Mesenchymal stem cells in cancer immunotherapy: Promises and challenges
“MSCs hold great promise as a therapeutic tool in cancer immunotherapy due to their immunomodulatory properties, tumor-homing abilities, and potential as carriers for delivering therapeutic agents.”
2024-12-03
(Press-News.org)
“MSCs hold great promise as a therapeutic tool in cancer immunotherapy due to their immunomodulatory properties, tumor-homing abilities, and potential as carriers for delivering therapeutic agents.”
BUFFALO, NY – December 3, 2024 – A new review was published in Oncotarget’s Volume 15 on November 22, 2024, entitled “Mesenchymal stem cells – the secret agents of cancer immunotherapy: Promises, challenges, and surprising twists.”
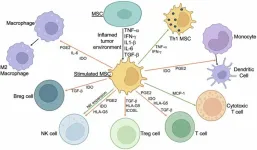
Authored by Theia Minev, Shani Balbuena, Jaya Mini Gill, Francesco M. Marincola, Santosh Kesari, and Feng Lin from CureScience Institute, Sonata Therapeutics, and Pacific Neuroscience Institute and Providence Saint John’s Health Center, this review explores the potential role of mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) in cancer treatment. These stem cells can naturally target tumors and deliver therapeutic agents directly to cancer cells, potentially improving treatment outcomes while reducing side effects commonly associated with traditional therapies like chemotherapy. However, the authors also note significant challenges, pointing out that under certain conditions, MSCs may unintentionally promote tumor growth, highlighting the need for careful therapeutic design.
MSCs are cells that can develop in different types of tissues, such as bone, fat, or cartilage, and act as natural repair agents. What makes them particularly special is their ability to respond to biological signals, like inflammation, which is often present in cancer. This enables them to locate tumors, and once there, they can deliver cancer treatments directly to the affected area.
Clinical trials are already investigating MSC-based treatments for cancers such as brain tumors, melanoma, and ovarian cancer. Some results are promising, showing that MSCs can effectively deliver treatments and boost the immune system’s fight against cancer. However, other trials have also revealed the complexities of MSC behavior, including variability in their effects and the potential to create conditions that support tumor growth.
“This variability may be due to the tumor immune microenvironment’s effects, where immune cells are inhibited by various factors, creating a conducive environment for tumor growth.”
The authors also suggest that “Developing personalized MSC therapies tailored to the specific characteristics of a patient’s tumor and immune system could enhance the efficacy and safety of MSC-based treatments.” Achieving this requires a deeper understanding of how MSCs interact with cancer cells and their surrounding environment.
In conclusion, this review highlights both the potential and challenges of (MSCs in cancer therapy. With ongoing research and technological advancements, MSCs could become a key component of personalized cancer treatments, offering new hope for patients worldwide.
Continue reading: DOI: https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.28672
Correspondence to: Feng Lin – flin@curescience.org
Video short: https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Wwc3zDDitlc
Keywords: cancer, mesenchymal stem cells, genetic engineering, cancer immunotherapy, mesenchymal stem cell homing, stem cell delivery
Click here to sign up for free Altmetric alerts about this article.
About Oncotarget:
Oncotarget (a primarily oncology-focused, peer-reviewed, open access journal) aims to maximize research impact through insightful peer-review; eliminate borders between specialties by linking different fields of oncology, cancer research and biomedical sciences; and foster application of basic and clinical science.
Oncotarget is indexed and archived by PubMed/Medline, PubMed Central, Scopus, EMBASE, META (Chan Zuckerberg Initiative) (2018-2022), and Dimensions (Digital Science).
To learn more about Oncotarget, visit Oncotarget.com and connect with us on social media:
X
Facebook
YouTube
Instagram
LinkedIn
Pinterest
Spotify, and available wherever you listen to podcasts
Click here to subscribe to Oncotarget publication updates.
For media inquiries, please contact media@impactjournals.com.
Oncotarget Journal Office
6666 East Quaker St., Suite 1
Orchard Park, NY 14127
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-12-03
About The Study: In this cohort study of 1,600 emergency medicine patient medical records, large language model (LLM)-generated emergency medicine-to-inpatient handoff notes were determined superior compared with physician-written summaries via conventional automated evaluation methods, but marginally inferior in usefulness and safety via a novel evaluation framework. This study suggests the importance of a physician-in-loop implementation design for this model and demonstrates an effective strategy to measure pre-implementation patient safety of LLM models.
Corresponding ...
2024-12-03
Patients with frontotemporal dementia often lack the ability to empathize. A study at Karolinska Institutet has now shown that these patients do not show the same brain activity as healthy individuals when they witness the pain of others, a finding that it is hoped will increase understanding of this specific dementia disease.
Around 25 000 Swedes are affected by dementia every year. Of these, about three percent are diagnosed with frontotemporal dementia. The disease is difficult to diagnose, but one of its characteristics is that sufferers lose the ability to empathize, which can lead to problems for them, and not least ...
2024-12-03
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- Gastric balloons — silicone balloons filled with air or saline and placed in the stomach — can help people lose weight by making them feel too full to overeat. However, this effect eventually can wear off as the stomach becomes used to the sensation of fullness.
To overcome that limitation, MIT engineers have designed a new type of gastric balloon that can be inflated and deflated as needed. In an animal study, they showed that inflating the balloon before a meal caused the animals to reduce their food intake by 60 percent.
This type of intervention ...
2024-12-03
WASHINGTON, D.C. — The Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) has approved funding awards totaling more than $156 million for new patient-centered comparative clinical effectiveness research (CER), as well as research to improve methods and strengthen the science of engagement in CER. The awards will support 13 CER studies, including three focused on sleep interventions.
“Poor sleep affects more than 50 million people in the United States and is linked to multiple chronic conditions and negative health outcomes,” said PCORI Executive Director Nakela L. Cook, M.D., MPH. “These ...
2024-12-03
ATLANTA — Debra Bangasser, a professor of neuroscience and director of the Center for Behavioral Neuroscience (CBN) at Georgia State University, has been awarded the Daniel H. Efron Research Award by the American College of Neuropsychopharmacology (ACNP).
The award recognizes outstanding basic research contributions to the field of neuropsychopharmacology, which integrates neuroscience and pharmacology to advance understanding of the causes of psychiatric disorders and develop new therapies. Bangasser’s research identifies how stress throughout the lifespan affects the brain to promote ...
2024-12-03
SEATTLE, WASH.—December 3, 2024—The funding, provided through the Allen Distinguished Investigators, a program of The Paul G. Allen Frontiers Group at the Allen Institute, will fuel innovative research in Organelle Communication and Membrane Biophysics. Together these awards represent a total of $9 million dollars in funding from the Paul G. Allen Family Foundation, which will be distributed between 14 researchers investigating the biological principles governing fundamental cellular functions and how they interact. These ...
2024-12-03
Voice experiments in people with epilepsy have helped trace the circuit of electrical signals in the brain that allow its hearing center to sort out background sounds from their own voices.
Such auditory corollary discharge signals start and end in two subregions of the brain’s top folded surface, or cortex, a new study shows. One large part of the cortex, the motor cortex, is known to control the body’s voluntary muscle movements, including those involved in speech, while another large section, the auditory cortex, is known to control hearing.
In terms of evolution, the ability of animals and humans to tell ...
2024-12-03
CLEVELAND—With a new five-year, $3.2 million grant from the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communications Disorders, researchers at Case Western Reserve University and Mass Eye and Ear will study what causes acquired hearing loss (AHL) and seek new ways to protect against it.
AHL is among the most common health conditions affecting older adults, according to the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention. Although hearing aids can help, AHL has no known cure and, in many cases, scientists are still unsure of its exact cause.
AHL significantly ...
2024-12-03
Florida Atlantic University’s Marcus Institute of Integrative Health has been awarded a monumental $6 million grant from the late Bernie Marcus and The Marcus Foundation to broaden its services, enhance educational programs, and expand community wellness initiatives, ultimately aiming to create a national model that demonstrates the effectiveness of comprehensive integrative health as the optimal approach for achieving overall well-being for everyone.
This latest grant to FAU from The Marcus Foundation, which was made prior to the passing of Marcus in early November, brings its total contributions for advancing integrative health to more than $10 million, ...
2024-12-03
Researchers led by Uljana Kravčenko and her colleagues in the lab of Professor Misha Kudryashev, Group Leader of the In Situ Structural Biology lab at the Max Delbrück Center, have revealed new features of the molecular architecture of synaptic vesicles. Using cryo-electron tomography, the team was able to visualize SVs in 3D and confirm a potentially important protein-protein interaction. They also broadened our understanding of SV function and of how the vesicles are recycled. The study was published in the Proceedings ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Mesenchymal stem cells in cancer immunotherapy: Promises and challenges
“MSCs hold great promise as a therapeutic tool in cancer immunotherapy due to their immunomodulatory properties, tumor-homing abilities, and potential as carriers for delivering therapeutic agents.”