(Press-News.org) Cigarette smoking from childhood into early adulthood is associated with an increased risk of premature cardiac injury, according to a study published today in JACC, the flagship journal of the American College of Cardiology. This early damage to the structure and function of the heart can also significantly increase the chance of future cardiovascular (CVD) mortality in mid-life.
“Our goal is to provide data for policymakers, clinicians, and public health practitioners on crucial timing for preventing smoking and its early consequences in youth,” said Andrew Agbaje, MD, MPH, PhD, lead and senior author of the study and an associate Professor of Clinical Epidemiology and Child Health at the University of Eastern Finland, Kuopio, Finland. “Parents and caregivers must lead by example and government agencies should be bold to address the preventable heart disease risk by creating a smoke and nicotine-free country. Raising tobacco taxes is insufficient because the cost of health care due to smoking-related diseases twice exceeds tobacco tax profits. Why should we pay for what is killing our teenagers softly?”
Researchers from the University of Eastern Finland collaborating with the University of Bristol used the Avon Longitudinal Study of Parents and Children (ALSPAC) birth cohort data to examine the impact of tobacco smoking during growth from childhood to young adulthood and its association with structural and functional cardiac injury.
Cardiac injury refers to damage to the heart muscle, or the myocardium, and can occur from causes such as ischemia (reduced blood flow), inflammation, trauma or chronic diseases. Cardiac mass increase is the increase in size or weight of the heart and is often associated with cardiac hypertrophy, or the thickening of the heart muscle walls. Both conditions can affect heart function. Adolescent smoking has been associated with vascular injury in adolescence and CVD mortality in midlife. However, studies of cardiac structure and function in healthy children are scarce, since cardiac injury in childhood is usually due to rare clinical events.
The analysis included 1,931 young adults with complete smoking and echocardiographic measures at 24 years. The prevalence of smoking was 0.3%, 1.6%, 13.6%, 24%, and 26.4% at ages 10, 13, 15, 17, and 24 years, respectively, and 60% of those who initiated smoking in childhood continued smoking at 24 years.
Researchers found that tobacco smoking from age 10 to 24 years was associated with 33% to 52% odds of premature structural and functional cardiac injury. Additionally, it was associated with cardiac mass increase, even after controlling for competing risk factors.
Key study results include:
Left ventricular (LV) hypertrophy prevalence increased from 2.8% to 7.5% at age 24.
Left ventricular diastolic (LVD) dysfunction prevalence increased from 10.4% to 16.9% at age 24.
Increased risk of high relative wall thickness (RWT) and high left ventricular filling pressure (LVFP).
Increased left ventricular mass index (LVMI) in both unadjusted and adjusted models from ages 17 – 24 years.
“The increase of cardiac mass structure in just a few years of smoking should convey how dangerous the consequences are for people who continue to smoke from a young age,” Agbaje said.
“This study shows that teen smoking doesn’t just increase the risk of heart disease later in life – it causes early and lasting damage to heart muscle and function,” said Emily Bucholz MD, PhD, MPH, Assistant Professor of Pediatrics at the University of Colorado School of Medicine and Associate Editor of JACC. “It’s a wake-up call for prevention efforts to protect young hearts early.”
Limitations of the study include insufficient data on socio-environmental influences, including parental smoking, friends and peer smoking, or consuming alcohol. Also, cotinine levels, which help quantify true nicotine exposure, were unavailable to analyze. Lastly, most study participants were Caucasian, which may make findings ungeneralizable to other racial groups.
For embargoed copies of the paper, contact Olivia Walther, media relations manager for JACC, at owalther@acc.org.
The American College of Cardiology (ACC) is the global leader in transforming cardiovascular care and improving heart health for all. As the preeminent source of professional medical education for the entire cardiovascular care team since 1949, ACC credentials cardiovascular professionals in over 140 countries who meet stringent qualifications and leads in the formation of health policy, standards and guidelines. Through its world-renowned family of JACC Journals, NCDR registries, ACC Accreditation Services, global network of Member Sections, CardioSmart patient resources and more, the College is committed to ensuring a world where science, knowledge and innovation optimize patient care and outcomes. Learn more at www.ACC.org or follow @ACCinTouch.
The ACC’s JACC Journals rank among the top cardiovascular journals in the world for scientific impact. The flagship journal, the Journal of the American College of Cardiology (JACC) — and specialty journals consisting of JACC: Advances, JACC: Asia, JACC: Basic to Translational Science, JACC: CardioOncology, JACC: Cardiovascular Imaging, JACC: Cardiovascular Interventions, JACC: Case Reports, JACC: Clinical Electrophysiology and JACC: Heart Failure — pride themselves on publishing the top peer-reviewed research on all aspects of cardiovascular disease. Learn more at JACC.org.
###
END
SAN ANTONIO —December 11, 2024 — Southwest Research Institute seeks support from residents or visitors of countries worldwide to assist with an international oil sampling program. Selected participants will be paid to purchase prequalified oil samples from retail stores and ship them to SwRI’s headquarters in San Antonio. Prequalification for the program will occur via an emailed photo exchange.
Participants will purchase four 1-quart or 1-liter containers, or one 1-gallon container, of specified brands ...
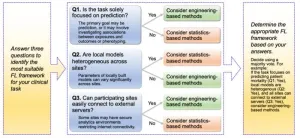
Statistical and Engineering Approaches to Federated Learning: Comprehensive Benchmarking for Healthcare Applications
A groundbreaking study conducted by Duke-NUS Medical School evaluates federated learning (FL) methods to guide healthcare researchers in choosing privacy-preserving algorithms tailored to their clinical goals. This comprehensive benchmark compared statistical and engineering FL frameworks, offering actionable insights to balance predictive accuracy and interpretability in medical research.
Federated learning (FL) has emerged as a powerful tool in healthcare, enabling collaboration across institutions without compromising patient ...
Drug addiction has been one of America’s growing public health concerns for decades. Despite the development of effective treatments and support resources, few people who are suffering from a substance use disorder seek help. Reluctance to seek help has been attributed to the stigma often attached to the condition. So, in an effort to address this problem, researchers at Drexel University are raising awareness of the stigmatizing language present in online forums and they have created an artificial intelligence tool to help educate users and offer alternative language.
Presented at the recent ...
Religious believers are no more generous than atheists – at least as long as they don’t know what the recipient believes in. Finding this out increases generosity significantly, mainly because people give more to those who share their religion. This is the conclusion of a study carried out at Linköping University, Sweden.
Nathalie Hallin is an atheist. Her colleague Hajdi Moche is a Christian. They both have a postdoc position at the Department of Behavioural Sciences and Learning at Linköping. Together they wanted to find out if a religious belief makes a person more generous, which research has so far disagreed on and they themselves have ...
SAN ANTONIO – Patients with high-risk, BRCA-positive breast cancer who received olaparib (Lynparza) after standard treatment continued to have better survival outcomes than those who received placebo after a median follow-up of 6.1 years, according to the latest results from the phase III OlympiA clinical trial presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS), held December 10-13, 2024.
“The OlympiA trial examines adding one year of the oral PARP inhibitor olaparib after completion of standard treatment ...
SAN ANTONIO – Patients with germline BRCA mutations who were diagnosed with breast cancer at or before age 40 and who underwent a bilateral risk-reducing mastectomy (RRM) and/or a risk-reducing salpingo-oophorectomy (RRSO) had lower rates of recurrence, secondary breast and/or ovarian malignancies, and death than those who did not undergo these surgeries, according to results presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS), held December 10-13, 2024.
“The benefits of RRM and RRSO have been shown for BRCA-mutation carriers without a prior history of cancer, but their impact for BRCA-mutation carriers with a history of early-onset breast cancer is less clear,” ...
SAN ANTONIO – Imlunestrant, an investigational next-generation selective estrogen receptor degrader (SERD), improved progression-free survival in patients with endocrine therapy-pretreated, ER-positive, HER2-negative advanced breast cancer—as monotherapy in patients with ESR1 mutations and as combination therapy with abemaciclib (Verzenio) in all patients, regardless of ESR1 mutation status—according to results from the phase III EMBER-3 clinical trial presented at the San Antonio ...
Carnegie Mellon University Africa and Challenger Center Collaborate to Deliver STEM Programs
Partnership Will Promote STEM Education and Careers to Secondary School Students in Africa
Carnegie Mellon University Africa, CMU’s College of Engineering location in Kigali, Rwanda, and Challenger Center, will partner to deliver Challenger Center’s Virtual Missions to hundreds of secondary school students on the continent. This project will help grow the population of African students who are motivated to pursue higher education and careers in science, technology, engineering, and math (STEM) fields.
Challenger Center’s Virtual Missions are space-themed experiences for students ...
Identifying novel therapeutic strategies and making fundamental discoveries related to small cell lung cancer. Creating environmental and sustainable solutions for lithium-ion battery technology. Improving the safety and efficacy of gene editing and understanding the mechanisms of DNA repair to potentially cure diseases. Discovering the most distant and massive galaxies that have reshaped our understanding of early Universe star formation and supermassive black holes. Pioneering geochemical fingerprinting technology to optimize energy production processes.
These are the breakthroughs ...
DNA stores the instructions for life and, along with enzymes and other molecules, computes everything from hair color to risk of developing diseases. Harnessing that prowess and immense storage capacity could lead to DNA-based computers that are faster and smaller than today’s silicon-based versions. As a step toward that goal, researchers report in ACS Central Science a fast, sequential DNA computing method that is also rewritable — just like current computers.
“DNA computing as a liquid computing paradigm has unique application ...