(Press-News.org) Sweetpotatoes are an agricultural powerhouse that feeds millions globally. However, their complex genetics make it challenging for breeders to understand and improve traits like yield, disease resistance, and nutritional content. A new study reveals insights into the significance of leveraging “allele dosages” in sweetpotato breeding practices.
“Sweetpotatoes are hexaploid, meaning they have six copies of each chromosome, unlike diploid crops like tomato or rice, which have two," explained Zhangjun Fei, a professor at the Boyce Thompson Institute and one of the study's lead authors. “This genetic complexity allows for more variation and adaptability but makes selective breeding difficult. Unlike diploid crops, where single genetic changes can have noticeable effects, sweetpotatoes require a more nuanced approach.”
The researchers created a detailed map of genetic variations by analyzing 294 sweetpotato varieties. This map didn’t just look at what genes were present but also how many copies of favorable variants existed in each plant. They discovered that the differences in allele dosage significantly impact important agricultural traits such as root weight, plant architecture, and flesh color.
The study found that successful breeding programs have unknowingly targeted allele dosage over time. Modern sweetpotato varieties tend to have more copies of beneficial alleles compared to their ancestors, which explains why today's crops generally perform better.
The study focused on China, which produces over half of the world's sweetpotatoes. The researchers found that Chinese breeders have been especially successful at selecting varieties with optimal gene copies for desirable traits like larger tuberous root size and better growth in crowded conditions.
Through their research, the scientists identified an important candidate gene called IbEXPA4, which was suspected to influence tuberous root weight. They conducted a series of experiments and found that when IbEXPA4 was suppressed, the sweetpotato root grew larger, validating the gene's impact on size.
The study, recently published in Nature Plants, also revealed how sequence variations alter the expression of the Orange gene, which regulates flesh color. Understanding this mechanism could help breeders develop sweetpotatoes with enhanced nutritional content, such as increased beta-carotene.
With this new understanding, breeders can develop improved sweetpotato varieties by adjusting allele dosages at specific locations in the genome. In a world where food security is a growing concern, this research could contribute to creating high-yielding, nutritious, and resilient crop varieties.
About the Boyce Thompson Institute (BTI)
Founded in 1924 and located in Ithaca, New York, BTI is at the forefront of plant science research. Our mission is to advance, communicate, and leverage pioneering discoveries in plant sciences to develop sustainable and resilient agriculture, improve food security, protect the environment, and enhance human health. As an independent nonprofit research institute affiliated with Cornell University, we are committed to inspiring and training the next generation of scientific leaders. Learn more at BTIscience.org.
END
Study reveals role of allele dosage in improving sweetpotato traits
2024-12-12
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Dan M. Frangopol and Sunyong Kim co-author third book on structural performance
2024-12-12
Dan M. Frangopol, the inaugural Fazlur R. Khan Endowed Chair of Structural Engineering and Architecture at Lehigh University, has co-authored a new book on probabilistic structural performance assessments.
System Reliability, Risk, Longevity, Sustainability and Optimal Decision-Making: Emphasis on Marine Structures (available April 11, 2025) offers a comprehensive framework for analyzing and predicting the time-dependent performance of deteriorating structures. The book emphasizes marine infrastructure, addressing system reliability, risk, longevity, sustainability, and optimal decision-making processes. It is a valuable resource for students, engineers, researchers, decision-makers, ...
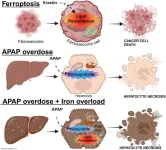
Ferroptosis and intrinsic drug-induced liver injury by acetaminophen and other drugs: a critical evaluation and historical perspective
2024-12-12
DILI is broadly categorized into intrinsic and idiosyncratic types. Intrinsic hepatotoxins, such as APAP, cause dose-dependent injury, while idiosyncratic DILI involves complex immune and metabolic interactions that remain poorly understood. Mechanistic studies of intrinsic hepatotoxins have revealed oxidative stress and mitochondrial dysfunction as key contributors to injury. Historically, LPO and iron-catalyzed free radical generation were central to understanding DILI, but the focus shifted toward apoptosis in the late 20th century.
The discovery of ferroptosis—a regulated form of cell death characterized ...
Reiki therapy demonstrates significant symptom relief for cancer patients receiving infusion treatments
2024-12-12
CLEVELAND - A recent study conducted at University Hospitals Connor Whole Health has evaluated a Reiki program designed for outpatients with cancer and receiving infusion treatments at two University Hospitals infusion centers.
The study, entitled “Evaluation of a Reiki Volunteer Program within Two Cancer Infusion Centers,” was recently published in the Journal of Pain and Symptom Management, a peer-reviewed journal that serves as an interdisciplinary audience of professionals. This retrospective review, conducted between March 2022 and February 2024, evaluated the effects of Reiki on outpatients receiving infusion treatments such as chemotherapy. During Reiki sessions, a ...
Long-term exposure to air pollution linked to blood clots in veins that bring blood to the heart
2024-12-12
WHAT: A large study found that greater exposure to long-term air pollution was linked with increased risks for blood clots that can occur in deep veins, which, if untreated, can block blood flow and cause serious complications, even death.
These findings came from a longitudinal study funded by the National Institutes of Health (NIH) that included 6,651 U.S. adults who were followed for an average of 17 years between 2000 and 2018. Participants lived in or near one of six major metropolitan areas: New York, Baltimore, Chicago, Los Angeles, Minneapolis, and Winston-Salem, North Carolina.
Throughout the study, 248 adults, 3.7% of the study sample, developed blood clots ...
National Academy of Inventors partners with PMU to recognize three exceptional innovators
2024-12-12
The National Academy of Inventors (NAI) is proud to announce the recipients of the inaugural Prince Mohammad bin Fahd University (PMU)-National Academy of Inventors International Patent Award. This year’s recipients will be honored at a special ceremony on December 12th, 2024 at PMU’s campus in Al-Khobar, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia.
The PMU-NAI International Patent Award was created to recognize and honor distinguished scientists, research institutions, research centers, and universities across the globe for their outstanding patents and inventions that create positive societal ...
Deep learning model accurately diagnoses COPD
2024-12-12
OAK BROOK, Ill. – Using just one inhalation lung CT scan, a deep learning model can accurately diagnose and stage chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), according to a study published today in Radiology: Cardiothoracic Imaging, a journal of the Radiological Society of North America (RSNA).
COPD is a group of progressive lung diseases that impair a person’s ability to breathe. Symptoms typically involve shortness of breath and fatigue. There currently is no cure for COPD, and it is the third leading cause of death worldwide, according to the World Health Organization.
A ...
Alliance Foundation Trials phase III PATINA study shows promise for patients with HR+, HER2+ metastatic breast cancer
2024-12-12
Alliance Foundation Trials, LLC (AFT) and Pfizer Inc. today announced results from the phase III PATINA trial demonstrating that the addition of palbociclib (IBRANCE®) to current standard-of-care first-line maintenance therapy (following induction chemotherapy) resulted in statistically significant and clinically meaningful improvement in progression-free survival (PFS) by investigator assessment in patients with hormone receptor-positive (HR+), human epidermal growth factor receptor 2-positive (HER2+) metastatic ...
COMET trial finds quality of life similar among patients with low- risk DCIS whether they received active monitoring or surgery
2024-12-12
SAN ANTONIO – Patients with low-risk ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) who underwent active monitoring reported comparable physical, emotional, and psychological outcomes to patients who received upfront treatment, according to results from the COMET clinical trial presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS), held December 10-13, 2024.
The results of this study were simultaneously published in JAMA Oncology.
“Active monitoring” is a strategy in which patients are monitored closely, with surgery reserved for those patients who ...
Adjuvant tamoxifen may reduce recurrence risk for patients with ‘good-risk’ DCIS who forgo radiation
2024-12-12
SAN ANTONIO – For patients with “good-risk” ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS) who underwent breast- conserving surgery and did not receive radiotherapy, tamoxifen significantly decreased the risk of recurrence in the same breast, according to results presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS), held December 10-13, 2024.
“Good-risk” DCIS was defined as grade 1 or 2, 2.5 cm or smaller, and having clear surgical margins of 3 mm or greater.
Current guidelines from the National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) advise that patients who undergo breast-conserving surgery after a diagnosis ...
COMET trial finds active monitoring is a viable option for some patients with low-risk DCIS
2024-12-12
SAN ANTONIO – Among patients with hormone receptor (HR)-positive, HER2-negative, low-risk ductal carcinoma in situ (DCIS), those who underwent active monitoring had similar two-year invasive ipsilateral breast cancer recurrence rates as those who underwent guideline-concordant treatment, according to results from the COMET clinical trial presented at the San Antonio Breast Cancer Symposium (SABCS), held December 10-13, 2024.
The results of this study were simultaneously published in JAMA.
“Active monitoring” is a strategy in which patients are monitored closely, with surgery reserved for those patients who develop cancer.
A steady increase ...