(Press-News.org) Among tree species in the Ecuadorian Amazon, investigators at the Universidad de las Américas, in Ecuador, found that 14% are critically endangered and 47% are endangered. The Plants, People, Planet study indicates that trees with smaller fruits face the greatest threats due to declines of specific animal species that disperse them.
The findings reveal that the extinction risk for endemic trees is associated not only with extrinsic factors such as deforestation but also with complex relationships with other living organisms in their environment.
“Thus, our results highlight the importance of incorporating meaningful ecological traits in extinction risk estimates, such as those related to reproduction and life history strategies,” said co–corresponding author María-José Endara, PhD.
Results of this research also call into question the effectiveness of conservation strategies in formally protected areas. "For example, we found that some endemic tree species populations are experiencing high levels of threat by deforestation inside the Yasuní National Park, the biggest and most iconic protected area in the Ecuadorian Amazon,” said lead author Juan Ernesto Guevara-Andino, PhD.
URL upon publication: https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1002/ppp3.10606
Additional Information
NOTE: The information contained in this release is protected by copyright. Please include journal attribution in all coverage. For more information or to obtain a PDF of any study, please contact: Sara Henning-Stout, newsroom@wiley.com.
About the Journal
Plants, People, Planet publishes innovative research at the interface between plants, society, and the planet. Owned by the New Phytologist Foundation, we aim to publish studies that generate societal impact and address global issues with plant-focused solutions.
About Wiley
Wiley is one of the world’s largest publishers and a trusted leader in research and learning. Our industry-leading content, services, platforms, and knowledge networks are tailored to meet the evolving needs of our customers and partners, including researchers, students, instructors, professionals, institutions, and corporations. We empower knowledge-seekers to transform today’s biggest obstacles into tomorrow’s brightest opportunities. For more than two centuries, Wiley has been delivering on its timeless mission to unlock human potential. Visit us at Wiley.com. Follow us on Facebook, X, LinkedIn and Instagram.
END
Research uncovers high extinction risk for many Amazonian tree species
2024-12-18
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
How did the COVID-19 pandemic and lockdown affect the identity of trans and gender diverse youth?
2024-12-18
Research published in the British Journal of Developmental Psychology indicates that the COVID-19 pandemic and lockdown had largely positive impacts on gender identity development in trans and gender diverse youth.
For the study, 295 transgender and gender diverse U.S. youth, ages 13–22 years, were asked the open-ended question “How has the COVID pandemic changed or affected your own understanding of your gender identity?”
Responses revealed several themes. The most prevalent was “time for identity development,” ...
Does having more chronic conditions increase older adults’ risk of declining kidney function?
2024-12-18
Older adults with multiple chronic conditions may face a high risk of kidney function decline, according to new research published in the Journal of the American Geriatrics Society.
In the study, 3,094 older individuals from the Swedish National Study on Aging and Care in Kungsholmen were followed for 15 years.
There was an independent dose-response relationship between the number of chronic conditions and kidney function decline, so that as the number of chronic conditions increased, kidney function decline became more likely and steeper.
When considering the makeup of conditions rather than just ...
Experts issue new ethical standards for body donation programs
2024-12-18
A new report in the journal Anatomical Sciences Education outlines best practices and standards for human body donation programs across the United States, which accept whole body donations after death for research and education.
The report, issued by a task force of American Association for Anatomy members, seeks to align body donation programs with evolving societal values and legal frameworks. It aims to maintain the highest ethical standards for donors by upholding the principles of informed consent, oversight, and dignity.
The report emphasizes the importance of ensuring potential donors and their families ...
Does an infant breast milk supplement commonly used in Sweden contribute to childhood obesity?
2024-12-18
Many infants in Sweden are given milk cereal drinks, ready-to-mix liquid drink complements to breast milk, after six months of age. New research in Acta Paediatrica found evidence that these products are linked to early rapid weight gain but not to higher anthropometric measures—such as body mass index or waist-to-height ratio—later in childhood.
In the study of 1,333 children from three communities in Western Sweden, physical characteristics and food habits were collected in 2007–2008 family surveys. Follow-up data for 656 children were collected in 2013–2014.
At baseline, 820 (62%) of the 658 boys and 675 girls consumed milk cereal drinks, and 229 (18%) had early ...
Dr. Gerta Hoxhaj named recipient of the Mary Beth Maddox Award and Lectureship for Cancer Research
2024-12-18
TAMEST (Texas Academy of Medicine, Engineering, Science and Technology) has announced Gerta Hoxhaj, Ph.D., Assistant Professor at the Children’s Medical Center Research Institute at UT Southwestern (CRI), as recipient of the 2025 Mary Beth Maddox Award and Lectureship in cancer research. She was chosen for her work in cancer metabolism and revealing new mechanisms crucial for the growth and survival of cancer cells.
The Mary Beth Maddox Award and Lectureship recognizes women scientists in Texas bringing new ideas and innovations to the fight against cancer. It was established in 2022 in honor of Mary Beth Maddox, former ...
Mind’s ear: Investigating the sounds in your head
2024-12-18
Some people can’t imagine a dog barking or a police siren. Songs can’t get stuck in their heads. They have no inner voices.
‘Anauralia’ was proposed in 2021 by scientists from Waipapa Taumata Rau, University of Auckland to describe the little-known condition of a silent mind.
Now, as their investigations into the phenomenon continue, the University will host a global conference on sounds imagined in the mind, an event intended not just for scientists but also philosophers, musicians, poets and writers. ‘Mind’s ...
Robot rehabilitation can offer optimal post-stroke treatment
2024-12-18
The increasing number of strokes and subsequent rehabilitation has highlighted the growing need for effective care strategies. Serious side effects, such as motor paralysis, can be challenging to mend, but the recent incorporation of robots into treatment has shown promise.
Automated robots repeatedly provide the proper movements necessary to recover motor function. However, to ensure appropriate care tailored to the degree of motor paralysis, knowledge of robots and rehabilitation is needed.
Osaka Metropolitan University Professor Takashi Takebayashi of the Graduate School of Rehabilitation Science led a team in collecting data from ...
Nonheterosexual women may maintain better sexual functioning during menopause transition
2024-12-18
CLEVELAND, Ohio (Dec 18, 2024)–A woman’s sex drive may diminish with age—partially because of problems with genitourinary symptoms during the menopause transition. Yet, some older women maintain very active sex lives. Why? A new study suggests that one difference could be sexual identity, with nonheterosexual women more likely to report better sexual functioning, despite menopause. Results of the study are published online today in Menopause, the journal of The Menopause Society.
An estimated 25% to 85% of postmenopausal women report challenges ...
Giant virus encodes key piece of protein-making machinery of cellular life
2024-12-18
Researchers at the University of Hawai‘i at Mānoa recently discovered that a virus, FloV-SA2, encodes one of the proteins needed to make ribosomes, the central engines in all cells that translate genetic information into proteins, the building blocks of life. This is the first eukaryotic virus (a virus that infects eukaryotes, such as plants, animals, fungi) found to encode such a protein.
Viruses are packets of genetic material surrounded by a protein coating. They replicate by getting inside of a cell where they take over the cell’s replication machinery and direct it to make more viruses. ...
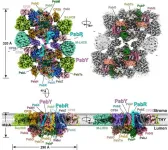
Scientists provide insights into Photosystem II under low-light conditions
2024-12-18
In higher plants and green algae, Photosystem II (PSII) usually combines with Light Harvesting Complex II (LHCII) to form the PSII-LHCII supercomplex. Under low-light conditions, the PSII-LHCII supercomplexes are organized laterally into higher-order PSII-LHCII megacomplexes and semi-crystalline arrays to optimize photosynthetic efficiency.
A recent collaborative study has deciphered the cryo-EM structure of the spinach type I PSII-LHCII megacomplex, providing insights into the principles of higher-order ...