Emotional cognition analysis enables near-perfect Parkinson's detection
2024-12-16
(Press-News.org)
A joint research team from the University of Canberra and Kuwait College of Science and Technology has achieved groundbreaking detection of Parkinson's disease with near-perfect accuracy, simply by analyzing brain responses to emotional situations like watching video clips or images. The findings offer an objective way to diagnose the debilitating movement disorder, instead of relying on clinical expertise and patient self-assessments, potentially enhancing treatment options and overall well-being for those affected by Parkinson's disease. The study was published Oct. 17 in Intelligent Computing, a Science Partner Journal, in an article titled “Exploring Electroencephalography-Based Affective Analysis and Detection of Parkinson’s Disease.”
Their emotional brain analysis focuses on the difference in implicit emotional reactions between Parkinson's patients, who are generally believed to suffer from impairments in recognizing emotions, and healthy individuals. The team demonstrated they can identify patients and healthy individuals with an F1 score of 0.97 or higher, based solely on brain scan readings of emotional responses. This diagnostic performance edges very close to 100% accuracy from brainwave data alone. The F1 score is a metric that combines precision and recall, where 1 is the best possible value.
The results show that Parkinson's patients displayed specific emotional perception patterns, comprehending emotional arousal better than emotional valence, which means they are more attuned to the intensity of emotions rather than the pleasantness or unpleasantness of those emotions. The patients were also found to struggle most with recognizing fear, disgust and surprise, or to confuse emotions of opposite valences, such as mistaking sadness for happiness.
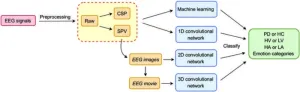
The researchers recorded electroencephalography — or EEG — data, measuring electrical brain activity in 20 Parkinson's patients and 20 healthy controls. Participants watched video clips and images designed to trigger emotional responses. After the recording of EEG data, multiple EEG descriptors were processed to extract key features and these were transformed into visual representations, which were then analyzed using machine learning frameworks such as convolutional neural networks, for automatic detection of distinct patterns in how the patients processed emotions compared to the healthy group. This processing enabled the highly accurate differentiation between patients and healthy controls.
Key EEG descriptors used include spectral power vectors and common spatial patterns. Spectral power vectors capture the power distribution across various frequency bands, which are known to correlate with emotional states. Common spatial patterns enhance interclass discriminability by maximizing variance for one class while minimizing it for another, allowing for better classification of EEG signals.
As the researchers continue refining EEG-based techniques, emotional brain monitoring has the potential to become a widespread clinical tool for Parkinson's diagnosis. The study demonstrates the promise of combining neurotechnology, AI and affective computing to provide objective neurological health assessments.
END
[Attachments] See images for this press release:

ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2024-12-16
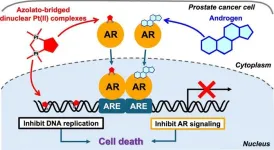
Prostate cancer remains a global health challenge, ranking as the second most commonly diagnosed cancer among men. Although treatments like androgen deprivation therapy have been effective for early-stage prostate cancer, advanced stages, such as castration-resistant prostate cancer, present significant treatment challenges due to resistance to therapies. Current approaches targeting androgen receptor (AR) signaling, such as taxanes and newer agents, show limited success. Cisplatin, a widely used anticancer drug, has been used in combination therapies but its use is limited by severe ...
2024-12-16
Sign language serves as a sophisticated means of communication vital to individuals who are deaf or hard-of-hearing, relying on hand movements, facial expressions, and body language to convey nuanced meaning. American Sign Language exemplifies this linguistic complexity with its distinct grammar and syntax.
Sign language is not universal; rather, there are many different sign languages used around the world, each with its own grammar, syntax and vocabulary, highlighting the diversity and complexity of sign languages globally.
Various ...
2024-12-16
UTSA’s Office of Research today announced the launch of the Center for Space Technology and Operations Research (CSTOR), a new research center dedicated to advancing engineering, technology and operations that will support space missions between the Earth and the Moon, an area referred to as cislunar space, as well as the lunar surface. The center will address the growing demand for research and workforce development by civil, commercial and national security space agencies and companies. David Silva, UTSA distinguished professor of physics and astronomy, will serve as the center’s inaugural director.
CSTOR will provide enhanced support ...
2024-12-16
Craniopharyngioma (CP) is a rare brain tumor that develops in the regions close to the hypothalamus and pituitary gland. The CP tumors lead to complications like defective vision, neuronal defects, diabetes, and developmental problems. There are two primary subtypes of CPs: adamantinomatous craniopharyngioma (ACP) and papillary craniopharyngioma (PCP). These two subtypes are distinguished by their distinct genetic profiles. ACP is typically characterized by mutations in the CTNNB1 gene, while PCP is primarily associated with BRAF gene mutations.
The primary course of action for treating CP is surgical intervention. However, the tumor's invasive ...
2024-12-16
Among the many artificial intelligence and machine learning models available today for image translation, image-to-image translation models using Generative Adversarial Networks (GANs) can change the style of images. These models work by using two input images: a content image, which is altered to match the style of a reference image. These models are used for tasks like transforming images into different artistic styles, simulating weather changes, improving satellite video resolution, and helping autonomous vehicles recognize different lighting conditions, like day and night.
Now, researchers ...
2024-12-16
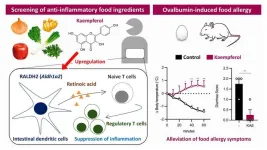
Allergic diseases such as asthma, atopic dermatitis, and food allergies have been increasing in frequency over the last few years. Food allergies in particular affect millions of people worldwide—this includes allergies to foods such as milk, peanuts, eggs and shellfish. They are typically caused by the immune system being hypersensitive to harmless substances in foods and the environment. Flavonoids are chemicals present in various fruits and vegetables that are known to have anti-allergic effects and show promise as natural allergic treatments.
To better understand how these allergies can be treated, let’s look at an interesting anti-allergic mechanism in our cells. ...
2024-12-16
How can we ensure that as many households as possible adopt not only solar panels, but also their own battery to store solar energy, a heat pump, and an electric car? Researchers at the Universities of Basel and Geneva have looked into just this question.
Climate protection and the energy revolution must continue to make progress, and private households could make a significant contribution to this goal if they would use environmentally friendly technologies such as solar panels, electric vehicles, and heat pumps. Dr. Mart van der Kam and Professor Ulf Hahnel at the University of Basel, Switzerland, conducted research into the political measures that would be necessary to fully realize ...
2024-12-16
A new scientific study published in the journal Foresight concludes that human civilisation is on the brink of the next ‘giant leap’ in evolution. However, progress could be thwarted by centralised far-right political projects such as the incoming Donald Trump administration.
"Industrial civilisation is facing 'inevitable' decline as it is replaced by what could turn out to be a far more advanced ‘postmaterialist’ civilisation based on distributed superabundant clean energy. The main challenge is that industrial civilisation is facing such rapid decline that this could derail the emergence of a ...
2024-12-16
Endocannabinoids in the brain play a key role in food intake and energy use. Modulating the action of these molecules could help fight obesity, say researchers at Université de Montréal’s affiliated hospital research centre (CRCHUM).
For years, Université de Montréal medical professor Stephanie Fulton and her team have been unravelling the mechanisms in the human nervous system that control people’s need to eat and to engage in physical activity, and how their metabolism affects their mood.
Their latest ...
2024-12-16
Trappist-1 b is one of seven rocky planets orbiting the star Trappist-1, located 40 light-years away. The planetary system is unique because it allows astronomers to study seven Earth-like planets from relatively close range, with three of them in the so-called habitable zone. This is the area in a planetary system where a planet could have liquid water on the surface. To date, ten research programmes have targeted this system with the James Webb Space Telescope (JWST) for 290 hours.
The current study, in which researchers from the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy (MPIA) ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Emotional cognition analysis enables near-perfect Parkinson's detection