(Press-News.org) About The Study: In adult trauma patients, an early restrictive oxygen strategy compared with a liberal oxygen strategy initiated in the prehospital setting or on trauma center admission for 8 hours did not significantly reduce death and/or major respiratory complications within 30 days.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Jacob Steinmetz, MD, PhD, email jacob.steinmetz@regionh.dk.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.25786)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, and funding and support.
# # #
Media advisory: This study is being presented at the Critical Care Reviews Down Under meeting.
Embed this link to provide your readers free access to the full-text article This link will be live at the embargo time https://jamanetwork.com/journals/jama/fullarticle/10.1001/jama.2024.25786?guestAccessKey=abe95d01-d7ca-4037-b048-412030f3ede7&utm_source=For_The_Media&utm_medium=referral&utm_campaign=ftm_links&utm_content=tfl&utm_term=121024
END
Early restrictive vs liberal oxygen for trauma patients
JAMA
2024-12-10
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Enabling AI to explain its predictions in plain language
2024-12-10
CAMBRIDGE, MA – Machine-learning models can make mistakes and be difficult to use, so scientists have developed explanation methods to help users understand when and how they should trust a model’s predictions.
These explanations are often complex, however, perhaps containing information about hundreds of model features. And they are sometimes presented as multifaceted visualizations that can be difficult for users who lack machine-learning expertise to fully comprehend.
To help people make sense of AI explanations, MIT researchers used large language models (LLMs) to transform plot-based explanations into plain language.
They developed ...
A greener, cleaner way to extract cobalt from ‘junk’ materials
2024-12-10
Siddarth Kara’s bestseller, “Cobalt Red: How the Blood of Congo Powers Our Lives,” focuses on problems surrounding the sourcing of cobalt, a critical component of lithium-ion batteries that power many technologies central to modern life, from mobile phones and pacemakers to electric vehicles.
“Perhaps many of us have read how lithium-ion batteries are vital for energy storage technologies,” says Eric Schelter, the Hirschmann-Makineni Professor of Chemistry at the University of Pennsylvania. “But how material that make up such batteries are sourced can be concerning and problematic, both ethically and environmentally.”
Schelter ...
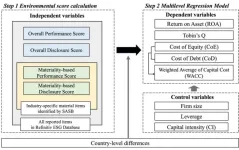
Better environmental performance boosts profits and cuts costs
2024-12-10
Fukuoka, Japan—Sustainable practices in business are more than just an ethical responsibility; they make sound financial sense. Researchers from Kyushu University, in a study published on December 10, 2024, in Corporate Social Responsibility and Environmental Management, reveal that companies with better environmental performance and transparent disclosures can lower costs and boost profits.
Investors are increasingly recognizing companies' contributions toward carbon neutrality, driving the growth of environmental, social, and governance (ESG) investing. To support this trend, the Sustainability Accounting Standards Board (SASB) has provided an industry-specific framework ...
Making self-driving cars safer, less accident prone
2024-12-10
Self-driving cars rely on artificial intelligence to predict where nearby cars will go. But when those predictions don’t match reality, that discrepancy can potentially lead to crashes and less safe roadways.
That’s why a recent study from the University of Georgia developed a new AI model to make self-driving cars safer.
This study introduces an AI model for self-driving cars, designed to predict the movement of nearby traffic and incorporate innovative features for planning safe vehicle movements.
"The planned trajectory of the self-driving car may turn out to collide with the actual trajectory of another vehicle.” —Qianwen Li, College ...
Rethinking the quantum chip
2024-12-10
Researchers at the UChicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (UChicago PME) have realized a new design for a superconducting quantum processor, aiming at a potential architecture for the large-scale, durable devices the quantum revolution demands.
Unlike the typical quantum chip design that lays the information-processing qubits onto a 2-D grid, the team from the Cleland Lab has designed a modular quantum processor comprising a reconfigurable router as a central hub. This enables any two qubits to connect and entangle, where in the ...
When does waiting stop being worth it?
2024-12-10
You’re standing at a bus stop, waiting for a ride that seems like it will never come. At first, you’re hopeful that it will be here any second. But as the minutes laggardly drag on, doubt creeps in. Should you keep waiting, or is it smarter to start walking or call for a ride?
“It’s a classic dilemma. “Do you persist with the belief that the bus is on its way, or do you cut your losses and move on to something else?” asks Joe Kable, a psychologist in the School of Arts ...
Nationwide study looks at when and where EV owners use public charging stations
2024-12-10
AUSTIN, TX, Dec 10, 2024 – Electric Vehicles (EVs) represent a promising mode of transportation that can help the United States reduce its carbon emissions. But barriers such as the high cost of installing and using EV Charging Stations (EVCS), their limitations in supplying emerging demand, and their uneven distribution throughout the country limit access for many Americans.
Researchers at the University of Maryland are using supercomputers and machine learning methods to analyze a full year of real-time data collected from individual EV charging ports at more than 50,000 publicly available stations throughout the country. The primary focus of the study is ...
A new discovery about the source of the vast energy in cosmic rays
2024-12-10
Ultra-high energy cosmic rays, which emerge in extreme astrophysical environments—like the roiling environments near black holes and neutron stars—have far more energy than the energetic particles that emerge from our sun. In fact, the particles that make up these streams of energy have around 10 million times the energy of particles accelerated in the most extreme particle environment on earth, the human-made Large Hadron Collider.
Where does all that energy come from? For many years, scientists believed it came from ...
Cancer ‘fingerprint’ can improve early detection
2024-12-10
Different types of cancer have unique molecular ‘fingerprints’ which are detectable in early stages of the disease and can be picked up with near-perfect accuracy by small, portable scanners in just a few hours, according to a study published today in the journal Molecular Cell.
The discovery by researchers at the Centre for Genomic Regulation (CRG) in Barcelona sets the foundation for creating new, non-invasive diagnostic tests that detect different types of cancer faster and earlier than currently possible.
The study centres around the ribosome, the protein factories of a cell. For decades, ribosomes were thought ...
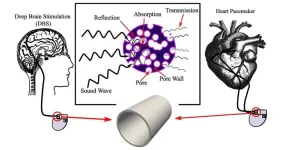
Rethinking the brain pacemaker: How better materials can improve signals
2024-12-10
WASHINGTON, Dec. 10, 2024 – Two years ago, a medical professional approached scientists at the University of Tabriz in Iran with an interesting problem: Patients were having headaches after pacemaker implants. Working together to investigate, they began to wonder if the underlying issue is the materials used in the pacemakers.
“Managing external noise that affects patients is crucial,” author Baraa Chasib Mezher said. “For example, a person with a brain pacemaker may experience interference from external electrical fields from phones ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
AI expert and industry leading toxicologist Thomas Hartung hails launch of agentic AI platform a “transformative moment” in chemical safety science
The RESIL-Card tool launches across Europe to strengthen cardiovascular care preparedness against crises
Tools to glimpse how “helicity” impacts matter and light
Smartphone app can help men last longer in bed
Longest recorded journey of a juvenile fisher to find new forest home
Indiana signs landmark education law to advance data science in schools
A new RNA therapy could help the heart repair itself
The dehumanization effect: New PSU research examines how abusive supervision impacts employee agency and burnout
New gel-based system allows bacteria to act as bioelectrical sensors
The power of photonics
From pioneer to leader: Alex Zhavoronkov chairs precision aging discussion and presents Luminary Award to OpenAI president at PMWC 2026
Bursting cancer-seeking microbubbles to deliver deadly drugs
In a South Carolina swamp, researchers uncover secrets of firefly synchrony
American Meteorological Society and partners issue statement on public availability of scientific evidence on climate change
How far will seniors go for a doctor visit? Often much farther than expected
Selfish sperm hijack genetic gatekeeper to kill healthy rivals
Excessive smartphone use associated with symptoms of eating disorder and body dissatisfaction in young people
‘Just-shoring’ puts justice at the center of critical minerals policy
A new method produces CAR-T cells to keep fighting disease longer
Scientists confirm existence of molecule long believed to occur in oxidation
The ghosts we see
ACC/AHA issue updated guideline for managing lipids, cholesterol
Targeting two flu proteins sharply reduces airborne spread
Heavy water expands energy potential of carbon nanotube yarns
AMS Science Preview: Mississippi River, ocean carbon storage, gender and floods
High-altitude survival gene may help reverse nerve damage
Spatially decoupling active-sites strategy proposed for efficient methanol synthesis from carbon dioxide
Recovery experiences of older adults and their caregivers after major elective noncardiac surgery
Geographic accessibility of deceased organ donor care units
How materials informatics aids photocatalyst design for hydrogen production
[Press-News.org] Early restrictive vs liberal oxygen for trauma patientsJAMA