Researchers develop polarization photodetector mimicking desert ant
2024-12-05
(Press-News.org)
Polarization photodetectors (pol-PDs) have widespread applications in geological remote sensing, machine vision, and biological medicine. However, commercial pol-PDs usually require bulky and complicated optical components and are difficult to miniaturize and integrate.
Chinese researchers have recently made important progress in this area by developing an on-chip integrated polarization photodetector.
This study, published in Science Advances on Dec. 4, was conducted by Prof. Li Mingzhu’s group from the Technical Institute of Physics and Chemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
The research team was inspired by the unique capacity of desert ants for polarization vision. With this capability, desert ants can travel back to their nests across barren landscapes without any landmarks since their compound eyes are able to perceive polarized sunlight. The researchers aimed to mimic this capacity with their polarization photodetector.
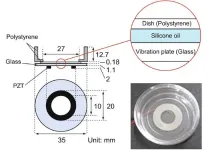
First, Li and her group proposed a one-step nanoimprinting crystallization method. They then used this method to fabricate a high-crystalline perovskite, single-crystal-thin film with high-throughput, quadridirectional grating arrays. Based on this film, the researchers constructed a single-shot, on-chip pol-PD without any additional polarization optics.
In addition, the nanoimprinting crystallization method provides a novel and universal solution for preparing patterned perovskite, single-crystal-thin films with high optoelectronic performance and superior light regulation capability.
This method makes it possible to use bio-inspired single-shot polarization photodetectors to build a simple, cost-effective, highly sensitive polarization imaging system. It also offers a pathway for the development of highly sensitive, miniaturized, on-chip integrated polarization imaging systems. Polarization imaging offers multiple advantages such as multi-dimensional detection, high precision, high contrast, and dehazing.
The polarization photodetector has now been applied in many fields including visual dehazing, polymer stress visualization, and detection of cancerous areas in tissues.
This work was supported by the National Science Fund of China for Distinguished Young Scholars, the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the National Key R&D Program of China, and the International Partnership Program of CAS.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-12-05
Researchers from Singapore and China have used a superconducting quantum processor to study the phenomenon of quantum transport in unprecedented detail.
A better understanding of quantum transport, which can refer to the flow of particles, magnetisation, energy or information through a quantum channel, could propel advances in technologies such as nanoelectronics and thermal management.
“We’re quite excited because this is, practically, a new paradigm of doing quantum transport experiments,” says Centre for Quantum Technologies (CQT) Fellow Dario Poletti, whose co-corresponding authors for the new work published in Nature ...
2024-12-05
An international team of researchers including The University of Tokyo Kavli Institute for the Physics and Mathematics of the Universe (Kavli IPMU, WPI) has found evidence showing that old elliptical galaxies in the universe can form from intense star formation within early galaxy cores. This discovery will deepen our understanding of how galaxies evolved from the early Universe, reports a new study in Nature.
Galaxies in today’s Universe are diverse in morphologies and can be roughly divided into two categories: younger, disk-like spiral galaxies, ...
2024-12-05
Bamboo invasion has been widely observed across Asia (e.g., China, Japan, and India), North America, South America (e.g., Brazil and Peru) and Africa. Moso bamboo (Phyllostachys edulis), a large-running bamboo species native to subtropical China, is known for its invasive nature and ability to encroach upon adjacent communities, particularly derived forests. While some plot-based studies exist, our understanding of how forest structural dynamics and diameter–height allometric relationships respond to bamboo invasion has remained limited.
In a study published in the KeAi journal Forest Ecosystems, researchers from China ...
2024-12-05
Developing reliable methods to replace dead or damaged tissue is one of the primary goals of regenerative medicine. With steady advances in tissue engineering and biomedicine, we are almost at a point where growing cell sheets in the lab and transplanting them onto damaged or diseased organs is becoming a reality rather than fiction. Notably, myoblast cell sheets have already been used to successfully treat severe heart failure, demonstrating the potential of this technology.
However, there are still a few unsolved challenges ...
2024-12-05
Earth's tropical rain belt, responsible for monsoons that sustain billions of people and vibrant ecosystems, has long been a reliable feature of the planet's climate. But new research reveals this vital system wasn't always so dependable. A study published in Geophysical Research Letters shows that during the early Eocene—the hottest period in the last 65 million years—the rain belt's seasonal shifts weakened dramatically. These ancient changes could offer critical warnings about the impact of modern global warming.
A Greenhouse Climate 50 Million Years ...
2024-12-05
Rice paddies, responsible for approximately 10% of global anthropogenic methane (CH₄) emissions, are increasingly recognized as a key contributor to global warming. Reducing emissions from rice cultivation is essential to achieving international climate goals, especially in light of commitments to carbon neutrality and peak emissions targets.
A team led by Prof. LI Tingting from the Institute of Atmospheric Physics at the Chinese Academy of Sciences has validated an independently developed methane emission model, CH4MOD, at the global scale. This research highlights the advantages of process-based models over the commonly ...
2024-12-05
Women who experience infertility but do not use fertility treatments have a higher risk of developing a group of conditions called systemic autoimmune rheumatic diseases (SARD) in the nine years after a naturally conceived birth compared to women without fertility problems.
The new research, published today (Thursday) in Human Reproduction [1], one of the world’s leading reproductive medicine journals, found that this was true even after accounting for higher rates of pre-eclampsia (high blood pressure during pregnancy), preterm birth ...
2024-12-05
Colorful auroras appeared around Japan's Honshu and Hokkaido islands on May 11, 2024, sparked by an intense magnetic storm. Usually, auroras observed at low latitudes appear red due to the emission of oxygen atoms. But on this day, a salmon pink aurora was observed throughout the night, while an unusually tall, blue-dominant aurora appeared shortly before midnight.
Smartphone videos and amateur photos captured the event, enabling scientists to combine public data with their own research and study the phenomenon.
In a ...
2024-12-05
Higher rates of certain cancers in countries, such as the UK, may be linked to two particular strains of bacteria. Targeting these with treatments or vaccines could help reduce the risk of colorectal, bladder, and prostate cancers.
Researchers from the Wellcome Sanger Institute, the University of Helsinki, and collaborators investigated the differences in cancer incidence for colorectal, bladder and prostate cancers, and compared these to global data tracking Escherichia coli (E.coli) strains. Specifically, they looked at the dominant two E.coli strains that produce a substance that has been previously identified as a risk factor for colorectal cancer.
Their ...
2024-12-05
Embargoed for release: Wednesday, Dec. 4, 6:30 PM ET
Key points:
Study participants who consumed at least five servings of any chocolate per week showed a 10% lower risk of type 2 diabetes (T2D) compared to those who rarely or never ate chocolate. Dark chocolate had an even bigger impact: Participants who consumed at least five servings of this chocolate per week showed a 21% lower risk of T2D.
Consumption of milk chocolate, but not dark chocolate, was not associated with T2D risk; it was associated ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Researchers develop polarization photodetector mimicking desert ant