(Press-News.org)
Sometimes, moving just a few inches can go a long way.
Osaka Metropolitan University researchers have developed a promising technique for head and neck reconstruction that shifts the placement of transferred tissue with blood vessels attached, offering a safer, faster option for patients with complex tissue defects, especially those at high risk.
Head and neck reconstruction plays a crucial role in the treatment of patients with head and neck cancer. The goal is to preserve functions vital for breathing, eating, and speaking, while maintaining the patient’s appearance and quality of life.
“Traditional reconstruction typically uses free flaps, which may not be feasible for some patients, such as those who have had prior radiation treatment or multiple surgeries,” said Tsubasa Kojima, a medical doctor and lecturer at Osaka Metropolitan University’s Graduate School of Medicine and lead author of the study.
A free flap is a section of tissue that is fully detached from a healthy part of the body (donor site) and reattached to new blood vessels at the defect (recipient site).
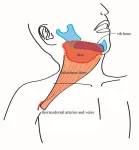
The research team cut a new path and worked instead with pedicled flaps taken from the back, called pedicled latissimus dorsi (LD) myocutaneous flaps. Unlike free flaps, pedicled flaps remain partially attached to the donor site, retaining their natural blood supply as they are transferred to the recipient site for reconstruction.
While the LD flap has been used in various reconstructive surgeries, the team developed a unique approach that placed the skin portion of the LD flap more distally, or lower on the back, than in conventional techniques. This design includes the lateral cutaneous branch of the 10th posterior intercostal artery, ensuring reliable blood flow to the flap.
“This setup provides flexibility, allowing the LD flap to cover extensive defects, including those in both the mouth and neck simultaneously, and even facilitates jaw reconstruction by incorporating rib bone,” Kojima said.
The study, conducted between 2003 and 2024, demonstrated that the pedicled LD flap was successfully integrated in all 22 patients with complex head and neck defects.
“Our results suggest that this pedicled LD flap technique provides a reliable, fast, and minimally invasive option for head and neck reconstruction, particularly in cases where free flaps are not suitable,” Kojima said. “We hope this approach will significantly improve treatment outcomes for patients undergoing head and neck reconstruction.”
Their findings were published in Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery—Global Open.
###
About OMU
Established in Osaka as one of the largest public universities in Japan, Osaka Metropolitan University is committed to shaping the future of society through “Convergence of Knowledge” and the promotion of world-class research. For more research news, visit https://www.omu.ac.jp/en/ and follow us on social media: X, Facebook, Instagram, LinkedIn.
END
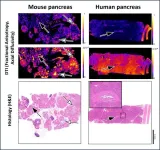
Precursor lesions of pancreatic cancer are very difficult to characterise with magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). But now, in a new study, researchers led by Noam Shemesh and Carlos Bilreiro – respectively head of the Preclinical MRI lab at Champalimaud Research and a doctor at the Champalimaud Clinical Centre’s Radiology Department – have shown, for the first time, that a particular form of MRI, called Diffusion Tensor Imaging (DTI), is capable of robustly detecting pre-malignant lesions in the pancreas. ...
New research from Karolinska Institutet in Sweden highlights the possibility of screening people with type 2 diabetes for liver damage at the same time as they undergo screening for eye disease. The study is published in Lancet Gastroenterology and Hepatology.
More than half of all people with type 2 diabetes have steatotic (or fatty) liver disease, but most do not realise it since liver disease rarely causes any symptoms in the earlier stages. Over time, liver fibrosis can develop. This is a type of scarring of the liver that can lead to cirrhosis or liver cancer in some patients. International ...
New research finds that giraffes much prefer flat terrain and do not traverse slopes of more than 20°, which severely limits the areas in, and outside, protected reserves they can access. The findings, which is are yet to be published, will be presented at the British Ecological Society’s (BES) Annual meeting in Liverpool on the 13th December.
A new study analysing the movements of 33 GPS collared giraffes in South Africa has found that they avoid steep terrain and are unable to navigate slopes with a gradient of more than 20° , most likely due to the energy required and the risk of falling.
The researchers from the University of Manchester ...
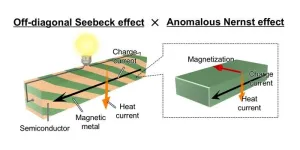
1. A research team from NIMS and UTokyo has proposed and demonstrated that the transverse magneto-thermoelectric conversion in magnetic materials can be utilized with much higher performance than previously by developing artificial materials comprising alternately and obliquely stacked multilayers of a magnetic metal and semiconductor.
2. When a temperature gradient is applied to a magnetic conductor, a charge current is generated in a direction orthogonal to directions of both temperature gradient and magnetization of the magnetic conductor. This transverse magneto-thermoelectric phenomenon, ...
-With images-
Durham University scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery in marine geoscience, revealing unprecedented insights into the dynamics of Earth’s longest runout sediment flows.
By using seabed seismographs placed safely outside the destructive paths of powerful underwater avalanches of sediment, researchers have successfully monitored turbidity currents—a natural phenomenon that shapes deep-sea landscapes, damages telecommunication cables, and transports large quantities of sediment and organic carbon to the ocean floor.
The study recorded two massive turbidity ...
Despite awe-inspiring diversity, nearly every lifeform – from bacteria to blue whales – shares the same genetic code. How and when this code came about has been the subject of much scientific controversy.
Taking a fresh approach at an old problem, Sawsan Wehbi, a doctoral student in the Genetics Graduate Interdisciplinary Program at the University of Arizona, discovered strong evidence that the textbook version of how the universal genetic code evolved needs revision. Wehbi is the first author of a study published in the journal PNAS suggesting the order with which amino acids – the code's building blocks –
were recruited is at odds with ...
A program designed to prepare future teachers and K-12 students for a lifetime of innovation recently received a $572,890 boost from the National Science Foundation.
The ChangeMaker K-12 program, designed by faculty from the University of Louisiana at Lafayette’s College of Education & Human Development, received a second round of grant funding to expand the teacher prep program to other universities. The new partners are the University of Louisiana Monroe, Louisiana Tech University and the University of Hawaii at Manoa.
The project is led by Dr. Doug Williams, director of UL Lafayette’s Center for Innovative Learning and Assessment Technologies, along with Dr. Aimee Barber, ...
A team of researchers at USC and the University of Utah has received a $2.7 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to map out how an incurable eye disease affects the wiring that powers vision in the eye, in hopes of discovering ways to slow or prevent blindness. Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a progressive disease with four known stages that affects the retina, the area at the back of the eye where light is turned into electrical signals that the brain processes to produce sight. The research ...
AI will soon receive a dose of empathy with the goal of helping to match people with depression to their best-fit medication. A team led by Farrokh Alemi, a professor in the College of Public Health (CPH), and Kevin Lybarger, an assistant professor in the College of Engineering and Computing (CEC), received $1,049,998 in research funding from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) to continue their work on developing an AI system that helps patients find the right depression medications.
With this funding support, Co-PIs Alemi and Lybarger will hone large language models (LLMs) to address known challenges in ...
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — The Midwest played a central role in the growth of Black freedom movements in the 20th century. It was a key site for incubating and expanding the ideas of political activist Marcus Garvey, not only in the U.S., but globally, said University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign professor of African American studies and history Erik S. McDuffie.
McDuffie examined the influence of Garvey and the importance of the Midwest in the growth of Black internationalism and radicalism in his new book, “The Second Battle for Africa: Garveyism, the U.S. Heartland and Global Black Freedom.”
McDuffie ...