(Press-News.org) Chestnut Hill, Mass (12/10/2024) – As opposed to a constant flow from sources above and below ground, periods of heavy rain and runoff deliver the greatest amounts of fertilizer-derived nitrogen through creeks, rivers, and storm drains into the northern Gulf of Mexico, a team of scientists led by Boston College researchers reports today in the journal Communications Earth and Environment.
The findings clarify how nitrogen is delivered to the gulf and can be used to develop policies to protect the northern Gulf of Mexico, according to Boston College Assistant Professor of Earth and Environmental Sciences Xingchen (Tony) Wang, a lead author of the report.
“The northern Gulf of Mexico faces significant environmental challenges, including nutrient overloading, harmful algal blooms, and oxygen-depleted ‘dead zones’,” Wang said. “These issues are primarily driven by nitrogen pollution transported via rivers, with the Mississippi-Atchafalaya River Basin—a major agricultural hub in North America—being a key contributor.”
With funding from the Army Corps of Engineers, Wang's lab teamed up with researchers from Caltech and the University of California, Santa Barbara, to determine how different nitrogen sources, particularly fertilizers, are mobilized and transported into the Gulf under different hydrological conditions. The answers, Wang said, can improve the understanding of these pollution dynamics and guide effective mitigation strategies.
The Gulf of Mexico is fed by 33 major rivers that drain water from 31 states and 2 Canadian provinces. In 2021, the researchers collected water and particle samples from the Wax Lake Delta, a key distributary of the Mississippi-Atchafalaya River Basin. At BC, the nitrogen isotopic composition of the samples was analyzed in the Wang Stable Isotope Biogeochemistry Lab.
Nitrogen contains two stable isotopes: nitrogen-14 and nitrogen-15, Wang said. Different nitrogen sources often exhibit distinct nitrogen-15 to nitrogen-14 ratios, allowing the scientists to effectively trace and characterize the sources of nitrogen in the Wax Lake Delta.
Lower nitrogen isotope ratios characterize nitrogen derived from fertilizers. The team found that the nitrogen-15 to nitrogen-14 ratios in samples collected during the wet season were consistently lower than those from the dry season, according to Wang and co-authors including U.C. Santa Barbara’s Gen Li, Caltech’s Michael Lamb, and Boston College professors Noah Snyder and Hanqin Tian.
In contrast, samples collected during the dry season showed that groundwater nitrogen becomes the dominant nitrogen source in those months, Wang said.
“We were somewhat surprised to observe such a significant shift in anthropogenic nitrogen sources between the dry and wet seasons, which had not been identified in previous studies,” said co-author Jian-Jhih (Kenji) Chen, a postdoc researcher in the Wang Lab during the project, who is now an assistant professor at National Kaohsiung University of Science and Technology in Taiwan.
The findings underscore the critical role of hydrology in driving nitrogen pollution in the northern Gulf of Mexico, Wang said.
“With climate change predicted to increase the frequency of extreme precipitation events, the transport of fertilizer-derived nitrogen into the Gulf is likely to intensify, further exacerbating hypoxic conditions,” Wang said.
The study suggests the impacts can be mitigated by optimizing the timing of fertilizer application to crops to reduce nitrogen loading and its environmental consequences in the Gulf of Mexico.
The next steps involve exploring the fate of anthropogenic nitrogen in the Gulf of Mexico, Wang said. Specifically, the researchers want to determine whether this nitrogen remains confined to coastal zones or is transported into the open waters of the Gulf.
END
Heavy rains deliver largest amounts of fertilizer-derived nitrogen pollution to the Gulf of Mexico, new study finds
The findings clarify how nitrogen is delivered to the gulf and can be used to develop policies to protect the northern Gulf of Mexico, according to a team led by Boston College researchers
2024-12-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
MD Anderson and AmMax Bio announce agreements to advance development of AMB-066 in colorectal cancer patients with minimal residual disease
2024-12-10
HOUSTON and REDWOOD CITY, Calif. ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and AmMax Bio, Inc. today announced a worldwide exclusive license agreement and clinical trial agreement to develop and advance AmMax’s AMB-066 monoclonal antibody therapy as a first-in-class treatment option for patients with colorectal cancer (CRC) and minimal residual disease (MRD) as well as those with MRD in other solid tumors.
Under the agreements, AmMax and MD Anderson will build upon preclinical discoveries made by MD Anderson researchers to evaluate the potential for AMB-066, which targets colony stimulating factor ...
Choosing between human and algorithmic decision-makers
2024-12-10
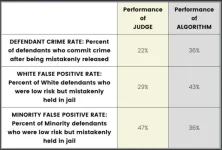
Society increasingly uses algorithms to make weighty decisions in contexts including criminal justice, healthcare, and finance, a trend that has been criticized for institutionalizing bias and sacrificing fairness. In a pre-registered study, Kirk Bansak and Elisabeth Paulson asked 9,000 US-based study participants to choose between decision-makers for two high stakes situations: pretrial release and bank loan applications. Participants chose either between two human decision-makers, between two algorithmic decision-makers, or between ...
High-speed rail and regional environmental inequality
2024-12-10
The introduction of high-speed rail reduced spatial environmental inequality in China by helping elements such as green technologies spread across the country. Shengjun Zhu and colleagues hypothesized that the introduction of high-speed rail between 1998 and 2010 helped facilitate the spread of elements including capital, labor, green technology, and information, particularly from leading to lagging areas. These trends could contribute to the reduction of industrial pollution, and the authors hypothesized that ...
Long-distance friendships can provide conservation benefits
2024-12-10
PULLMAN, Wash. – While sustaining friendships from afar can be challenging, they may offer unexpected benefits for environmental conservation.
A Washington State University-led study, recently published in Conservation Letters, found that these social ties can positively influence community-based conservation. While the study focused on 28 fishing villages in northern Tanzania, it has potential broader implications for global conservation efforts.
“Our findings challenge the notion that external connections undermine conservation,” said Kristopher Smith, the study’s lead author and a postdoctoral ...
The biomechanics of the rose prickle
2024-12-10
It is said that every rose has its thorn, but technically speaking, roses have prickles. Prickles are derived from the epidermis of the plant, whereas true thorns are modified stems. Rose prickles defend the plant from herbivores and help the plant support itself on surrounding objects. Liat Levavi and Benny Bar-On investigated the biomechanical properties of the prickles of the dog rose (Rosa canina Linnaeus) with a view towards features that might be used in the design of miniature anchoring platforms. ...
Machine learning prediction of human intelligence
2024-12-10
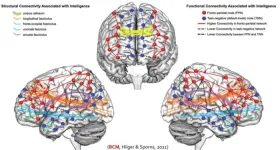
AI can predict human intelligence by looking at the connections of a working human brain. Neuroscientists can predict intelligence from brain structure and function—to a point. Previous studies have suggested that intelligence is widely distributed across the brain. Kirsten Hilger and colleagues used machine learning models to predict multiple kinds of intelligence from brain connections of 806 healthy adults while resting and while completing tasks. Fluid intelligence includes inductive and deductive reasoning abilities that do not rely on context, while crystallized intelligence reflects the ability to apply knowledge from ...
Empowering older adults with home-care robots
2024-12-10
Advances in medicine have led to an increase in human longevity. Estimates suggest that by 2030, one in every six individuals globally will be aged over 60 years. This rapid increase in the aging population implies a larger number of aged individuals requiring care. Family members and professional caregivers may not be able to meet this increasing demand. Furthermore, reports suggest a significant shortage of workforce, including nurses, in several developed countries, underscoring the need for additional strategies that ...
New concept for sustainable fuel cell polymer electrolytes overcomes barriers in high-temperature, low-humidity use, advancing net-zero carbon goals
2024-12-10
A research group led by Atsushi Noro at Nagoya University in Japan has announced a novel design concept for fuel cell electrolytes, utilizing a phosphonic acid polymer with hydrocarbon spacers. This innovative concept allows fuel cells to operate effectively under high-temperature (above 100°C) and low-humidity conditions, addressing crucial barriers to their broader use. The research has been published in ACS Applied Polymer Materials.
By electrochemically reacting hydrogen and oxygen, fuel cells produce electricity while emitting only water, highlighting their clean energy capabilities. However, perfluorosulfonic ...
Sculpting the brain (without chisel or scalpel)
2024-12-10
Imagine being able to inscribe a new pattern of activity into a person’s brain that would allow for faster learning, or better treatment of psychiatric and developmental disorders such as depression or autism. Now imagine being able to do that in a way that doesn’t require brain surgery or any physical manipulation. Sounds like science fiction?
It still is. But that’s exactly what Coraline Iordan, an assistant professor of brain and cognitive sciences and of neuroscience at the University of Rochester has been working toward, showing for the ...
Wrong trees in the wrong place can make cities hotter at night, study reveals
2024-12-10
University of Cambridge media release
Wrong trees in the wrong place can make cities hotter at night, study reveals
UNDER STRICT EMBARGO UNTIL 10:00 AM UK TIME / 05:00 AM (US ET) ON TUESDAY 10TH DECEMBER 2024
While trees can cool some cities significantly during the day, new research shows that tree canopies can also trap heat and raise temperatures at night. The study aims to help urban planners choose the best combinations of trees and planting locations to combat ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
BSO recapitulates anti-obesity effects of sulfur amino acid restriction without bone loss
Chinese Neurosurgical Journal reports faster robot-assisted brain angiography
[Press-News.org] Heavy rains deliver largest amounts of fertilizer-derived nitrogen pollution to the Gulf of Mexico, new study findsThe findings clarify how nitrogen is delivered to the gulf and can be used to develop policies to protect the northern Gulf of Mexico, according to a team led by Boston College researchers