Fukuoka, Japan – Researchers at Kyushu University have revealed how spatial distance between specific regions of DNA is linked to bursts of gene activity. Using advanced cell imaging techniques and computer modeling, the researchers showed that the folding and movement of DNA, as well as the accumulation of certain proteins, changes depending on whether a gene is active or inactive. The study, published on December 6 in Science Advances, sheds insight into the complicated world of gene expression and could lead to new therapeutic techniques for diseases caused by improper regulation of gene expression.
Gene expression is a fundamental process that occurs within cells, with two main phases: transcription, where DNA is copied into RNA, and translation, where the RNA is used to make proteins. For each cell to carry out its specific functions in the body, or to respond to changing conditions, the right amount of a protein must be produced at the right time, meaning genes must be carefully switched on and off.
Previously, gene transcription was thought to occur in a continuous, smooth process. But with better technology to observe individual cells, scientists now know that transcription occurs in short, unpredictable bursts.
“A gene will randomly switch on for a few minutes and large amounts of RNA will be produced. Then, the gene will suddenly switch off again,” says Professor Hiroshi Ochiai, from Kyushu University’s Medical Institute of Bioregulation and the study’s senior author. “It happens in nearly all genes, and in all living things, from plants, to animals, to bacteria.”
This erratic and dynamic nature of transcription, known as transcriptional bursting, is a key mechanism for controlling gene activity in individual cells. It’s one reason why cells within the same tissue or culture environment show variability in their gene expression levels, which is crucial for processes like early embryonic development and cancer evolution. However, the exact mechanisms behind bursting remains unknown.
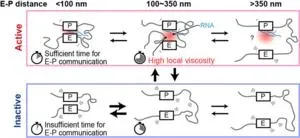
In this study, the researchers decided to look into the role of DNA sequences known as enhancers and promoters, and how their spatial distance impacts transcriptional bursting. The promoter is usually located right next to the gene, and is where the protein that carries out transcription attaches to the DNA. Enhancers, on the other hand, are often many hundreds of thousands of bases away from the gene, but as DNA strands move and fold, enhancers can still end up close to genes in 3D space, amplifying gene activity.
“We believe that enhancers play a crucial role in why transcription occurs in bursts of activity, but so far, the research is unclear,” says Ochiai.
To test this idea, Ochiai and his team used an advanced imaging technique called seq-DNA/RNA-IF-FISH, which labels DNA, RNA and specific proteins with fluorescent probes. This triple-layered technique allowed the researchers to simultaneously capture the location of DNA, RNA and specific proteins in 3D space within individual mouse embryonic stem cells. With that information, the team could determine whether certain genes were on or off, see how the promoters and enhancers were interacting during bursts of activity, and where the proteins were accumulating, at an unprecedented level of detail.
As an example, the researchers focused on a gene called Nanog, a 770,000-base length of DNA on chromosome 6, which has a promoter and three enhancer regions and is known to undergo transcriptional bursting in cultured mouse embryonic stem cells.
The researchers found that in imaged cells where Nanog RNA was present (meaning the gene was active), the most distant enhancer was located in close spatial proximity to the Nanog gene. In contrast, when Nanog was inactive, the imaging showed that the same enhancer region was physically further away.
Additionally, the scientists also found that proteins involved in regulating transcription also accumulated in the area around the enhancers and promoters when Nanog was active.
To better understand the mechanism, Ochiai and his team used computer modeling to simulate how the different parts of DNA interact and move inside the cell, both when the Nanog gene is active and inactive.
They developed their model by using data from their imaging experiments to make a “map” of how frequently different regions of DNA interacted with each other and how the DNA was folded in space. Using this map, the model then simulated how the DNA chain might randomly move.
The model predicted that when in the active state, each enhancer region interacted for more than twice as long with the promoters, compared to when the gene was inactive.
The model showed that these longer periods of interaction occurred due to “friction” around the DNA. Due to the accumulation of proteins and RNA when Nanog was active, the fluid became more viscous, and caused the modelled DNA strand to move slowly. Therefore, the gene was able to stay active for longer bursts of time. In contrast, the simulated DNA moved quicker when Nanog was inactive, meaning that the promoter and enhancers didn’t have time to interact.
“The modeling suggests that bursting is stabilized due to these reinforcing loops,” concluded Ochiai. “Of course, this is just a simulation. The next step is to prove this mechanism also occurs in cells.”
###
For more information about this research, see “Transcription-coupled changes in genomic region proximities during transcriptional bursting,” Hiroaki Ohishi, Soya Shinkai, Hitoshi Owada, Takeru Fujii, Kazufumi Hosoda, Shuichi Onami, Takashi Yamamoto, Yasuyuki Ohkawa, Hiroshi Ochiai, Science Advances, https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.adn0020
About Kyushu University
Founded in 1911, Kyushu University is one of Japan's leading research-oriented institutes of higher education, consistently ranking as one of the top ten Japanese universities in the Times Higher Education World University Rankings and the QS World Rankings. The university is one of the seven national universities in Japan, located in Fukuoka, on the island of Kyushu—the most southwestern of Japan’s four main islands with a population and land size slightly larger than Belgium. Kyushu U’s multiple campuses—home to around 19,000 students and 8000 faculty and staff—are located around Fukuoka City, a coastal metropolis that is frequently ranked among the world's most livable cities and historically known as Japan's gateway to Asia. Through its VISION 2030, Kyushu U will “drive social change with integrative knowledge.” By fusing the spectrum of knowledge, from the humanities and arts to engineering and medical sciences, Kyushu U will strengthen its research in the key areas of decarbonization, medicine and health, and environment and food, to tackle society’s most pressing issues.
END