Enhancing transverse thermoelectric conversion performance in magnetic materials with tilted structural design
A new approach to developing practical thermoelectric technologies
2024-12-13
(Press-News.org)
1. A research team from NIMS and UTokyo has proposed and demonstrated that the transverse magneto-thermoelectric conversion in magnetic materials can be utilized with much higher performance than previously by developing artificial materials comprising alternately and obliquely stacked multilayers of a magnetic metal and semiconductor.
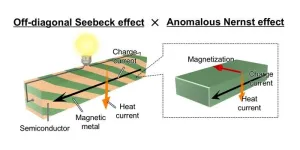
2. When a temperature gradient is applied to a magnetic conductor, a charge current is generated in a direction orthogonal to directions of both temperature gradient and magnetization of the magnetic conductor. This transverse magneto-thermoelectric phenomenon, known as the anomalous Nernst effect (ANE), has attracted considerable interest for potentially versatile, durable, and low-cost thermoelectric applications. Currently, the search for new magnetic materials focusing on topological natures of materials is being actively pursued with the aim of further improving the performance of ANE. Despite these efforts, no material has yet been identified with the performance of ANE at room temperature exceeding that of a cobalt-based topological magnet, i.e., Co2MnGa, reported in 2018, limiting further progress in this field. In addition, even this current record-high performance of Co2MnGa would have to be improved around more than 100 times for practical thermoelectric applications.
3. This research team recently developed an artificially tilted multilayer composed of alternating layers of a magnetic metal and semiconductor to simultaneously exhibit both the off-diagonal Seebeck effect (ODSE) and ANE (see Figure). Here, ODSE realizes the transverse thermoelectric conversion arising from tilted multilayer structures without the need for external magnetic fields or magnetization. The team demonstrated that the dimensionless figure of merit for ANE in the artificial material was improved by more than one order, compared to that of the same single magnetic metal alone, owing to the synergetic action of ANE and ODSE. These findings indicate that factors, such as certain physical parameters and structures, which have not been the focus of previous studies on ANE, are important for improving the performance of transverse thermoelectric conversion.
4. This research provides new guidelines for the design of new materials for transverse thermoelectric conversion materials based on structural design, as well as new ways of utilizing ANE, from a completely different perspective from the previous research. Based on these guidelines, the research team aims to develop artificial materials with high thermoelectric performance for practical applications such as power generation using waste heat and electronic cooling and heat sensing technologies.
***
5. This project was carried out by Takamasa Hirai (Researcher, Research Center for Magnetic and Spintronic Materials (CMSM), NIMS), Fuyuki Ando (Special Researcher, CMSM, NIMS), Hossein Sepehri-Amin (Group Leader, CMSM, NIMS) and Ken-ichi Uchida (Distinguished Group Leader, CMSM, NIMS; Professor, Department of Advanced Materials Science, Graduate School of Frontier Sciences, UTokyo).
This work was supported by ERATO “Uchida Magnetic Thermal Management Materials Project” from JST, Japan.
6. This research was published in Nature Communications, an open access journal, at 7:00 pm on November 14, 2024, Japan Time.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-12-13
-With images-
Durham University scientists have made a groundbreaking discovery in marine geoscience, revealing unprecedented insights into the dynamics of Earth’s longest runout sediment flows.
By using seabed seismographs placed safely outside the destructive paths of powerful underwater avalanches of sediment, researchers have successfully monitored turbidity currents—a natural phenomenon that shapes deep-sea landscapes, damages telecommunication cables, and transports large quantities of sediment and organic carbon to the ocean floor.
The study recorded two massive turbidity ...
2024-12-12
Despite awe-inspiring diversity, nearly every lifeform – from bacteria to blue whales – shares the same genetic code. How and when this code came about has been the subject of much scientific controversy.
Taking a fresh approach at an old problem, Sawsan Wehbi, a doctoral student in the Genetics Graduate Interdisciplinary Program at the University of Arizona, discovered strong evidence that the textbook version of how the universal genetic code evolved needs revision. Wehbi is the first author of a study published in the journal PNAS suggesting the order with which amino acids – the code's building blocks –
were recruited is at odds with ...
2024-12-12
A program designed to prepare future teachers and K-12 students for a lifetime of innovation recently received a $572,890 boost from the National Science Foundation.
The ChangeMaker K-12 program, designed by faculty from the University of Louisiana at Lafayette’s College of Education & Human Development, received a second round of grant funding to expand the teacher prep program to other universities. The new partners are the University of Louisiana Monroe, Louisiana Tech University and the University of Hawaii at Manoa.
The project is led by Dr. Doug Williams, director of UL Lafayette’s Center for Innovative Learning and Assessment Technologies, along with Dr. Aimee Barber, ...
2024-12-12
A team of researchers at USC and the University of Utah has received a $2.7 million grant from the National Institutes of Health to map out how an incurable eye disease affects the wiring that powers vision in the eye, in hopes of discovering ways to slow or prevent blindness. Retinitis pigmentosa (RP) is a progressive disease with four known stages that affects the retina, the area at the back of the eye where light is turned into electrical signals that the brain processes to produce sight. The research ...
2024-12-12
AI will soon receive a dose of empathy with the goal of helping to match people with depression to their best-fit medication. A team led by Farrokh Alemi, a professor in the College of Public Health (CPH), and Kevin Lybarger, an assistant professor in the College of Engineering and Computing (CEC), received $1,049,998 in research funding from the Patient-Centered Outcomes Research Institute (PCORI) to continue their work on developing an AI system that helps patients find the right depression medications.
With this funding support, Co-PIs Alemi and Lybarger will hone large language models (LLMs) to address known challenges in ...
2024-12-12
CHAMPAIGN, Ill. — The Midwest played a central role in the growth of Black freedom movements in the 20th century. It was a key site for incubating and expanding the ideas of political activist Marcus Garvey, not only in the U.S., but globally, said University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign professor of African American studies and history Erik S. McDuffie.
McDuffie examined the influence of Garvey and the importance of the Midwest in the growth of Black internationalism and radicalism in his new book, “The Second Battle for Africa: Garveyism, the U.S. Heartland and Global Black Freedom.”
McDuffie ...
2024-12-12
In most research labs, the scientists are on the same page about why they’re pursuing a research project.
But the Rubin Lab at HHMI's Janelia Research Campus isn’t an ordinary research lab.
The lab is examining how aggression affects vision in female fruit flies, but Janelia Senior Group Leader Gerry Rubin doesn’t care too much about the specific answer. Instead, he simply wants to see if the neuroscience research tools that he spent the last decade building are adequate to uncover the underlying mechanisms at play.
Postdoc Katie Schretter, on the other hand, is interested in understanding how neurons in the fly brain ...
2024-12-12
HOUSTON, Dec. 12 2024 – A group of ambitious students from the University of Houston and Texas A&M University, identifying as the “Dream Team,” secured third place in the prestigious global Switch Competition. This annual virtual event, sponsored by the Switch Energy Alliance, challenges university students to develop innovative solutions for addressing energy poverty worldwide — a critical issue affecting millions.
The team is comprised of Sarah Grace Kimberly and Pranjal Sheth, both senior finance majors at UH, and Nathan Hazlett, a finance graduate student at A&M who previously earned a bachelor’s degree in petroleum engineering. Competing ...
2024-12-12
For experiments that require ultra-precise measurements and control over atoms — think two-photon atomic clocks, cold-atom interferometer sensors and quantum gates — lasers are the technology of choice, the more spectrally pure (emitting a single color/frequency), the better. Conventional lab-scale laser technology currently achieves this ultra low-noise, stable light via bulky, costly tabletop systems designed to generate, harness and emit photons within a narrow spectral range.
But what if these atomic applications ...
2024-12-12
A new analysis published in the journal Science reveals that overfishing has caused populations of chondrichthyan fishes – sharks, rays, and chimaeras – to decline by more than 50 per cent since 1970. To determine the consequences, a team of researchers developed an aquatic Red List Index (RLI) which shows that the risk of extinction for chondrichthyan has increased by 19 per cent. The study also highlights that the overfishing of the largest species in nearshore and pelagic habitats could eliminate up to 22 per cent of ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Enhancing transverse thermoelectric conversion performance in magnetic materials with tilted structural design
A new approach to developing practical thermoelectric technologies