(Press-News.org) The war in Ukraine is causing hunger thousands of miles from the battlefields, according to a study released today.
Nearly three years of war in the “breadbasket of the world” has left croplands destroyed and forced laborers who grow, harvest and process a bounty of wheat, barley and oats to flee. Combined with export bans from other countries, ripple effects resonated through global trade and upended food supply systems.
But understanding how far those disruptions reached, who suffered and who gained has been difficult. Researchers at Michigan State University’s Center for Systems Integration and Sustainability (CSIS) lead a unique effort, relying on satellite images to quantify loss of cropland and employing a holistic method called the metacoupling framework and network analysis to analyze connections within a region, between neighboring areas, and across distant ones.
The work was published in Nature’s Communication Earth & Environment.
“The most striking aspect of our research is its ability to connect a regional conflict to its far-reaching impacts on global food accessibility,” said Nan Jia, a PhD student and lead author.
The stakes are high. The United Nations Food and Agriculture Organization models suggest that 13 million more people would be undernourished in 2022 due to the Russia-Ukraine war. . Ukraine's lost production of three winter cereals in 2021 could have met the caloric needs of 76 million adults for a year.
The study revealed that regarding wheat, barley, and oats, the war has had a much greater impact on distant countries than on countries next to the Ukraine and disproportionately harms poor countries.
“It’s remarkable how interconnected our world is—an event in one part of the globe can lead to food insecurity thousands of kilometers away,” said Jianguo “Jack” Liu, Rachel Carson Chair in Sustainability and senior author. “By using the metacoupling framework to trace these connections, we were able to reveal the unequal impact of the war, highlighting how distant and low-income nations are often left more vulnerable in times of crisis.”
Countries far from Ukraine were disproportionately affected, facing higher costs and fewer options to secure food supplies. Among these, lower-income nations in Africa, such as Sierra Leone, the Democratic Republic of Congo and Somalia – and Montenegro, Albania and Belarus in Europe, bore the brunt of the crisis, as they lacked the resources to adapt to soaring prices or find alternative suppliers.
However, amidst this challenge, the study also revealed hope: over time, major exporting countries like the United States, Canada, and Australia stepped up, partially filling the gaps left by Ukraine. But these changes can compromise biodiversity in these exporting countries, as shown in another paper “Telecoupled impacts of the Russia-Ukraine war on global cropland expansion and biodiversity “ published in Nature Sustainability earlier this year by Liu and collaborators. (see news release "War a biodiversity enemy – even in peaceful locales")
“By revealing the hidden vulnerabilities in global food systems, our study emphasizes the need for international cooperation to ensure food security,” Jia said. “Policymakers and global organizations can use these insights to build more resilient food networks, invest in local production in vulnerable countries, and create strategies to mitigate the impacts of future crises.”
In addition to Jia and Liu, “The Russia-Ukraine war reduced food production and exports with a disparate geographical impact worldwide” was written by Zilong Xia, Yinshuai Li, Xiang Yu, Xutong Wu, Yingjie Li, Rongfei Su, Mengting Wang, Ruishan Chen. The work was financially supported by the USDA-NIFA, the National Science Foundation and Michigan AgBioResearch.
END
Russia-Ukraine War’s unexpected casualties: Hungry people in distant nations
2024-12-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
York U professor’s new paper challenges tokenizing women of colour in academia
2024-12-20
TORONTO, December 20, 2024 — The unspoken rule for women of colour in academia is to be everything to everyone – mentor, diversity champion, tireless scholar, and silent workhorse, says York University equity studies Assistant Professor Yvonne Su in her recent paper published today in Nature Human Behaviour.
“We are expected to carry the banner of inclusion, but we are not truly included. Inclusion, as it’s currently defined, is about optics, not transformation,” observes Su in the Faculty of Liberal Arts and Professional Studies. “It’s about showing diversity on the surface ...
Tiny antennas on cells offer new ALS insights
2024-12-20
Leuven, 20 December 2024- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a devastating neurodegenerative disease that affects motor neurons. The average life span after diagnosis of this incurable disease is two to five years. In the relentless pursuit of understanding the cause of motor neuron death, scientists from KU Leuven and the VIB Center for Brain and Disease Research have identified an intriguing new lead: tiny, antenna-like structures 0n cells called primary cilia. Their study, published in Brain, could open a potential new avenue for therapeutic development.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s ...
Geothermal aquifers offer green potential but quality checks required
2024-12-20
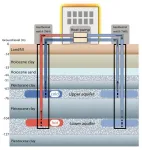
The aquifer thermal energy storage (ATES) system, which uses geothermal heat as a renewable energy source, is one of the solutions to reducing fuel consumption and carbon dioxide emission. This system stores heat underground in aquifers, using groundwater as a heat medium. The heat is then extracted as needed according to the season to efficiently heat and cool buildings.
Its use is mainly expanding in Europe, and its widespread introduction is expected in Japan. However, regular inspection is required to utilize ...
Large Hadron Collider regularly makes magic
2024-12-20
A brotherly research duo has discovered that when the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) produces top quarks – the heaviest known fundamental particles – it regularly creates a property known as magic.
This finding, published in Physical Review D, has implications for the progression of quantum computing, with magic being a measure that describes how difficult a quantum system is for a non-quantum computer to calculate.
“The higher the magic, the more we need quantum computers to describe the behaviour,” explains Professor Martin White, from the University ...
Functionality of a grapevine transport protein defined
2024-12-20
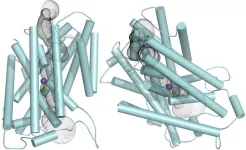
Researchers at the University of Adelaide have discovered that a protein which mediates the transport of alkali metal ions, such as potassium, and halides ions across plant membranes acts similarly to a protein found in animals.
The protein is a cation-chloride cotransporter (CCC), and these are present in all cellular life forms. Some CCCs are able to transport two types of ions, both potassium and halide chloride, while others can also transport a third – sodium.
The selectivity of plant CCCs has been controversial, and it was previously understood ...
Changes in store for atmospheric rivers
2024-12-20
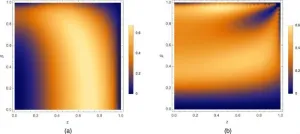
Communities up and down the West Coast of the United States can expect the potent storms known as atmospheric rivers to evolve as the climate warms. But residents in Southern California will see much different changes than residents in more northerly locations like Seattle.
New research, led by scientists at the U.S. National Science Foundation National Center for Atmospheric Research (NSF NCAR), found that warming conditions will increase evaporation of ocean waters and significantly alter atmospheric rivers to the south. Farther north, however, atmospheric rivers will be most influenced by rising temperatures in the ocean and atmosphere.
While ...
First results from 2021 rocket launch shed light on aurora’s birth
2024-12-20
Newly published results from a 2021 experiment led by a University of Alaska Fairbanks scientist have begun to reveal the particle-level processes that create the type of auroras that dance rapidly across the sky.
The Kinetic-scale Energy and momentum Transport experiment — KiNET-X — lifted off from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on May 16, 2021, in the final minutes of the final night of the nine-day launch window.
UAF professor Peter Delamere’s analysis of the experiment’s results was published Nov. 19 in Physics of Plasmas.
“The ...
Patience isn't a virtue; it's a coping mechanism
2024-12-20
Patience — like its corollary impatience — has always been a sort of “I know it when I see it” concept. And that didn’t sit well with UC Riverside psychology researcher Kate Sweeny.
“Philosophers and religious scholars call patience a virtue, yet most people claim to be impatient,” Sweeny said. “That made me wonder if maybe patience is less about being a good person and more about how we deal with day-to-day frustrations.”
For purposes of her research, Sweeny sought to better define what constitutes patience, and impatience, and the factors that determine them.
Impatience, ...
The Lancet Psychiatry: Autism spectrum disorder ranks among the top 10 causes of non-fatal health burden in youth
2024-12-20
A new global analysis reveals that an estimated 61.8 million people in 2021 were autistic —equivalent to 1 in every 127 individuals. Conducted as part of the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2021, the research identifies autism spectrum disorder (ASD) as one of the top ten causes of non-fatal health burden for youth under 20 years old.
Key findings reveal stark disparities: the global prevalence of ASD is significantly higher among males, at 1,065 cases per 100,000 males, almost double of global prevalence among females (508 per 100,000 females). Regions like High-Income ...
Innovative glue maker chosen for Japanese startup program
2024-12-20
The eco-friendly glue company D-Glue, co-created by a Cal Poly chemistry research team with student involvement in partnership with an East Coast company, has joined an international corporate incubator program as of Dec. 1.
Plug and Play, a global innovation platform that links startups, corporations, investors, universities and government agencies, has over 60 locations across the world, reaching across 25 industries. Plug and Play’s three-month international program matches startups with business investors among its 45 Japanese corporate ...