(Press-News.org) Mosasaurs are extinct marine lizards, spectacular examples of which were first discovered in 1766 near Maastricht in the Netherlands, fueling the rise of the field of vertebrate palaeontology (the study of fossil remains of animals with backbones). Palaeontologist Michael Polcyn presented the most comprehensive study to date on the early evolution and ecology of these extinct marine reptiles. On 16 December, Polcyn will receive his PhD from Utrecht University for his research into the evolution of the mosasaurs. "Mosasaurs are a textbook example of macroevolution, the emergence of new and distinct groups of animals, above the level of species. Although they have been studied for centuries, new discoveries, novel research approaches, and the application of technology, are still teaching us about their relationships and behaviors, some of which continues to surprise us. For example, through the use of detailed comparative anatomy aided by micro-CT scanning technology, we have gained a much better understanding of what group of lizards mosasaurs likely evolved from.”
Additionally, use of these advanced imaging technologies has allowed him to study the internal structures of the braincases of mosasaurs, and sort out the early evolutionary relationships of some previously problematic fossil taxa. “This study not only addressed the early evolution of the group, but also explored small- and large-scale aspects of their feeding biology,” Polcyn continued. “One spectacular example was a specimen I discovered in Angola, that had the remains of three other mosasaurs in its stomach, one of which was the same taxon as the predator, and documented the first occurrence of cannibalism in mosasaurs."
To the sea
Mosasaurs belong to a group of lizards that took to the sea about 100 million years ago (just like the ancestors of the whales later did). Throughout their 34-million-year history, they evolved into well-adapted marine animals that occupied a wide variety of niches and habitats. Together with a large number of other species, they became extinct 66 million years ago, in the aftermath of the meteorite impact that also wiped out the dinosaurs. "A relatively large number of fossils are known from the second half of the evolutionary history of mosasaurs, allowing a good understanding of the relationships among those species, which have been classified into four major groups," says Polcyn. “Much less is known about their early evolutionary history, and how those major groups are related to one another, their origins, and the origin of mosasaurs as a whole.” To address these gaps, Polcyn has focused on bringing new discoveries to light and restudying historical specimens with advanced imaging technologies, providing significant new anatomical information that is used to infer phylogenetic relationships. Polcyn’s work helps resolve a long-running scientific debate, concluding mosasaurs are not very closely related to snakes, but supporting the idea that their closest relatives are near the monitor lizards.
You are what you eat
Not much was previously known about the feeding habits of mosasaurs either, but a small, yet no less remarkable gap in that knowledge was filled with the discovery, by Polcyn in Angola, of a fossilized mosasaur with three other mosasaurs in its stomach, one being the same species as the predator. "Whether that mosasaur was a scavenger or actively hunted its prey cannot be said with certainty; however, we do have the first documented example of cannibalism in mosasaurs. Additionally, we gained insights into how mosasaurs processed their prey, and relative body size of prey and predator." Also included in his dissertation is a large-scale study of the feeding behaviour of mosasaurs, looking at how mosasaurs divided their foraging areas through the evolutionary history of the group. Polcyn integrated previously published data, along with a new, very large sample that covered a period from 92 to 66 million years ago and included finds from all over the world. The result of that study illuminate patterns of foraging area segregation, and feeding diversity in mosasaurs.
About
Polcyn's entry into palaeontology followed a non-traditional academic path. After serving in the U.S. submarine service and a career in technology and engineering, he devoted himself to research on extinct vertebrates, with a focus on marine reptiles. He is currently a Senior Research Fellow at ISEM at Southern Methodist University in Dallas, Texas.
END
New insights into the evolution and paleoecology of mosasaurs: most comprehensive study to date
Iconic extinct marine lizards continue to surprise us
2024-12-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
New insights into brain mechanisms underlying empathy
2024-12-12
Genova (Italy), 12th December 2024 – A specific brain mechanism modulates how animals respond empathetically to others’ emotions. This is the latest finding from the research unit Genetics of Cognition, led by Francesco Papaleo, Principal Investigator at the Istituto Italiano di Tecnologia (IIT - Italian Institute of Technology) and affiliated with IRCCS Ospedale Policlinico San Martino in Genova. The study, recently published in Nature Neuroscience, provides new insights into psychiatric ...
Semiconductor device technology recognized by the "Olympics of Semiconductors"
2024-12-12
The Korea Institute of Materials Science (KIMS) announced that Dr. Yong-Hun Kim from the Energy & Environment Materials Research Division and Dr. Kyung Song from the Material Characterization Center, in collaboration with Professor Hyun-Sang Hwang's team from POSTECH, have successfully developed a groundbreaking heterojunction technology. This technology integrates tungsten disulfide (WS₂), a two-dimensional (2D) material, with hafnium zirconium oxide (HZO), a ferroelectric material, achieving both interfacial stability and superior crystallinity. The results have been accepted by the International Electron Devices Meeting 2024 (IEDM 2024), ...
What brings richness to sparkling wines?
2024-12-12
“Rich” and “full-bodied” are terms that people often use to describe the taste of wine. They are also the properties that kokumi compounds bring to foods like mature Gouda cheese, though scientists haven’t widely explored them in wines. In ACS’ Journal of Agricultural and Food Chemistry, researchers now connect the dots and report 11 probable kokumi compounds in sparkling wines.
Kokumi is often confused with the better-known term umami. Umami is a savory, meaty flavor and is one of the basic five tastes, along with sweet, ...
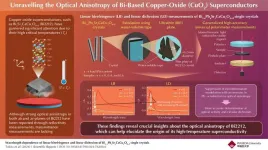
Towards room-temperature superconductivity: Insights into optical properties of bi-based copper-oxide superconductors
2024-12-12
Superconductors are materials which conduct electricity without any resistance when cooled down below a critical temperature. These materials have transformative applications in various fields, including electric motors, generators, high-speed maglev trains, and magnetic resonance imaging. Among these materials, CuO2 superconductors like Bi2212 stand out due to their high critical temperatures that surpass the Bardeen–Cooper–Schrieffer limit, a theoretical maximum temperature limit for superconductivity. However, ...
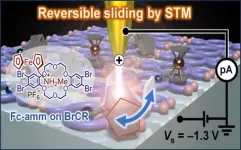
World’s smallest molecular machine: reversible sliding motion in ammonium-linked ferrocene
2024-12-12
Artificial molecular machines, nanoscale machines consisting of a few molecules, offer the potential to transform fields involving catalysts, molecular electronics, medicines, and quantum materials. These machines operate by converting external stimuli, like electrical signals, into mechanical motion at the molecular level. Ferrocene, a special drum-shaped molecule composed of an iron (Fe) atom sandwiched between two five-membered carbon rings, is a promising foundational molecule for molecular machinery. Its discovery earned the Nobel Prize in Chemistry in 1973, and it has since ...
Researchers reveal key factors behind Japan’s plastic waste removal rates in rivers
2024-12-12
Plastic pollution is an ever-growing problem in today’s world, as most societies have become overly dependent on plastics for packaging, medical supplies, and general goods. Plastic litter accumulation in the ocean, either through deliberate dumping or by being transported from a river, poses significant environmental challenges. Additionally, this plastic eventually degrades into small fragments called microplastics, which then impact diverse marine and land ecosystems by working their way up the food chain and into most living organisms. Though their negative effects on cell health are still under study, many nations have taken a cautionary stance, ...
Implantable sensors are helping scientists improve injury recovery
2024-12-12
EUGENE, Ore. — Dec. 12, 2024 — Tiny implantable sensors are helping University of Oregon researchers optimize the process of recovery from severe bone injuries.
Scientists at the UO’s Phil and Penny Knight Campus for Accelerating Scientific Impact have developed miniature implantable sensors that transmit real-time data about what’s happening at an injury site. In a new study, they use the technology to show that a resistance-training rehabilitation program can significantly improve femur injuries in rats ...
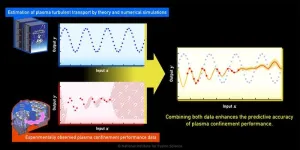
Improved predictive accuracy of fusion plasma performance by data science
2024-12-12
Fusion energy research is being pursued around the world as a means of solving energy problems. Magnetic confinement fusion reactors aim to extract fusion energy by confining extremely hot plasma in strong magnetic fields. Its development is a comprehensive engineering project involving many advanced technologies, such as superconducting magnets, reduced-activation materials, and beam and wave heating devices. In addition, predicting and controlling the confined plasma, in which numerous charged particles and electromagnetic fields interact in complex ...
Common brain network links brain atrophy patterns seen in schizophrenia
2024-12-12
A new study led by investigators from Mass General Brigham has identified a unique brain network that links varied patterns of brain atrophy, or shrinkage, associated with schizophrenia. By combining neuroimaging data from multiple studies involving more than 8,000 participants, the research team found a specific connectivity pattern of atrophy that was present across different stages and symptoms of schizophrenia — and distinct from brain networks associated with other psychiatric disorders. The findings will help to guide a clinical trial that will start recruiting patients soon and will ...
“Us” vs. “them” biases plague AI, too
2024-12-12
Research has long shown that humans are susceptible to “social identity bias”—favoring their group, whether that be a political party, a religion, or an ethnicity, and disparaging “outgroups.” A new study by a team of scientists finds that AI systems are also prone to the same type of biases, revealing fundamental group prejudices that reach beyond those tied to gender, race, or religion.
“Artificial Intelligence systems like ChatGPT can develop ‘us versus them’ biases similar to humans—showing favoritism toward their perceived ‘ingroup’ while expressing ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Spring fatigue cannot be empirically proven
Do prostate cancer drugs interact with certain anticoagulants to increase bleeding and clotting risks?
Many patients want to talk about their faith. Neurologists often don't know how.
AI disclosure labels may do more harm than good
The ultra-high-energy neutrino may have begun its journey in blazars
Doubling of new prescriptions for ADHD medications among adults since start of COVID-19 pandemic
“Peculiar” ancient ancestor of the crocodile started life on four legs in adolescence before it began walking on two
AI can predict risk of serious heart disease from mammograms
New ultra-low-cost technique could slash the price of soft robotics
Increased connectivity in early Alzheimer’s is lowered by cancer drug in the lab
Study highlights stroke risk linked to recreational drugs, including among young users
Modeling brain aging and resilience over the lifespan reveals new individual factors
ESC launches guidelines for patients to empower women with cardiovascular disease to make informed pregnancy health decisions
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
[Press-News.org] New insights into the evolution and paleoecology of mosasaurs: most comprehensive study to dateIconic extinct marine lizards continue to surprise us