lifetime exposure across U.S. census tracts.
Census tracts with the highest estimated cancer risk were found in urban communities, with racial demographics showing stronger correlations with disparities than either income or education level. Communities with the highest levels of estimated cancer risk, like “Cancer Alley” in southern Louisiana, have significantly more Black and Hispanic community members compared to White individuals. This racial disparity was not consistent in rural and suburban communities, where larger White populations showed higher burdens of cancer risk.
“There is a definite effect of the social makeup of an area with respect to their estimated risk from air pollution,” Hurbain says.
The study found that racial disparities peaked in 2011, with the magnitude of the disparity improving in later years. “That means that air pollution control measures are doing better, and people are, in fact, getting less air toxics across the country, which is exciting,” Hurbain says.
Disparities for lower income communities, however, were found to be consistent through time.
Hurbain hopes to expand on the research by focusing on the most impacted communities and taking a closer look at factors like the age of housing, poverty levels, and surrounding industries to identify ways to improve public health.
With publicly available data like the map used for this study, Hurbain hopes that more people will get involved in examining the risks in their own communities. “Everyone can be a citizen scientist and start looking at the state of our environment,” he says.
-----
More information: The full study, Environmental Inequality in Estimated Cancer Risk from Airborne Toxic Exposure across United States Communities from 2011 to 2019, is available from Environmental Science & Technology at https://pubs.acs.org/doi/10.1021/acs.est.4c02526
Study authors include: Patrick Hurbain (DRI), Matthew Strickland (UNR), Yan Liu (UNR), and Dingsheng Li (UNR)
About DRI
We are Nevada’s non-profit research institute, founded in 1959 to empower experts to focus on science that matters. We work with communities across the state — and the world — to address their most pressing scientific questions. We’re proud that our scientists continuously produce solutions that better human and environmental health.
Scientists at DRI are encouraged to follow their research interests across the traditional boundaries of scientific fields, collaborating across DRI and with scientists worldwide. All faculty support their own research through grants, bringing in nearly $5 to the Nevada economy for every $1 of state funds received. With more than 600 scientists, engineers, students, and staff across our Reno and Las Vegas campuses, we conducted more than $52 million in sponsored research focused on improving peoples’ lives in 2024 alone.
At DRI, science isn’t merely academic — it’s the key to future-proofing our communities and building a better world. For more information, please visit www.dri.edu.
END
Regional, racial, and economic disparities in cancer risk from air pollution exposure persist, but improving, new research suggests
A nationwide assessment of estimated cancer risk from airborne toxics shows that risk is concentrated in urban communities, those with lower incomes, and those with higher proportions of racial minorities
2024-12-03
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
COVID infection and age-related blindness
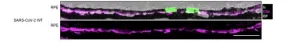
2024-12-03
An experimental study in mice shows that SARS-CoV-2 infection can damage the retinas, with long-term implications for vision. Post-acute sequelae of SARS-CoV-2 infection include various neurocognitive symptoms, suggesting the virus can affect the central nervous system. The eyes are also part of the central nervous system, but little is known about the virus’s effects on these organs. David Williams and Nan Hultgren led a study in which transgenic mice that express human SARS-CoV-2 receptor ACE2 were infected with ...
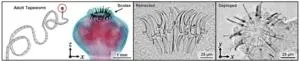
Parasite-inspired medical devices
2024-12-03
Inspired by the diverse attachment organs of parasites, researchers have designed a millimeter-scale mechanism for soft tissue anchoring. Robert J. Wood and colleagues turned to the world of parasites as inspiration for developing methods to affix small-scale medical devices to the gastrointestinal tract or other soft tissues for sensing, sample collection, and extended drug release. While evolution has produced a wide range of different biomechanical structures that can attach to soft tissues, the authors ...
Twenty-seven scientists become EMBO Young Investigators
2024-12-03
3 December 2024 – EMBO announces the selection of 27 life scientists as the newest members of the EMBO Young Investigator Programme. The programme supports young group leaders in Europe and beyond. The new young investigators will start in January, be active members of the programme for four years, and become part of an international network of nearly 800 current and former EMBO Young Investigators, Installation Grantees and Global Investigators. They carry out research across a wide range of life sciences topics from cell and computational biology to immunology and neuroscience.
"EMBO welcomes ...
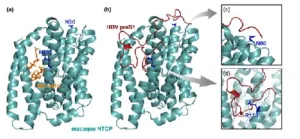
The viral puzzle of why humans are susceptible to hepatitis B virus, but monkeys are not!
2024-12-03
Hepatitis B virus (HBV) infection is a leading cause of chronic liver diseases, that spreads among individuals through blood or body fluids. According to the World Health Organization, globally 1.2 million new HBV infections are reported every year. Caused by the HBV, these infections are limited to a few species, including humans and chimpanzees. Despite their close evolutionary relationship with these animals, old-world monkeys are not susceptible to HBV infections. In a new study published in Nature Communications on October 25, 2024, scientists including Dr. Kaho Shionoya from the Tokyo University of Science, Dr. Jae-Hyun Park, Dr. Toru Ekimoto, Dr. Mitsunori Ikeguchi, and Dr. Sam-Yong ...
Microfiber plastics appear to tumble, roll and move slowly in the environment
2024-12-03
PULLMAN, Wash. -- The first-known direct observations of the movement of microfiber plastics through a thin layer of soil-like particles show that they tend to tumble, roll and sometimes get stuck in spaces.
The findings, reported in the journal, Water Resources Research, mean that the fibers could get easily trapped in sediment. The work helps to improve understanding of the exposure risks and possible health impacts of the pervasive pieces of plastic, which are the largest pollutant in the world by mass.
“The ...
Prestigious EU research grants awarded to two Hebrew University researchers
2024-12-03
The Hebrew University of Jerusalem proudly congratulates two of its esteemed researchers for receiving prestigious European Research Council (ERC) grants. These grants, each valued at approximately 2 million euros, are awarded to researchers leading innovative projects and join a long tradition of Hebrew University scholars who have been recognized with this honor in previous years.
The recipients from Hebrew University are:
Prof. Dina Schneidman, The Rachel and Selim Benin School of Computer Science and Engineering, for her research titled "Deep Learning for Structure-Based Discovery of Adaptive Immune Receptors." Prof. Schneidman’s research ...
Experts reveal how revolutionary technological advances could use the sun to source hydrogen fuel
2024-12-03
In the future, we could fuel the world with sunlight and water – using sunlight to derive hydrogen fuel from H2O. Currently, most hydrogen that’s used as feedstock and fuel is derived from natural gas, and therefore doesn’t help us cut out fossil fuels. But Japanese scientists are leading the way towards a future powered by hydrogen, with new, easily-manufactured photocatalytic sheets and a proof-of-concept panel reactor which shows that it is possible to refine hydrogen fuel from water at scale.
“Sunlight-driven water splitting using photocatalysts is an ideal technology for solar-to-chemical ...
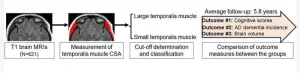
Muscle loss could increase dementia risk
2024-12-03
CHICAGO – Skeletal muscle loss is a risk factor for developing dementia, according to a study being presented today at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
Skeletal muscles make up about one-third of a person’s total body mass. They are connected to the bones and allow for a wide range of movements. As people grow older, they begin to lose skeletal muscle mass.
Because age-related skeletal muscle loss is often seen in older adults with Alzheimer’s disease (AD) dementia, this study aimed to examine whether temporalis muscle ...
Minimally invasive procedure relieves knee arthritis
2024-12-03
CHICAGO – A minimally invasive procedure provides significant relief from knee pain and may prevent the need for knee replacement surgery in people with osteoarthritis, according to a study being presented this week at the annual meeting of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
“This study addresses osteoarthritis, which is a significant public health issue and the leading cause of chronic pain and disability worldwide,” said the study’s lead author, Florian Nima Fleckenstein, M.D., interventional radiologist at Charité – University Hospital Berlin in Germany. “With millions of people affected by knee ...
Scientists question the use of “tipping point” metaphor in climate change discussions
2024-12-03
A group of scientists, including researchers from Rutgers University-New Brunswick, Princeton University and Carleton University, has questioned the accuracy and utility of the metaphor “tipping point” in calling attention to the threat of climate change.
The phrase, while perhaps initially useful as a clarion call that warns about sudden, drastic changes, may now be confusing the public and impeding action, researchers said.
Writing a perspective in Nature Climate Change, the scientists, from the Rutgers Climate and Energy Institute, Princeton’s Center ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Marshall University, Intermed Labs announce new neurosurgical innovation to advance deep brain stimulation technology
Preclinical study reveals new cream may prevent or slow growth of some common skin cancers
Stanley Family Foundation renews commitment to accelerate psychiatric research at Broad Institute
What happens when patients stop taking GLP-1 drugs? New Cleveland Clinic study reveals real world insights
American Meteorological Society responds to NSF regarding the future of NCAR
Beneath Great Salt Lake playa: Scientists uncover patchwork of fresh and salty groundwater
Fall prevention clinics for older adults provide a strong return on investment
People's opinions can shape how negative experiences feel
USC study reveals differences in early Alzheimer’s brain markers across diverse populations
300 million years of hidden genetic instructions shaping plant evolution revealed
High-fat diets cause gut bacteria to enter brain, Emory study finds
Teens and young adults with ADHD and substance use disorder face treatment gap
Instead of tracking wolves to prey, ravens remember — and revisit — common kill sites
Ravens don’t follow wolves to dinner – they remember where the food is
Mapping the lifelong behavior of killifish reveals an architecture of vertebrate aging
Designing for hard and brittle lithium needles may lead to safer batteries
Inside the brains of seals and sea lions with complex vocal behavior learning
Watching a lifetime in motion reveals the architecture of aging
Rapid evolution can ‘rescue’ species from climate change
Molecular garbage on tumors makes easy target for antibody drugs
New strategy intercepts pancreatic cancer by eliminating microscopic lesions before they become cancer
Embryogenesis in 4D: a developmental atlas for genes and cells
CNIO research links fertility with immune cells in the brain
Why do lithium-ion batteries fail? Scientists find clues in microscopic metal 'thorns'
Surface treatment of wood may keep harmful bacteria at bay
Carsten Bönnemann, MD, joins St. Jude to expand research on pediatric catastrophic neurological disorders
Women use professional and social networks to push past the glass ceiling
Trial finds vitamin D supplements don’t reduce covid severity but could reduce long COVID risk
Personalized support program improves smoking cessation for cervical cancer survivors
Adverse childhood experiences and treatment-resistant depression
[Press-News.org] Regional, racial, and economic disparities in cancer risk from air pollution exposure persist, but improving, new research suggestsA nationwide assessment of estimated cancer risk from airborne toxics shows that risk is concentrated in urban communities, those with lower incomes, and those with higher proportions of racial minorities