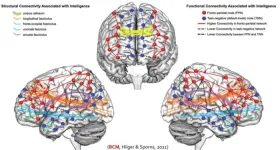
(Press-News.org) AI can predict human intelligence by looking at the connections of a working human brain. Neuroscientists can predict intelligence from brain structure and function—to a point. Previous studies have suggested that intelligence is widely distributed across the brain. Kirsten Hilger and colleagues used machine learning models to predict multiple kinds of intelligence from brain connections of 806 healthy adults while resting and while completing tasks. Fluid intelligence includes inductive and deductive reasoning abilities that do not rely on context, while crystallized intelligence reflects the ability to apply knowledge from individual experience and culture. General intelligence captures both types of intelligence. The prediction performance of the model developed by Hilger and colleagues was highest for general intelligence, followed by crystallized intelligence, and then fluid intelligence. Cognitively demanding tasks produced the most accurate predictions. Interestingly, models trained with connections between brain regions proposed in most popular neurocognitive intelligence theories outperformed models trained with the same number of connections between randomly chosen regions, which empirically supports these theories. According to the authors, theory-driven models were outperformed by whole-brain models, indicating that there are still more aspects of intelligence waiting to be understood.
END
Machine learning prediction of human intelligence
2024-12-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Empowering older adults with home-care robots
2024-12-10
Advances in medicine have led to an increase in human longevity. Estimates suggest that by 2030, one in every six individuals globally will be aged over 60 years. This rapid increase in the aging population implies a larger number of aged individuals requiring care. Family members and professional caregivers may not be able to meet this increasing demand. Furthermore, reports suggest a significant shortage of workforce, including nurses, in several developed countries, underscoring the need for additional strategies that ...
New concept for sustainable fuel cell polymer electrolytes overcomes barriers in high-temperature, low-humidity use, advancing net-zero carbon goals
2024-12-10
A research group led by Atsushi Noro at Nagoya University in Japan has announced a novel design concept for fuel cell electrolytes, utilizing a phosphonic acid polymer with hydrocarbon spacers. This innovative concept allows fuel cells to operate effectively under high-temperature (above 100°C) and low-humidity conditions, addressing crucial barriers to their broader use. The research has been published in ACS Applied Polymer Materials.
By electrochemically reacting hydrogen and oxygen, fuel cells produce electricity while emitting only water, highlighting their clean energy capabilities. However, perfluorosulfonic ...
Sculpting the brain (without chisel or scalpel)
2024-12-10
Imagine being able to inscribe a new pattern of activity into a person’s brain that would allow for faster learning, or better treatment of psychiatric and developmental disorders such as depression or autism. Now imagine being able to do that in a way that doesn’t require brain surgery or any physical manipulation. Sounds like science fiction?
It still is. But that’s exactly what Coraline Iordan, an assistant professor of brain and cognitive sciences and of neuroscience at the University of Rochester has been working toward, showing for the ...
Wrong trees in the wrong place can make cities hotter at night, study reveals
2024-12-10
University of Cambridge media release
Wrong trees in the wrong place can make cities hotter at night, study reveals
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 10:00 AM UK TIME / 05:00 AM (US ET) ON TUESDAY 10TH DECEMBER 2024
While trees can cool some cities significantly during the day, new research shows that tree canopies can also trap heat and raise temperatures at night. The study aims to help urban planners choose the best combinations of trees and planting locations to combat ...
New gene therapy reverses heart failure in large animal model
2024-12-10
A new gene therapy can reverse the effects of heart failure and restore heart function in a large animal model. The therapy increases the amount of blood the heart can pump and dramatically improves survival, in what a paper describing the results calls “an unprecedented recovery of cardiac function.”
Currently, heart failure is irreversible. In the absence of a heart transplant, most medical treatments aim to reduce the stress on the heart and slow the progression of the often-deadly disease. But if the gene therapy shows similar ...
Young children less likely than adults to see discrimination as harmful
2024-12-10
A White House report earlier this year outlined how discrimination, and specifically racial discrimination, persists in the United States today, raising questions about when attitudes underlying these behaviors are formed.
Past scholarship has found discriminatory views increase as children grow older. However, new work by a team of New York University psychology researchers shows that young children in the US are less likely than adults to see discrimination as harmful, indicating these beliefs begin at an early age. Moreover, children ...
Tiny poops in the ocean may help solve the carbon problem
2024-12-10
A Dartmouth-led study proposes a new method for recruiting trillions of microscopic sea creatures called zooplankton in the fight against climate change by converting carbon into food the animals would eat, digest, and send deep into the ocean as carbon-filled feces.
The technique harnesses the animals' ravenous appetites to essentially accelerate the ocean's natural cycle for removing carbon from the atmosphere, which is known as the biological pump, according to the paper in Nature Scientific Reports.
It begins ...
Study offers insight into chloroplast evolution
2024-12-10
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — One of the most momentous events in the history of life involved endosymbiosis — a process by which one organism engulfed another and, instead of ingesting it, incorporated its DNA and functions into itself. Scientific consensus is that this happened twice over the course of evolution, resulting in the energy-generating organelles known as mitochondria and, much later, their photosynthetic counterparts, the plastids.
A new study published in the journal Nature Communications explores the origin of chloroplasts, the plastids that allow plants ...
Advancing the synthesis of two-dimensional gold monolayers
2024-12-10
Nanostructured two-dimensional gold monolayers offer possibilities in catalysis, electronics, and nanotechnology.
Researchers have created nearly freestanding nanostructured two-dimensional (2D) gold monolayers, an impressive feat of nanomaterial engineering that could open up new avenues in catalysis, electronics, and energy conversion.
Gold is an inert metal which typically forms a solid three-dimensional (3D) structure. However, in its 2D form, it can unlock extraordinary properties, such as unique electronic behaviors, enhanced surface reactivity, and immense potential for revolutionary applications in catalysis ...
Human disruption is driving ‘winner’ and ‘loser’ tree species shifts across Brazilian forests
2024-12-10
Fast-growing and small-seeded tree species are dominating Brazilian forests in regions with high levels of deforestation and degradation, a new study shows.
This has potential implications for the ecosystem services these forests provide, including the ability of these ‘disturbed’ forests to absorb and store carbon. This is because these “winning” species grow fast but die young, as their stems and branches are far less dense than the slow growing tree species they replace.
Wildlife species adapted to consuming and dispersing the large seeds of tree species that ...