(Press-News.org) Rising sea levels, melting glaciers, heatwaves at sea – 2023 set a number of alarming new records. The global mean temperature also rose to nearly 1.5 degrees above the preindustrial level, another record. Seeking to identify the causes of this sudden rise has proven a challenge for researchers. After all, factoring in the effects of anthropogenic influences like the accumulation of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere, of the weather phenomenon El Niño, and of natural events like volcanic eruptions, can account for a major portion of the warming. But doing so still leaves a gap of roughly 0.2 degrees Celsius, which has never been satisfactorily explained. A team led by the Alfred Wegener Institute puts forward a possible explanation for the rise in global mean temperature: our planet has become less reflective because certain types of clouds have declined.
“In addition to the influence of El Niño and the expected long-term warming from anthropogenic greenhouse gases, several other factors have already been discussed that could have contributed to the surprisingly high global mean temperatures since 2023,” says Dr Helge Goessling, main author of the study from the Alfred Wegener Institute, Helmholtz Centre for Polar and Marine Research (AWI): e.g. increased solar activity, large amounts of water vapour from a volcanic eruption, or fewer aerosol particles in the atmosphere. But if all these factors are combined, there is still 0.2 degrees Celsius of warming with no readily apparent cause.
“The 0.2-degree-Celsius ‘explanation gap’ for 2023 is currently one of the most intensely discussed questions in climate research,” says Helge Goessling. In an effort to close that gap, climate modellers from the AWI and the European Centre for Medium-Range Weather Forecasts (ECMWF) took a closer look at satellite data from NASA, as well as the ECMWF’s own reanalysis data, in which a range of observational data is combined with a complex weather model. In some cases, the data goes back to 1940, permitting a detailed analysis of how the global energy budget and cloud cover at different altitudes have evolved.
“What caught our eye was that, in both the NASA and ECMWF datasets, 2023 stood out as the year with the lowest planetary albedo,” says co-author Dr Thomas Rackow from the ECMWF. Planetary albedo describes the percentage of incoming solar radiation that is reflected back into space after all interactions with the atmosphere and the surface of the Earth. “We had already observed a slight decline in recent years. The data indicates that in 2023, the planetary albedo may have been at its lowest since at least 1940.” This would worsen global warming and could explain the ‘missing’ 0.2 degrees Celsius. But what caused this near-record drop in planetary albedo?
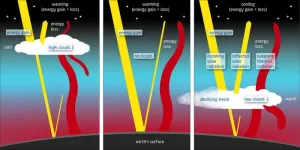
Decline in lower-altitude clouds reduces Earth’s albedo
The albedo of the surface of the Earth has been in decline since the 1970s – due in part to the decline in Arctic snow and sea ice, which also means fewer white areas to reflect back sunlight. Since 2016, this has been exacerbated by sea-ice decline in the Antarctic. “However, our analysis of the datasets shows that the decline in surface albedo in the polar regions only accounts for roughly 15 percent of the most recent decline in planetary albedo,” Helge Goessling explains. And albedo has also dropped markedly elsewhere. In order to calculate the potential effects of this reduced albedo, the researchers applied an established energy budget model capable of mimicking the temperature response of complex climate models. What they found: without the reduced albedo since December 2020, the mean temperature in 2023 would have been approximately 0.23 degrees Celsius lower.
One trend appears to have significantly affected the reduced planetary albedo: the decline in low-altitude clouds in the northern mid-latitudes and the tropics. In this regard, the Atlantic particularly stands out, i.e., exactly the same region where the most unusual temperature records were observed in 2023. “It’s conspicuous that the eastern North Atlantic, which is one of the main drivers of the latest jump in global mean temperature, was characterised by a substantial decline in low-altitude clouds not just in 2023, but also – like almost all of the Atlantic – in the past ten years.” The data shows that the cloud cover at low altitudes has declined, while declining only slightly, if at all, at moderate and high altitudes.
The fact that mainly low clouds and not higher-altitude clouds are responsible for the reduced albedo has important consequences. Clouds at all altitudes reflect sunlight, producing a cooling effect. But clouds in high, cold atmospheric layers also produce a warming effect because they keep the warmth emitted from the surface in the atmosphere. “Essentially it’s the same effect as greenhouse gases,” says Helge Goessling. But lower clouds don’t have the same effect. “If there are fewer low clouds, we only lose the cooling effect, making things warmer.”
But why are there fewer low clouds? Lower concentrations of anthropogenic aerosols in the atmosphere, especially due to stricter regulations on marine fuel, are likely a contributing factor. As condensation nuclei, aerosols play an essential part in cloud formation, while also reflecting sunlight themselves. In addition, natural fluctuations and ocean feedbacks may have contributed. Yet Helge Goessling considers it unlikely that these factors alone suffice and suggests a third mechanism: global warming itself is reducing the number of low clouds. “If a large part of the decline in albedo is indeed due to feedbacks between global warming and low clouds, as some climate models indicate, we should expect rather intense warming in the future,” he stresses. “We could see global long-term climate warming exceeding 1.5 degrees Celsius sooner than expected to date. The remaining carbon budgets connected to the limits defined in the Paris Agreement would have to be reduced accordingly, and the need to implement measures to adapt to the effects of future weather extremes would become even more urgent.”
Original publication
H. F. Goessling, T. Rackow, T. Jung, Recent global temperature surge intensified by record-low planetary albedo, Science (2024). doi: 10.1126/science.adq7280
END
Rapid surge in global warming mainly due to reduced planetary albedo
Researchers find a potential explanation for the unusually sudden temperature rise in 2023: reduced low-level cloud cover limits Earth’s ability to reflect solar radiation
2024-12-05
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Single mutation in bovine H5N1 switches viral binding specificity to human receptors
2024-12-05
A single mutation in bovine influenza H5N1 – a clade of the highly pathogenic avian influenza virus that has been increasingly detected among North American livestock herds – can cause the virus to switch affinity from animal-type receptors to human-type receptors, according to a new study. The findings highlight the crucial need for continuous surveillance of emerging H5N1 mutations, as even subtle genetic changes could increase the virus's capacity for human adaptation and transmission, potentially triggering a future influenza pandemic. In 2021, the highly pathogenic influenza H5N1 clade ...
Discovered: the neuroendocrine circuit that dictates when fish are ready to hatch
2024-12-05
Researchers have uncovered a previously unknown yet crucial role for thyrotropin-releasing hormone (Trh) in zebrafish hatching and reveal how this hormone activates a transient neuroendocrine circuit that controls when fish larvae are ready to leave the egg and swim free. For egg-born animals, hatching marks a pivotal shift, transitioning from the sheltered environment of an egg capsule to external conditions. This crucial event is not strictly hardwired into the embryo’s developmental program. Rather, hatching is a regulated ...
Climate change threatens global biodiversity, with extinction risks escalating at higher temperatures
2024-12-05
Climate change is driving global extinction risks, with 1.6% of species threatened at 1.3°C of warming and risks escalating to 29.7% at 5.4°C, according to a new meta-analysis encompassing more than 30 years of research. Climate change is reshaping ecosystems and biodiversity globally, altering species distributions, interactions, and population dynamics. While some species adapt or migrate to track shifting climates, others face population declines, shrinking ranges, and potential extinction. ...
Scientists ‘turn up the heat’ on understanding coffee wilt disease which threatens our favourite daily brew
2024-12-05
Scientists, including those from Imperial College London, University of Oxford and CABI, have ‘turned up the heat’ on how repeated outbreaks of coffee wilt disease threatened arabica and robusta varieties of our favourite daily coffee brew.
The scientists, who present their findings in the journal PLoS Biology, say the fungal pathogen Fusarium xylarioides continues to pose a significant threat to coffee production and incomes across sub-Saharan Africa.
Their work supports earlier findings, based on DNA markers and crossing experiments which suggested that F. xylarioides is ...
Researchers crack the code of how fish pick their own birthday
2024-12-05
New research has revealed that fish embryos actively control their hatching timing through a neurohormone, Thyrotropin-Releasing Hormone (TRH), which triggers the release of enzymes that dissolve the egg wall. This groundbreaking discovery uncovers a previously unknown neural mechanism that governs a critical life-stage transition, showing that embryos are not passive but instead actively make life-or-death decisions. The finding has significant evolutionary implications, offering new insights into neurobiology, survival strategies, and environmental adaptation in vertebrates.
Dr. ...
Shaking sensor continuously monitors inflammation
2024-12-05
Northwestern University scientists have designed a new implantable device that can monitor fluctuating levels of proteins within the body in real time.
Inspired by fruit shaking off the branches of a tree, the device comprises strands of DNA that stick to proteins, shake them off and then grab more proteins. This creative strategy enables the device to sample various proteins over time to measure changes in inflammatory markers.
In proof-of-concept experiments, the sensors accurately and sensitively measured protein biomarkers of inflammation in diabetic rats. ...
Scripps Research scientists identify mutation that could facilitate H5N1 “bird flu” virus infection and potential transmission in humans
2024-12-05
LA JOLLA, CA—Avian influenza viruses typically require several mutations to adapt and spread among humans, but what happens when just one change can increase the risk of becoming a pandemic virus? A recent study led by scientists at Scripps Research reveals that a single mutation in the H5N1 “bird flu” virus that has recently infected dairy cows in the U.S. could enhance the virus’ ability to attach to human cells, potentially increasing the risk of passing from person to person. The findings—published in ...
Queen Mary University of London vaccination tool boosts uptake of MMR vaccine in children
2024-12-05
A software tool developed by Queen Mary University of London’s Clinical Effectiveness Group (CEG) and used as part of a facilitated quality improvement programme has increased the number of children receiving their first MMR vaccination on time in North East London. The success of this programme highlights the potential of a learning health system and data-driven solutions to enhance public health and improve vaccination uptake across the UK.
An evaluation published in Vaccine revealed that the APL-Imms ...
Implantable sensors unlock ability to continuously monitor inflammation
2024-12-05
Implantable Sensors Unlock Ability to Continuously Monitor Inflammation
The Chan Zuckerberg Biohub Chicago’s milestone achievement tracks protein levels in real time, enabling monitoring of inflammation at the cellular level
Proteins are the building blocks of life, and changes in protein levels can indicate improving health or impending illness, including signs of inflammation. While protein levels can be measured in periodic blood or urine tests, it has been an uphill challenge to figure out how to continuously monitor protein levels in the human body in real time.
Now, a team of bioengineers at Chan Zuckerberg Biohub Chicago, supported by the ...
Buffalo besties: Feral female buffalo build friendships based on similar personality traits
2024-12-05
HONG KONG (29 November 2024)—Similar social personalities strongly influence friendships in humans, yet we know relatively little about how animals choose their friends.
But a new study by researchers at City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) investigating a unique free-ranging feral population of water buffalo on Lantau Island in Hong Kong has discovered that close spatial proximity serves as an indicator of friendship based on the predictive patterns of certain personality traits.
“Our research provides evidence that friendships among water buffalo can form among individuals with similar behaviours. These findings ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
National policy to remedy harms of race-based kidney function estimation associated with increased transplants for Black patients
Study finds teens spend nearly one-third of the school day on smartphones, with frequent checking linked to poorer attention
Team simulates a living cell that grows and divides
Study illuminates the experiences of people needing to seek abortion care out of state
Digital media use and child health and development
Seeking abortion care across state lines after the Dobbs decision
Smartphone use during school hours and association with cognitive control in youths ages 11 to 18
Maternal acetaminophen use and child neurodevelopment
Digital microsteps as scalable adjuncts for adults using GLP-1 receptor agonists
Researchers develop a biomimetic platform to enhance CAR T cell therapy against leukemia
Heart and metabolic risk factors more strongly linked to liver fibrosis in women than men, study finds
Governing with AI: a new AI implementation blueprint for policymakers
Recent pandemic viruses jumped to humans without prior adaptation, UC San Diego study finds
Exercise triggers memory-related brain 'ripples' in humans, researchers report
Increased risk of bullying in open-plan offices
Frequent scrolling affects perceptions of the work environment
Brain activity reveals how well we mentally size up others
Taiwanese and UK scientists identify FOXJ3 gene linked to drug-resistant focal epilepsy
[Press-News.org] Rapid surge in global warming mainly due to reduced planetary albedoResearchers find a potential explanation for the unusually sudden temperature rise in 2023: reduced low-level cloud cover limits Earth’s ability to reflect solar radiation