(Press-News.org) An MRI-based imaging technique developed at the University of Cambridge predicts the response of ovarian cancer tumours to treatment, and rapidly reveals how well treatment is working, in patient-derived cell models.
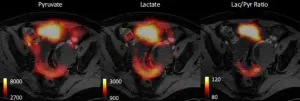
The technique, called hyperpolarised carbon-13 imaging, can increase the detected signal in an MRI scanner by more than 10,000 times. Scientists have found that the technique can distinguish between two different subtypes of ovarian cancer, to reveal their sensitivities to treatment.
They used it to look at patient-derived cell models that closely mimic the behaviour of human high grade serous ovarian cancer, the most common lethal form of the disease. The technique clearly shows whether a tumour is sensitive or resistant to Carboplatin, one of the standard first-line chemotherapy treatments for ovarian cancer.
This will enable oncologists to predict how well a patient will respond to treatment, and to see how well the treatment is working within the first 48 hours.
Different forms of ovarian cancer respond differently to drug treatments. With current tests, patients typically wait for weeks or months to find out whether their cancer is responding to treatment. The rapid feedback provided by this new technique will help oncologists to adjust and personalise treatment for each patient within days.
The study compared the hyperpolarised imaging technique with results from Positron Emission Tomography (PET) scans, which are already widely used in clinical practice. The results shows that PET did not pick up the metabolic differences between different tumour subtypes, so could not predict the type of tumour present.
The report is published today in the journal Oncogene.
“This technique tells us how aggressive an ovarian cancer tumour is, and could allow doctors to assess multiple tumours in a patient to give a more holistic assessment of disease prognosis so the most appropriate treatment can be selected,” said Professor Kevin Brindle in the University of Cambridge’s Department of Biochemistry, senior author of the report.
Ovarian cancer patients often have multiple tumours spread throughout their abdomen. It isn’t possible to take biopsies of all of them, and they may be of different subtypes that respond differently to treatment. MRI is non-invasive, and the hyperpolarised imaging technique will allow oncologists to look at all the tumours at once.
Brindle added: “We can image a tumour pre-treatment to predict how likely it is to respond, and then we can image again immediately after treatment to confirm whether it has indeed responded. This will help doctors to select the most appropriate treatment for each patient and adjust this as necessary.
“One of the questions cancer patients ask most often is whether their treatment is working. If oncologists can speed their patients onto the best treatment, then it’s clearly of benefit.”
The next step is to trial the technique in ovarian cancer patients, which the scientists anticipate within the next few years.
Hyperpolarised carbon-13 imaging uses an injectable solution containing a ‘labelled’ form of the naturally occurring molecule pyruvate. The pyruvate enters the cells of the body, and the scan shows the rate at which it is broken down - or metabolised – into a molecule called lactate. The rate of this metabolism reveals the tumour subtype and thus its sensitivity to treatment.
This study adds to the evidence for the value of the hyperpolarised carbon-13 imaging technique for wider clinical use. Brindle, who also works at the Cancer Research UK Cambridge Institute, has been developing this imaging technique to investigate different cancers for the last two decades, including breast, prostate and glioblastoma - a common and aggressive type of brain tumour. Glioblastoma also shows different subtypes that vary in their metabolism, which can be imaged to predict their response to treatment. The first clinical study in Cambridge, which was published in 2020, was in breast cancer patients.
Each year about 7,500 women in the UK are diagnosed with ovarian cancer - around 5,000 of these will have the most aggressive form of the disease, called high-grade serous ovarian cancer (HGSOC).
The cure rate for all forms of ovarian cancer is very low and currently only 43% of women in England survive five years beyond diagnosis. Symptoms can easily be missed, allowing the disease to spread before a woman is diagnosed - and this makes imaging and treatment challenging.
END
Imaging technique allows rapid assessment of ovarian cancer subtypes and their response to treatment
2024-12-06
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Genetic study of native hazelnut challenges misconceptions about how ancient Indigenous peoples used the land
2024-12-06
By decoding the DNA of the beaked hazelnut (Corylus cornuta), a native plant that thrives in British Columbia, a team of multidisciplinary scientists is providing new insight into how ancestral Indigenous peoples stewarded plants across the province.
Led by Chelsey Geralda Armstrong, an assistant professor in Simon Fraser University’s (SFU) Department of Indigenous Studies, the innovative study was recently published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Science (PNAS), a major scientific journal.
“The misconception that Indigenous ...
Greater patient education needed around antidepressants which may reduce genital sensitivity, SFU study finds
2024-12-06
The use of antidepressants is associated with sexual side effects including reduced genital sensitivity that persists after stopping the medication, a new Simon Fraser University study finds.
The study, published in Social Psychiatry and Psychiatric Epidemiology, indicates that 13 per cent of people who used antidepressants reported a reduction in genital sensitivity, compared to one per cent of users of other psychiatric medications.
“It’s gone under the radar for so long, largely due to stigma, shame and embarrassment,” says Yassie Pirani, an SFU alumnus and lead author on the study. ...
Increases in US life expectancy forecasted to stall by 2050, poorer health expected to cause nation’s global ranking to drop
2024-12-06
SEATTLE, Wash., Dec. 5, 2024 – The U.S. is failing to keep pace with dozens of countries around the world due to the steady decline of the nation’s health progress, according to a detailed analysis of all 50 states and Washington, D.C., published in The Lancet. Researchers at the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) produced health estimates and forecasts (the most likely future) of life expectancy, mortality, and morbidity due to more than 350 diseases and injuries and 68 risks in the U.S. from 1990 to 2050.
U.S. life expectancy improvements slow, global ranking drops
Life expectancy (LE) in the U.S. is forecasted to increase from ...
Gut microbiota: A consensus paper to regulate the "wild west" of diagnostic tests
2024-12-06
The gut microbiota might perhaps one day become a routine tool for the early diagnosis of many diseases and to guide treatment, but at present there is a lack of solid scientific evidence to support these claims. Yet, day by day, there are more and more offers of commercial kits for do-it-yourself testing, at the moment totally lacking in meaning and scientific solidity. To put a stop to this drift, an international panel of experts, coordinated by Dr Gianluca Ianiro, has drawn up ‘instructions for use’ for best practice in microbiota testing and recommendations for its indications, methods of analysis, presentation of results and potential clinical ...
Pacific curators restore Indigenous voices to colonial-era collections
2024-12-06
Fault Lines: Imagining Indigenous futures for colonial collections, at the University of Cambridge’s Museum of Archaeology and Anthropology (MAA) from 6th December 2024 to 21st December 2025, examines interactions between Indigenous communities and colonial institutions in this vast and culturally diverse region. From the 18th century, Indigenous peoples across the Pacific have navigated a changing roster of imperial powers including Great Britain, France, Germany, the United States, Australia and New Zealand.
The exhibition combines historic artefacts with newly commissioned artistic responses to examine the enduring legacies of cultural extraction and destruction during ...
What’s next for science: NRL to showcase advanced technology and research at AGU 2024
2024-12-05
WASHINGTON — The U.S. Naval Research Laboratory (NRL) will feature advanced technologies and research ranging from Earth to space sciences during the 24th Annual American Geophysical Union (AGU) Conference at the Walter E. Washington Convention Center in Washington, D.C., Dec. 9-13.
In addition to more than 70 NRL oral presentations and poster displays and an exhibit hall booth, attendees will have the opportunity to view the premier of the 5-minute CCOR-1 (Compact Coronagraph) film which details ...
Research alert: Changes in blood cell production over the lifetime could impact leukemia outcomes
2024-12-05
Researchers at University of California San Diego School of Medicine and their colleagues have developed the first comprehensive map of the dramatic changes that take place in the blood system over the course of the human lifetime.
The team quantified the gene expression of more than 58,000 individual hematopoietic (blood) stem cells at seven stages, from early fetal development to old age. They documented consistent changes in the types of blood cells that are produced in response to the functional demands of each life stage:
The ...
Controlling cancer cells’ gluttony for glutamine
2024-12-05
Cancer cells are like booming cities without urban planners. They expand quickly, and in doing so, the resulting tumors consume more energy and other resources than they can acquire from nearby blood vessels.
Rather than limiting their growth to more sustainable rates, cancer cells adapt by finding alternative ways to scavenge what they need. One scrounging strategy prevalent in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma (PDAC) involves cancer cells reshaping their cell surfaces to snatch extra nutrients from the jelly-like substance between cells or extracellular ...
NASA’s Hubble takes the closest-ever look at a quasar
2024-12-05
Astronomers have used the unique capabilities of NASA's Hubble Space Telescope to peer closer than ever into the throat of an energetic monster black hole powering a quasar. A quasar is a galactic center that glows brightly as the black hole consumes material in its immediate surroundings.
The new Hubble views of the environment around the quasar show a lot of "weird things," according to Bin Ren of the Côte d'Azur Observatory and Université Côte d'Azur in Nice, France. "We've got a few blobs of different sizes, and a mysterious L-shaped filamentary structure. This is all within 16,000 light-years of the black hole."
Some ...
BeginNGS® newborn screening by genome sequencing shown to be safe and effective in two clinical studies
2024-12-05
San Diego – Dec. 5, 2024 – Two studies published today in the American Journal of Human Genetics show the potential for genomic screening in newborns to address high rates of infant hospitalization and mortality in the United States. Presently, hundreds of genetic diseases are either preventable or treatable but currently are detected only after a child falls ill and endures a years-long “diagnostic odyssey,” often receiving diagnoses too late to achieve the best outcomes.
The first study, titled “Prequalification of genome-based newborn screening for severe childhood genetic diseases ...