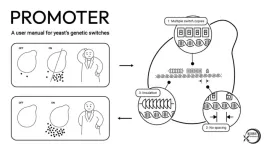
(Press-News.org) When introducing genes into yeast to make it produce drugs and other useful substances, it is also necessary to reliably switch the production on or off. A Kobe University team found three gene regulation design principles that provide a flexible guideline for the effective control of microbiological production.
It’s said that DNA is the blueprint of life, telling our cells what to produce. But DNA also contains the switches telling those cells when to produce something and how much of it. Therefore, when introducing new genes into cells to produce useful chemicals such as drugs or raw materials for chemical production, it is also necessary to include a genetic switch, a piece of DNA called a “promoter,” that tells the cells to start production as needed. Kobe University bioengineer TOMINAGA Masahiro says: “The problem is that these promoters cannot be used in a plug-and-play manner unless researchers deeply understand how they interact with other genetic elements. Indeed, there are not so many cases in which researchers use artificial promoters to precisely control the cellular production and achieve their research purpose.” Sometimes the production is too low, sometimes it is “leaky,” meaning that it cannot be turned off at will. This is especially true for bioengineering yeast, which is more complex in its genetic regulation compared to bacteria. But this increased complexity also enables its use to produce many useful chemicals.
As experts in modifying yeast cells, Tominaga and colleagues from the team led by ISHII Jun took a systematic approach to working out how to design effective promoters. “We came up with the idea that by carefully describing our process of improving a prototype promoter, we could prepare a ‘user manual’ for how to achieve high-performance and precise control so that these genetic systems could be more widely used,” Tominaga explains.
In a paper now published in the journal Nature Communications, they describe three design principles for yeast promoters. First, if researchers not only need large amounts of the product but also the ability to switch the production on or off at will, they should introduce multiple copies of the regulatory elements enabling this within the promoter. This reduces leakiness and increases the productivity. Second, the distance between promoter elements should be as small as possible to enhance the productivity even more. And third, the promoter should be insulated from surrounding DNA by including extra DNA before it to further reduce leakiness. Tominaga says: “We showed that a promoter’s performance can be improved more than 100-fold by simply modifying its surrounding sequence. This is the first study to clearly propose a solution to the problem why potent yeast promoters work in some environments and not in others.”
The Kobe University bioengineers demonstrated the usefulness of their system by showcasing the production of two pharmaceutically useful proteins, so-called “biologics.” Not only could they produce these two biologics in separate yeast strains but also in the same strain and with the ability to independently control which biologic is produced at any time. The latter is important because it has potential applications in hospitals, as the team explains in the study: “In addition to the conventional fermentation of single biologics, the rapid and single-dose production of multiple biologics with a single yeast strain at the point of care is crucial for emergencies that require production speed and flexibility rather than purity and productivity.” They also achieved the notoriously difficult production of a coronavirus protein that can be used for the production of treatments, further showcasing both the usefulness and the flexibility of their design principles.
Tominaga explains his wider outlook on the implications of this study: “Synthetic biology advocates creating new biological functions by rewriting genome sequences. The reality is however that we are often confused by unexpected changes resulting from our edits. We hope that our study is the first step towards the ability to design every single base in the genome with clear intentions.”
This research was funded by the Japan Agency for Medical Research and Development (grants JP21ae0121002, JP21ae0121005, JP21ae0121006, JP21ae0121007, JP20ae0101055 and JP20ae0101060), the Japan Science and Technology Agency (grants JPMJCR21N2 and JPMJGX23B4) and the Japan Society for the Promotion of Science (grants JP23K26469, JP23H01776 and JP18K14374). It was conducted in collaboration with researchers from the Pharma Foods International Co. Ltd and National Institute of Health Sciences.
Kobe University is a national university with roots dating back to the Kobe Higher Commercial School founded in 1902. It is now one of Japan’s leading comprehensive research universities with nearly 16,000 students and nearly 1,700 faculty in 10 faculties and schools and 15 graduate schools. Combining the social and natural sciences to cultivate leaders with an interdisciplinary perspective, Kobe University creates knowledge and fosters innovation to address society’s challenges.
END
A user manual for yeast’s genetic switches
2024-12-19
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
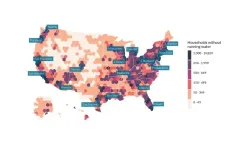
More people living without running water in US cities since the global financial crisis
2024-12-19
More American cities – even those seen as affluent – are home to people living without running water as people are being ‘squeezed’ by unaffordable housing and the cost-of-living crisis, new research finds.
Published in Nature Cities, the study revealed the problem worsened following changes to the housing market triggered by the 2008 global crash. And since 2017 it has been “expanding in scope and severity” to affect a broader array of US cities including Portland (OR), Phoenix, Houston, Atlanta, Dallas-Fort Worth, and Philadelphia, as well as large urban areas such as Los Angeles, New York City and San Francisco.
The research ...
Study finds slowing of age-related declines in older adults
2024-12-19
A new study from the Robert N. Butler Columbia Aging Center at the Mailman School of Public Health reveals significant improvements in the health of older adults in England when compared to previous generations. Rather than considering health through the presence or absence of disease, the study, published in Nature Aging, applied a new approach that examined trends in people’s functioning – their cognitive, locomotor, psychological, and sensory capacities.
Using data from the English Longitudinal Study ...
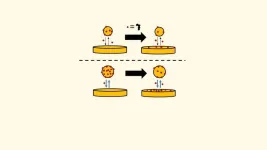
Tinkering with the “clockwork” mechanisms of life
2024-12-19
Living organisms monitor time – and react to it – in many different ways, from detecting light and sound in microseconds to responding physiologically in pre-programmed ways, via their daily sleep cycle, monthly menstrual cycle, or to changes in the seasons.
Such ability to react at different timescales is made possible via molecular switches or nanomachines that act or communicate as precise molecular timers, programmed to turn on and off in response to the environment and time.
Now, ...
Machine psychology – a bridge to general AI
2024-12-19
Artificial intelligence that is as intelligent as humans may become possible thanks to psychological learning models, combined with certain types of AI. This is the conclusion of Robert Johansson, who in his dissertation from Linköping University has developed the concept of Machine Psychology and how it can contribute to AI development.
Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) has been the holy grail of AI research since the 1950s. So far, humanity has not managed to create an artificial intelligence that can solve intellectual tasks in the same way ...
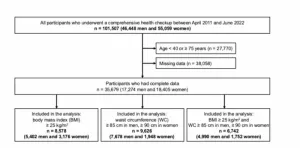
Walking speed as a simple predictor of metabolic health in obese individuals
2024-12-19
Walking speed can provide insights into health, extending beyond mere mobility, so much so that it is considered to be the “sixth vital sign.” Past studies have suggested that a slow walking speed is correlated with the development of cardiovascular diseases and an increased risk of mortality in the elderly.
A recent study led by Prof. Kojiro Ishii from Doshisha University, in collaboration with Dr. Yukio Yamamoto, Dr. Kentaro Ikeue, Dr. Kan Oishi, and Dr. Takaaki Mori from Doshisha University, ...
Houston Methodist scientists make surprising discovery pinpointing when good cholesterol becomes harmful
2024-12-19
HOUSTON-(Dec. 18, 2024) –Houston Methodist researchers have discovered that certain components of so-called “good” cholesterol -- high-density lipoproteins (HDL) – may be associated with an increased prevalence of cardiovascular disease.
Led by Henry J. Pownall, Ph.D., professor of biochemistry in medicine at the Houston Methodist Research Institute, and Khurram Nasir, M.D., M.P.H., a cardiologist and division chief of cardiovascular prevention and wellness at Houston Methodist, the research team is using innovative methods to investigate the role of certain properties of HDL in heart health.
“During ...
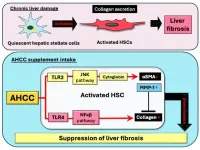
Shiitake-derived functional food shows suppression of liver fibrosis progression
2024-12-19
Chronic liver damage can lead to hepatitis, which causes fibrosis of the liver. This buildup of collagen and other fibrous tissue accelerates when hepatic stellate cells become activated during hepatitis, often resulting in liver cancer or cirrhosis, both of which can be fatal. As there are no effective drugs to treat cirrhosis, suppressing the activation of the stellate cells is considered as a way of controlling the progression of liver fibrosis.
“It is estimated that one out of every 3-4 ...
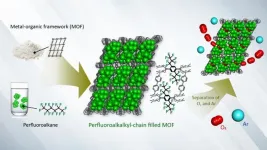
Breathing new life into technology: New way of separating oxygen from argon
2024-12-19
Efficient gas separation is vital in various industries, from medical applications to energy production. However, isolating oxygen from mixtures presents a significant technological challenge. Because many gases, including argon and oxygen, share similar physical properties, separating them is difficult. Now, Ryotaro Matsuda and his team at Nagoya University have developed a unique porous metal-organic framework (MOF), which represents a novel approach to gas separation: a combined phenomenon of "adsorption" and "dissolution" that they term the "adsorptive-dissolution" ...
Leveraging AI to assist clinicians with physical exams
2024-12-19
Physical examinations are important diagnostic tools that can reveal critical insights into a patient’s health, but complex conditions may be overlooked if a clinician lacks specialized training in that area. While previous research has investigated using large language models (LLMs) as tools to aid in providing diagnoses, their use in physical exams remains untapped. To address this gap, researchers from Mass General Brigham prompted the LLM GPT-4 to recommend physical exam instructions based on patient symptoms. ...
Brain inflammation alters behaviour according to sex
2024-12-19
Inflammation in the hippocampus – the brain’s memory centre – significantly alters motivation and behaviour in mice, including food-seeking behaviour, with notable differences between males and females, a recent study reveals.
The hippocampus plays a crucial role in memory formation, learning and emotional regulation. Hippocampal neuroinflammation occurs in a range of diseases and disorders such as Alzheimer’s, Multiple Sclerosis and Depression.
People with these diseases often experience common symptoms such as apathy, difficulty with daily activities and changes to food preferences. These symptoms also tend to be more severe in women than in men.
“While ...