(Press-News.org) An average of four minutes of incidental vigorous physical activity a day could almost halve the risk of major cardiovascular events, such as heart attacks, for middle-aged women who do not engage in structured exercise, according to new research from the University of Sydney, published in the British Journal of Sports Medicine.
“We found that a minimum of 1.5 minutes to an average of 4 minutes of daily vigorous physical activity, completed in short bursts lasting up to 1 minute, were associated with improved cardiovascular health outcomes in middle-aged women who do no structured exercise,” said lead author Professor Emmanuel Stamatakis, Director of the Mackenzie Wearable Hub at the Charles Perkins Centre and the Faculty of Medicine and Health.
High-intensity physical activity that forms part of a daily routine is known as “vigorous intermittent lifestyle physical activity” (VILPA). Longer sessions of VILPA are linked to significantly lower cardiovascular disease risk. The researchers say that, given fewer than 20 percent of middle-aged or older adults engage in regular structured exercise, engaging in VILPA could be a good alternative.
“Making short bursts of vigorous physical activity a lifestyle habit could be a promising option for women who are not keen on structured exercise or are unable to do it for any reason. As a starting point, it could be as simple as incorporating throughout the day a few minutes of activities like stair climbing, carrying shopping, uphill walking, playing tag with a child or pet, or either uphill or power walking,” said Professor Stamatakis.
The study drew on data from 22,368 participants (13,018 women and 9,350 men) aged 40–79 who reported they did not engage in regular structured exercise. The data was collected from the UK Biobank, whose participants wore physical activity trackers for almost 24 hours a day for 7 days between 2013 and 2015.
Cardiovascular health was monitored through hospital and mortality records, tracking major adverse cardiovascular events (MACE), such as heart attack, stroke, and heart failure, until November 2022.
After adjusting for factors such as lifestyle, socioeconomic position, cardiovascular health, co-existing conditions, and ethnicity, the researchers found that the more VILPA women did, the lower their risk of a major cardiovascular event. Women who averaged 3.4 minutes of VILPA daily were 45 percent less likely to experience a major cardiovascular event. They were also 51 percent less likely to have a heart attack and 67 percent less likely to develop heart failure than women who did no VILPA.
Even when amounts of daily VILPA were lower than 3.4 minutes they were still linked to lower cardiovascular event risk. A minimum of 1.2 to 1.6 minutes of VILPA per day was associated with a 30 percent lower risk of total major cardiovascular events, a 33 percent lower risk of heart attack, and a 40 percent lower risk of heart failure.
However, men reaped fewer benefits from tiny bursts of VILPA. Those who averaged 5.6 minutes daily were only 16 percent less likely to experience a major cardiovascular event compared with men who did none. A minimum of 2.3 minutes per day was associated with only an 11 percent risk reduction.
Professor Stamatakis said more testing was needed to understand how VILPA may improve cardiovascular health.
“To date, it hasn’t been clear whether short bursts of VILPA lower the risk of specific types of cardiovascular events, like heart attack or stroke. We aimed to identify minimum daily thresholds and feasible amounts for testing in community programs and future trials,” he said.
“Importantly, the beneficial associations we observed were in women who committed to short bursts of VILPA almost daily. This highlights the importance of habit formation, which is not always easy. VILPA should not be seen as a quick fix—there are no magic bullets for health. But our results show that even a little bit higher intensity activity can help and might be just the thing to help people develop a regular physical activity – or even exercise – habit,” he said.
Research: Stamatakis, et al, Device-measured vigorous intermittent lifestyle physical activity (VILPA) and major adverse cardiovascular events: evidence of sex differences, British Journal of Sports Medicine. DOI: 10.1136/bjsports-2024-108484
For the purposes of this story, physical activity is incidental, e.g. carrying shopping or briefly power walking, and exercise is structured, e.g. going to the gym or playing sport.
Declaration:
Professor Emmanuel Stamatakis is a paid consultant and holds equity in Complement One, a US-based startup whose services relate to physical activity. The research was funded by the Australian National Health and Medical Research Council.
The researchers note that this study is observational, so it cannot definitively prove cause and effect. An average of 5.5 years passed between the collection of data on risk factors and activity tracker recordings.
Academic contact:
Professor Emmanuel Stamatakis, Mackenzie Wearables Research Hub, Charles Perkins Centre, University of Sydney; and Faculty of Medicine and Health, University of Sydney, Sydney, New South Wales, Australia | emmanuel.stamatakis@sydney.edu.au | +61 432 704 690 | X (Twitter) @M_Stamatakis
Media contact:
Luisa Low, Senior Media and PR Adviser, University of Sydney | luisa.low@sydney.edu.au | +61 438 021 390
END
Tiny, daily bursts of vigorous incidental physical activity could almost halve cardiovascular risk in middle-aged women
Four minutes of daily vigorous physical activity greatly reduces the risk of heart attacks and heart failure among middle-aged women
2024-12-04
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Long-term benefit from anti-hormonal treatment is influenced by menopausal status
2024-12-04
Today, women with oestrogen-sensitive breast cancer receive anti-hormonal therapy. Researchers now show that postmenopausal women with low-risk tumours have a long-term benefit for at least 20 years, while the benefit was more short-term for younger women with similar tumour characteristics who had not yet gone through the menopause. The results are reported in the Journal of the National Cancer Institute (JNCI).
In Sweden, 9 000 women are diagnosed with breast cancer each year, with hormone-sensitive breast cancer accounting for about 75 percent of women diagnosed with the disease. In patients with hormone-sensitive breast cancer tumour growth is mainly driven by oestrogen and ...
Most of growth in high intensity hospital stays not explained by patient details
2024-12-03
In five states over nearly a decade, hospitals have increased how frequently they document patients as needing the highest intensity care, which has led to hospitals receiving billions in extra payments from health plans and government programs, according to a new RAND study.
Among thousands of cases involving hospitals stays for 239 conditions, researchers examined how often hospitals upcoded patients to the sickest end of the care spectrum, where hospitals charge payers at the highest rate.
The study found that from ...
OHSU study in neurosurgery patients reveals numerical concepts are processed deep in ancient part of brain
2024-12-03
New research reveals the unique human ability to conceptualize numbers may be rooted deep within the brain.
Further, the results of the study by Oregon Health & Science University involving neurosurgery patients suggests new possibilities for tapping into those areas to improve learning among people bedeviled by math.
“This work lays the foundation to deeper understanding of number, math and symbol cognition — something that is uniquely human,” said senior author Ahmed Raslan, ...
Predicting cardiac issues in cancer survivors using a serum protein panel test
2024-12-03
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – December 3, 2024) Early disease detection is beneficial for securing the best possible outcomes for patients. But finding noninvasive, effective ways to predict disease risk is a tremendous challenge. Findings from scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital are showing promise for assessing cardiomyopathy risk in childhood cancer survivors. Heart disease is a well-established late effect for pediatric cancer survivors treated with anthracycline chemotherapy. The researchers identified a panel ...
Research on neurodegeneration in spider brain leads Vermont neuroscientists to groundbreaking new discovery in Alzheimer’s-affected human brains
2024-12-03
COLCHESTER, VT – Researchers from Saint Michael’s College and the University of Vermont have made a groundbreaking new discovery that provides a better understanding of how Alzheimer’s disease develops in the human brain.
Guided by previous research of spider brains, the scientists uncovered evidence of a “waste canal system” in the human brain that internalizes waste from healthy neurons. They discovered that this system can undergo catastrophic swelling, which leads to the degeneration of brain tissue, a hallmark of Alzheimer’s disease.
With over 50 million affected people worldwide, Alzheimer’s ...
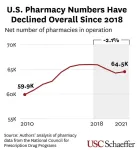
Nearly 1 in 3 retail pharmacies have closed since 2010
2024-12-03
Key study findings:
The rate of pharmacy store closures in recent years has more than doubled, affecting about 1 in 3 pharmacies between 2010 and 2021 and contributing to an unprecedented decline in the availability of pharmacies in the U.S
About one-third of counties experienced an overall decline in pharmacies, and the risk of closure was higher in predominantly Black and Latino neighborhoods.
Independent pharmacies, often excluded from networks by pharmacy benefit managers, were more than twice as likely to face closure compared to chain pharmacies.
Policymakers should consider several ...
‘Alaska’s Changing Environment’ — a new report
2024-12-03
The University of Alaska Fairbanks released a new report this week highlighting environmental changes and extremes that impact Alaskans and their livelihoods.
“Alaska’s Changing Environment” provides people with timely, reliable and understandable information on topics ranging from temperature and precipitation changes to salmon and polar bears.
The report was led by the Alaska Center for Climate Assessment and Policy at the UAF International Arctic Research Center, with contributions from more ...
nTIDE Deeper Dive November 2024: Employment trends highlight strength of veterans with disabilities
2024-12-03
East Hanover, NJ – December 3, 2024 – Veterans with disabilities continue to outperform the general population of people with disabilities in employment rates, highlighting the possible impact of specialized training and participation in essential industries, according to a new analysis shared during a National Trends in Disability Employment (nTIDE) Deeper Dive Lunch & Learn Webinar held on November 22. nTIDE is a joint effort by Kessler Foundation and the University of New Hampshire’s Institute on Disability (UNH-IOD).
Despite ...
Truck drivers need tailored health supports to Keep on Truckin’
2024-12-03
It might seem out of place on the side of a highway, but purpose-built exercise equipment installed at truck stops across Australia could be just the thing to encourage truck drivers to take a break and take control of their health and wellbeing.
In the first meta-analysis of how health behaviour interventions can affect truck drivers, researchers at the University of South Australia have found that tailored, multi-level and innovative approaches to truck driver health are required to enact positive change, as current interventions are not working.
Reviewing the effectiveness of health interventions for more than 2000 truck drivers across 19 studies, researchers found ...
Gluing treatment to cancer
2024-12-03
Treatment for more advanced and difficult-to-treat head and neck cancers can be improved with the addition of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA), the same ingredient used in children’s glue. Researchers found that combining PVA with a boron-containing compound, D-BPA, improved the effects of a type of radiation therapy for cancer, compared to currently clinically used drugs. The PVA made the drug more selective of tumor cells and prolonged drug retention, helping to spare healthy cells from unnecessary radiation damage.
Japan became the first country to approve boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT), a type of targeted radiotherapy for cancer, in 2020. Doctors ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Scientists discover why we know when to stop scratching an itch
A hidden reason inner ear cells die – and what it means for preventing hearing loss
Researchers discover how tuberculosis bacteria use a “stealth” mechanism to evade the immune system
New microscopy technique lets scientists see cells in unprecedented detail and color
Sometimes less is more: Scientists rethink how to pack medicine into tiny delivery capsules
Scientists build low-cost microscope to study living cells in zero gravity
The Biophysical Journal names Denis V. Titov the 2025 Paper of the Year-Early Career Investigator awardee
Scientists show how your body senses cold—and why menthol feels cool
Scientists deliver new molecule for getting DNA into cells
Study reveals insights about brain regions linked to OCD, informing potential treatments
Does ocean saltiness influence El Niño?
2026 Young Investigators: ONR celebrates new talent tackling warfighter challenges
Genetics help explain who gets the ‘telltale tingle’ from music, art and literature
Many Americans misunderstand medical aid in dying laws
Researchers publish landmark infectious disease study in ‘Science’
New NSF award supports innovative role-playing game approach to strengthening research security in academia
Kumar named to ACMA Emerging Leaders Program for 2026
AI language models could transform aquatic environmental risk assessment
New isotope tools reveal hidden pathways reshaping the global nitrogen cycle
Study reveals how antibiotic structure controls removal from water using biochar
Why chronic pain lasts longer in women: Immune cells offer clues
Toxic exposure creates epigenetic disease risk over 20 generations
More time spent on social media linked to steroid use intentions among boys and men
New study suggests a “kick it while it’s down” approach to cancer treatment could improve cure rates
Milken Institute, Ann Theodore Foundation launch new grant to support clinical trial for potential sarcoidosis treatment
New strategies boost effectiveness of CAR-NK therapy against cancer
Study: Adolescent cannabis use linked to doubling risk of psychotic and bipolar disorders
Invisible harms: drug-related deaths spike after hurricanes and tropical storms
Adolescent cannabis use and risk of psychotic, bipolar, depressive, and anxiety disorders
Anxiety, depression, and care barriers in adults with intellectual and developmental disabilities
[Press-News.org] Tiny, daily bursts of vigorous incidental physical activity could almost halve cardiovascular risk in middle-aged womenFour minutes of daily vigorous physical activity greatly reduces the risk of heart attacks and heart failure among middle-aged women