(Press-News.org) New guidelines on the diagnosis and management of premature ovarian insufficiency (POI) – developed by the Centre for Research Excellence in Women’s Health in Reproductive Life (CRE-WHiRL) at Monash University, and key international women’s health organisations with an international team of experts including women with lived experience – will be published today (TBC) simultaneously in three leading journals.
POI is defined as loss of ovarian function before 40 years. This is much earlier than the usual age of menopause; occurring at an average age of 48-51 years in women globally.
POI affects approximately 4 per cent of women globally and is associated with infertility, psychological distress and an increased risk of osteoporosis, cardiovascular disease, mortality, dementia and cognitive dysfunction. While hormone therapy has been shown to mitigate some of these effects, the management of POI globally remains sub-optimal with delayed diagnosis, variation in care and patient dissatisfaction.
The guidelines were last updated in 2015 and the 2024 update of the POI Guidelines of the European Society of Human Reproduction and Embryology (ESHRE), for the first time, involved an international partnership between ESHRE and the International Menopause Society, American Society for Reproductive Medicine and NHMRC-funded CRE-WHiRL, which is led by the Monash Centre for Health Research and Implementation (MCHRI), at Monash University.
The 2024 guidelines provide 145 recommendations on symptoms, diagnosis, causation, sequelae and treatment of POI. The recommendations were developed using the best available evidence and graded according to the strength of that evidence. Topics to cover in the guideline were informed by an international survey of women and healthcare professionals. New information is provided about the genetic causes of POI, the impact of POI on muscle health, use of anti-mullerian hormone, non-hormonal therapies, lifestyle interventions and complementary therapies.
According to Co-Chair of the guideline development group, Associate Professor Amanda Vincent, from CRE-WHiRL, a key change of the updated 2024 guidelines is the recommendation regarding the diagnosis of POI; only one elevated follicle stimulating hormone (FSH) level is needed combined with irregular or absent menstrual periods for at least four months. The FSH level only requires repeating if the diagnosis remains unclear. Women with lived experience provided recommendations on how to convey the diagnosis and care of women with POI.
“The new Guideline means faster diagnosis of POI, conveyed in a sensitive manner and involving shared decision making between the healthcare professional and the woman experiencing POI,” said Associate Professor Vincent.
A comprehensive clinical evaluation requires more than assessing symptoms, “it must also include asking a patient about her sexual wellbeing, fertility needs, psychological health, cardiovascular and osteoporosis risks, and co-morbidities,” she said.
The updated guideline stresses the importance of personalised hormone therapy, unless contraindicated, for symptom relief and chronic disease prevention; with the need for prompt institution and continuation until the usual age of menopause.
“This provides healthcare professionals with the clear advice on best practice in POI care, based on the best evidence currently available,” Associate Professor Vincent said.
The POI guideline is accompanied by co-designed resources for consumers including an updated Ask Early menopause App (www.askearlymenopause.org) and a toolkit for healthcare professionals’
The Ask Early Menopause App – www.askearlymenopause.org - informs and supports women to manage early menopause with evidence-based resources, a personal dashboard and a discussion forum. The App has over 9,000 users worldwide.
END
New international guidelines announced for Premature Ovarian Insufficiency (POI)
New guidelines on the diagnosis and management of POI to be simultaneously published in 3 international journals
2024-12-09
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Supporting parents through “unimaginable pain” of losing child – new toolkit developed for clinicians involved in Child Death Review
2024-12-08
Parents who face the heartbreaking loss of their child should get a specific keyworker to support them through bereavement, wherever they are in the country, according to a set of recommendations informed by new research.
In an academic paper published in Archives of Disease in Childhood today, bereaved parents and academic experts from the University of Birmingham, University of Bristol and Birmingham Community Healthcare NHS Foundation Trust have outlined their recommendations for support that all bereaved parents ...
Could online technology be a clue as to why boys in Norway are outperforming girls in learning English as a second language?
2024-12-08
Bucking conventionality, boys in Norway are making early gains in reading English as a second language and even outperforming girls at age 10 and 13 – a new a study of more than one million students suggests.
Publishing their findings in the peer-reviewed journal Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice, experts from the University of Oslo propose the perhaps unexpected results might be explained by online gaming and experiences with other digital technologies such as YouTube – with English being the language of the internet.
“Our ...
A healthy diet helps the weighty battle with chronic pain
2024-12-08
Chronic pain is an acute and debilitating condition that affects millions of people worldwide. And while pain interventions are available, many people struggle without treatment at all.
Now new research from the University of South Australia shows that adopting a healthy diet can reduce the severity of chronic pain, presenting an easy and accessible way for sufferers to better manage their condition.
Exploring associations between body fat, diet, and pain, researchers found that a greater consumption of foods within the Australian Dietary Guidelines was directly associated with lower levels of body ...
ASH 2024: Antibody shows encouraging results for treating high-risk follicular lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma
2024-12-08
MIAMI, FLORIDA (STRICTLY EMBARGOED UNTIL DEC. 8, 2024, AT 12 NOON EST) – Two clinical trials testing the antibody loncastuximab tesirine (Zynlonta) showed encouraging results in patients with high-risk forms of two blood cancers – follicular lymphoma and marginal zone lymphoma. The findings, led by physician-scientists at Sylvester Comprehensive Cancer Center, part of the University of Miami Miller School of Medicine, will be presented at the American Society of Hematology’s 2024 meeting in San Diego.
One study, a phase 2 clinical trial led by Juan Alderuccio, M.D., ...
Observation of new electric field signals strong potential for assorted devices: new research at City University of Hong Kong
2024-12-08
HONG KONG (8 December 2024)—A new vortex electric field with the potential to enhance future electronic, magnetic and optical devices has been observed by researchers from City University of Hong Kong (CityUHK) and local partners.
The research, published in Science, is highly valuable as it can upgrade the operation of many devices, including strengthening memory stability and computing speed. With further research, the discovery of the vortex electric field can even later impact the fields of quantum computing, spintronics, and nanotechnology.
“Previously, generating a vortex electric field required expensive thin film deposition techniques and complex procedures. However, our ...
A sickle cell first: Base editing, a new form of gene therapy, leaves patient feeling ‘more than fine’
2024-12-07
Though he doesn’t remember it, Branden Baptiste had his first sickle cell crisis at age 2. Through elementary school, he was in and out of the hospital with pain episodes, not knowing why. As he got older, he learned he had sickle cell disease: His red blood cells were forming sickle shapes and getting stuck in his blood stream, preventing oxygen from reaching his tissues.
“From age 12, things skyrocketed,” says Branden, now 20. “I was in the hospital every other month with crises.” He estimates he missed 60 days of school every year.
In sixth grade, Branden had to have his left hip replaced ...
Keto diet metabolite may power up CAR T cells to kill cancer
2024-12-07
SAN DIEGO – A simple dietary supplement may provide a new approach to boost CAR T cell function, according to a study from researchers in the Perelman School of Medicine at the University of Pennsylvania and Penn Medicine’s Abramson Cancer Center. While the approach needs to be assessed in clinical trials, the early research, shared in a press briefing today at the 66th American Society of Hematology (ASH) Annual Meeting and Exposition (Abstract 4), hints at a potentially cost-effective strategy to improve CAR T cell function and cancer-fighting abilities.
CAR T cell therapy is a ...
New study reveals a fiber diet may delay a type of blood cancer
2024-12-07
Today researchers at Memorial Sloan Kettering Cancer Center (MSK) reported results from the first ever clinical trial to show that a high fiber plant based dietary intervention may delay progression to multiple myeloma, a type of rare, incurable blood cancer affecting the bone marrow. The study enrolled 20 participants with a precancerous blood disorder and an elevated body mass index (BMI) at risk for developing multiple myeloma. They received 12 weeks of high fiber plant-based meals and 24 weeks of coaching. Two participants with progressing disease prior to study showed a significant improvement of their disease progression trajectory. Additionally, at one year ...
Global clinical trial shows improved survival rates for common childhood leukemia
2024-12-07
Just days before his fourth birthday, Santiago was diagnosed with B-cell acute lymphoblastic leukemia (B-ALL), the most common cancer in children.
He began chemotherapy the next day, and the outlook was promising – disease-free survival rates for B-ALL are among the highest for paediatric cancers, at 80 to 85 per cent. However, limited progress has been made over the last 15 years, and relapsed B-ALL remains a leading cause of cancer death among children.
Seeking to explore all options, Santiago’s parents enrolled him in a Children’s Oncology Group clinical trial led by scientists ...
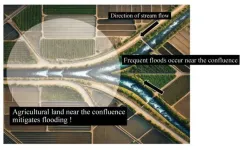
Agricultural land near where rivers meet can mitigate floods
2024-12-07
Tokyo, Japan – Researchers from Tokyo Metropolitan University showed that agricultural land preserved around river confluences can help mitigate floods. They make a case for Eco-DRR, an approach that uses existing environmental resources to improve resilience against flooding. Statistical analysis showed that municipalities with agricultural land in areas with high water storage potential suffered fewer floods, with stronger correlation when agricultural land was situated near river confluences. The team hope their findings inform effective land usage.
Climate change has brought ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tiny bubbles, big breakthrough: Cracking cancer’s “fortress”
A biological material that becomes stronger when wet could replace plastics
Glacial feast: Seals caught closer to glaciers had fuller stomachs
Get the picture? High-tech, low-cost lens focuses on global consumer markets
Antimicrobial resistance in foodborne bacteria remains a public health concern in Europe
Safer batteries for storing energy at massive scale
How can you rescue a “kidnapped” robot? A new AI system helps the robot regain its sense of location in dynamic, ever-changing environments
Brainwaves of mothers and children synchronize when playing together – even in an acquired language
A holiday to better recovery
Cal Poly’s fifth Climate Solutions Now conference to take place Feb. 23-27
Mask-wearing during COVID-19 linked to reduced air pollution–triggered heart attack risk in Japan
Achieving cross-coupling reactions of fatty amide reduction radicals via iridium-photorelay catalysis and other strategies
Shorter may be sweeter: Study finds 15-second health ads can curb junk food cravings
Family relationships identified in Stone Age graves on Gotland
Effectiveness of exercise to ease osteoarthritis symptoms likely minimal and transient
Cost of copper must rise double to meet basic copper needs
A gel for wounds that won’t heal
Iron, carbon, and the art of toxic cleanup
Organic soil amendments work together to help sandy soils hold water longer, study finds
Hidden carbon in mangrove soils may play a larger role in climate regulation than previously thought
Weight-loss wonder pills prompt scrutiny of key ingredient
Nonprofit leader Diane Dodge to receive 2026 Penn Nursing Renfield Foundation Award for Global Women’s Health
Maternal smoking during pregnancy may be linked to higher blood pressure in children, NIH study finds
New Lund model aims to shorten the path to life-saving cell and gene therapies
Researchers create ultra-stretchable, liquid-repellent materials via laser ablation
Combining AI with OCT shows potential for detecting lipid-rich plaques in coronary arteries
SeaCast revolutionizes Mediterranean Sea forecasting with AI-powered speed and accuracy
JMIR Publications’ JMIR Bioinformatics and Biotechnology invites submissions on Bridging Data, AI, and Innovation to Transform Health
Honey bees navigate more precisely than previously thought
Air pollution may directly contribute to Alzheimer’s disease
[Press-News.org] New international guidelines announced for Premature Ovarian Insufficiency (POI)New guidelines on the diagnosis and management of POI to be simultaneously published in 3 international journals