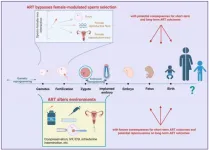
(Press-News.org) A Perspective summarizes the risks of bypassing natural selection when using assisted reproductive technologies (ART) in humans and livestock. The authors call for dialogue between the fields of assisted reproduction and evolutionary biology.
Jonathan P. Evans and Francisco Garcia-Gonzalez detail how techniques used in ART, including in vitro fertilization, artificial insemination, and intracytoplasmic sperm injection, can stress and damage gametes and embryos and lead to deleterious epigenetic changes in offspring. Some ART techniques also bypass a system of filters in the female reproductive tract that select healthy sperm and may lead to better genetic matches with the egg. ART-conceived offspring have higher risk of certain health problems than spontaneously conceived offspring, including preterm birth, congenital abnormalities, low birth weight and associated mitochondrial genotypes, childhood cancers, asthma, obesity, metabolic syndrome, diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and neurodevelopmental and psychiatric disorders. Some of these health risks could potentially be ameliorated by sorting sperm with techniques that mimic the filters in the female reproductive tract and incorporating female reproductive fluids—which play a critical selective role in filtering high quality sperm in vivo—into ART protocols. According to the authors, applying evolutionary principles to the future development of ART may improve outcomes both for human ART and animal production.
END
Simulating natural selection in assisted reproduction
2024-12-17
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Almost three quarters of adolescents experience depression or anxiety
2024-12-17
Almost three quarters of adolescents in Australia experience clinically significant depression or anxiety symptoms, with most being chronic, according to a new study. And preventive strategies outside our clinics are urgently required to address this considerable public health problem facing the nation.
The research, led by Murdoch Children’s Research Institute (MCRI) and published in The Lancet Psychiatry, found mental health problems were frequently chronic with 64 per cent reporting symptoms three or more times across their adolescent years.
MCRI Dr Ellie Robson said the rate and ...
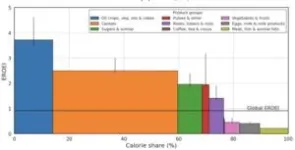
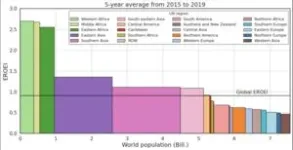
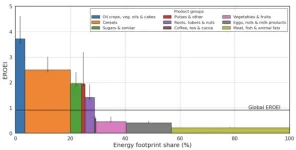
The energy return on investment of global agriculture
2024-12-17
A primary output of agriculture is food, an energy source for the human body. But agriculture also requires energy inputs. Kajwan Rasul and colleagues calculated the global energy return on investment for agriculture over time from 1995 to 2019. The authors constructed a model using two existing models, one that captures the energy use of agriculture and food processing and another that captures flows of agricultural commodities. The authors find that the return on energy investment for global agriculture has increased from .68 to .91 over ...
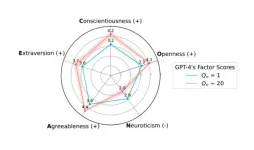
AI responses to personality tests aim to please
2024-12-17
Most major large language models (LLMs) can quickly tell when they are being given a personality test and will tweak their responses to provide more socially desirable results—a finding with implications for any study using LLMs as a stand-in for humans. Aadesh Salecha and colleagues gave LLMs from OpenAI, Anthropic, Google, and Meta the classic Big 5 personality test, which is a survey that measures Extraversion, Openness to Experience, Conscientiousness, Agreeableness, and Neuroticism. Researchers have given ...
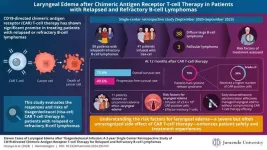
Risks of tisagenlecleucel therapy for relapsed or refractory b-cell lymphomas
2024-12-17
Chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy is a type of cancer immunotherapy where patients’ T-cells are collected and genetically modified to produce chimeric antigen receptors that recognize specific targets on cancer cells, allowing these T-cells to locate and destroy the cancer cells. CAR T-cell therapy shows promising results in treating relapsing or refractory B-cell lymphomas. To explore the risks associated with CAR T-cell therapy, researchers from Juntendo University, Japan, including Professor Jun Ando, Professor Miki Ando, and Dr. Erina Hosoya, published a study in Haematologica on October 17, 2024.
Elaborating about this study further, Dr. Hosoya, ...
Event Horizon Telescope: Moving towards a close-up of a black hole and its jets
2024-12-17
After taking the first images of black holes, the ground-breaking Event Horizon Telescope (EHT) is poised to reveal how black holes launch powerful jets into space. Now, a research team led by Anne-Kathrin Baczko from Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden has shown that the EHT will be able to make exciting images of a supermassive black hole and its jets in the galaxy NGC 1052. The measurements, made with interconnected radio telescopes, also confirm strong magnetic fields close to the black hole’s edge.
The main research question for the project’s ...
USC Norris Cancer Hospital earns Leapfrog Top Hospital award for fourth year in a row
2024-12-17
LOS ANGELES — USC Norris Cancer Hospital was named a Top Teaching Hospital by The Leapfrog Group, a leading national patient safety watchdog organization, for the fourth consecutive year.
“The Leapfrog Top Hospital award is one of the most competitive awards a hospital can receive, and we are delighted that USC Norris Cancer Hospital places among the highest-rated hospitals in the nation once again,” said Marty Sargeant, MBA, CEO of Keck Medical Center of USC, which includes USC Norris Cancer Hospital.
To qualify for the distinction, hospitals must rank top among peers ...
New insights into blood vessel formation
2024-12-17
The formation of blood vessels is a complex process involving the interplay of proteins and mechanic forces. In two studies, a research team at the Biozentrum of the University of Basel, Switzerland, has uncovered new mechanisms in blood vessel formation. The team demonstrated how cells interact during vascular lumen formation and the critical role of dynamic forces in this process. These new insights into blood vessel formation may provide potential approaches in the treatment of vascular diseases.
Blood vessels run throughout the entire body, delivering nutrients and oxygen through the circulating blood. During vessel formation, cells first form local ...
Described in Mallorca the world's oldest ancestor of mammals
2024-12-17
Gorgonopsians are an extinct group of synapsids that lived during the Permian, between 270 and 250 million years ago. They belong to the evolutionary lineage that would give rise to the first mammals 50 million years later. They were warm-blooded animals like modern mammals, but, unlike most of them, they laid eggs. They were carnivorous and were the first animals to develop the characteristic saber teeth. They were often the superpredators of the ecosystems in which they lived, and their appearance would be similar to a dog, ...
Fossil predator is the oldest known animal with “saber teeth”
2024-12-17
The first true mammals evolved roughly 200 million years ago, during the early days of the dinosaurs. But mammals are the last surviving members of an older group, called the therapsids. At first glance, many therapsids weren’t obviously mammal-like , but they also had subtle features that we recognize in mammals today, like a hole on the sides of their skull for the jaw muscle to attach and structures on their jaw bones that would eventually evolve into mammals' distinctive middle ear bones. In a new paper in the journal Nature Communications, scientists announce the discovery of a fossil therapsid ...
Scientists develop new scans that light-up aggressive cancer tumors for better treatment
2024-12-17
Researchers have used a chemical compound to light up treatment-resistant cancers on imaging scans, in a breakthrough that could help medical professionals better target and treat cancer.
The authors at King’s College London say that using the radiotracer – an injected compound used in PET scans – could help inform doctors that a patients aggressive cancer will not respond to chemotherapy before treatment is given. This would prevent the patients receiving unnecessary treatment and provide them with alternative options that will give them the best chance of beating the disease.
The ...