(Press-News.org) Scientists have discovered a way to remove toxic compounds from potatoes, making them safer to eat and easier to store. The breakthrough could cut food waste and enhance crop farming in space and other extreme environments.
Potato plants naturally produce chemicals that protect them from insects. The chemicals, called steroidal glycoalkaloids, or SGAs, are found in high quantities in the green parts of potato peels, and in the sprouting areas. They render the potatoes unsafe for insects as well as humans.
"These compounds are critical for plants to ward off insects, but they make certain parts of these crops inedible," said Adam Jozwiak, a UCR molecular biochemist who led the study. "Now that we’ve uncovered the biosynthetic pathway, we can potentially create plants that produce these compounds only in the leaves while keeping the edible parts safe."
Sunlight can induce the production of SGAs in potato tubers — the part of the potato plant that is eaten — even after they’ve been harvested. By identifying a key genetic mechanism in SGA production, UC Riverside researchers may be able reduce potatoes’ toxicity while preserving the plants' natural defenses. Taking SGA out of potatoes will also make them easier to store and transport in open air.
The research, published in Science, focuses on a protein dubbed "GAME15," which plays a key role in directing the plant's production of SGAs. This protein acts both as an enzyme and a scaffold, organizing other enzymes into a "conversion factory" that efficiently produce SGAs while preventing toxic compounds from leaking into other parts of plant cells, where they would wreak havoc.
Tomatoes also produce SGAs, primarily in the green, unripe fruit, as well as in the leaves, stems, and roots of the plants. When the researchers silenced the GAME15 gene in tomatoes, they eliminated SGA production but also made the plants highly susceptible to pests.
By engineering plants to control when and where SGAs are produced, for example, in the leaves but not the potatoes themselves, the researchers envision crops that can be stored without the risk of toxicity from sunlight exposure.
"You could store the potatoes in your kitchen and not worry about exposure to sun, which makes them produce more SGAs. And then you could eat them whenever you want, reducing food waste,” Jozwiak said.
Additionally, the findings could enable the use of other plant parts, such as leaves, for food in limited-space environments like space missions or vertical farming systems. "For space farming, where every part of a plant may need to be edible, these findings are especially promising,” Jozwiak said.
The team achieved these insights by initially recreating the SGA production process in tobacco plants. Surprisingly, they found that during evolution the process redirected protein from the plasma membrane or Golgi apparatus, where it is responsible for the production of cell wall components crucial for cell growth, to the endoplasmic reticulum, a part of the cell where toxin production begins.
“Essentially, the plant borrows from itself to create GAME15,” Jozwiak said. “We did not expect to find the plant hijacking protein it needs for the production of cell walls.”
Green, unripe fruit may be toxic, but during ripening these molecules convert to something edible. By limiting SGAs to non-edible parts of plants, farmers and consumers alike could benefit from safer, more versatile crops.
"Our work demonstrates that plants have evolved ingenious ways to balance growth, reproduction, and defense," Jozwiak said. "Understanding these systems allows us to redesign crops to meet modern needs without compromising their ability to thrive."
This research was a highly collaborative effort involving researchers from the Weizmann Institute of Science in Israel, as well as Kobe University, the RIKEN Center for Sustainable Resource Science, and Osaka University in Japan. The group’s findings not only hold the promise of healthier food but also represent a leap forward in sustainable agriculture and space exploration.
"We’re thrilled about the potential of this discovery," Jozwiak said. " It’s exciting to think about how we can now significantly extend the shelf life of crops like potatoes and reduce food waste on Earth and beyond.”
END
Growing safer spuds: removing toxins from potatoes
Using genetics to reduce food waste
2024-12-20
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Russia-Ukraine War’s unexpected casualties: Hungry people in distant nations
2024-12-20
The war in Ukraine is causing hunger thousands of miles from the battlefields, according to a study released today.
Nearly three years of war in the “breadbasket of the world” has left croplands destroyed and forced laborers who grow, harvest and process a bounty of wheat, barley and oats to flee. Combined with export bans from other countries, ripple effects resonated through global trade and upended food supply systems.
But understanding how far those disruptions reached, who suffered and who gained has been difficult. Researchers at Michigan State University’s Center for Systems Integration and Sustainability (CSIS) lead a unique effort, relying ...
York U professor’s new paper challenges tokenizing women of colour in academia
2024-12-20
TORONTO, December 20, 2024 — The unspoken rule for women of colour in academia is to be everything to everyone – mentor, diversity champion, tireless scholar, and silent workhorse, says York University equity studies Assistant Professor Yvonne Su in her recent paper published today in Nature Human Behaviour.
“We are expected to carry the banner of inclusion, but we are not truly included. Inclusion, as it’s currently defined, is about optics, not transformation,” observes Su in the Faculty of Liberal Arts and Professional Studies. “It’s about showing diversity on the surface ...
Tiny antennas on cells offer new ALS insights
2024-12-20
Leuven, 20 December 2024- Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS) is a devastating neurodegenerative disease that affects motor neurons. The average life span after diagnosis of this incurable disease is two to five years. In the relentless pursuit of understanding the cause of motor neuron death, scientists from KU Leuven and the VIB Center for Brain and Disease Research have identified an intriguing new lead: tiny, antenna-like structures 0n cells called primary cilia. Their study, published in Brain, could open a potential new avenue for therapeutic development.
Amyotrophic lateral sclerosis (ALS), also known as Lou Gehrig’s ...
Geothermal aquifers offer green potential but quality checks required
2024-12-20
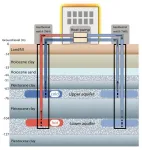
The aquifer thermal energy storage (ATES) system, which uses geothermal heat as a renewable energy source, is one of the solutions to reducing fuel consumption and carbon dioxide emission. This system stores heat underground in aquifers, using groundwater as a heat medium. The heat is then extracted as needed according to the season to efficiently heat and cool buildings.
Its use is mainly expanding in Europe, and its widespread introduction is expected in Japan. However, regular inspection is required to utilize ...
Large Hadron Collider regularly makes magic
2024-12-20
A brotherly research duo has discovered that when the Large Hadron Collider (LHC) produces top quarks – the heaviest known fundamental particles – it regularly creates a property known as magic.
This finding, published in Physical Review D, has implications for the progression of quantum computing, with magic being a measure that describes how difficult a quantum system is for a non-quantum computer to calculate.
“The higher the magic, the more we need quantum computers to describe the behaviour,” explains Professor Martin White, from the University ...
Functionality of a grapevine transport protein defined
2024-12-20
Researchers at the University of Adelaide have discovered that a protein which mediates the transport of alkali metal ions, such as potassium, and halides ions across plant membranes acts similarly to a protein found in animals.
The protein is a cation-chloride cotransporter (CCC), and these are present in all cellular life forms. Some CCCs are able to transport two types of ions, both potassium and halide chloride, while others can also transport a third – sodium.
The selectivity of plant CCCs has been controversial, and it was previously understood ...
Changes in store for atmospheric rivers
2024-12-20
Communities up and down the West Coast of the United States can expect the potent storms known as atmospheric rivers to evolve as the climate warms. But residents in Southern California will see much different changes than residents in more northerly locations like Seattle.
New research, led by scientists at the U.S. National Science Foundation National Center for Atmospheric Research (NSF NCAR), found that warming conditions will increase evaporation of ocean waters and significantly alter atmospheric rivers to the south. Farther north, however, atmospheric rivers will be most influenced by rising temperatures in the ocean and atmosphere.
While ...
First results from 2021 rocket launch shed light on aurora’s birth
2024-12-20
Newly published results from a 2021 experiment led by a University of Alaska Fairbanks scientist have begun to reveal the particle-level processes that create the type of auroras that dance rapidly across the sky.
The Kinetic-scale Energy and momentum Transport experiment — KiNET-X — lifted off from NASA’s Wallops Flight Facility in Virginia on May 16, 2021, in the final minutes of the final night of the nine-day launch window.
UAF professor Peter Delamere’s analysis of the experiment’s results was published Nov. 19 in Physics of Plasmas.
“The ...
Patience isn't a virtue; it's a coping mechanism
2024-12-20
Patience — like its corollary impatience — has always been a sort of “I know it when I see it” concept. And that didn’t sit well with UC Riverside psychology researcher Kate Sweeny.
“Philosophers and religious scholars call patience a virtue, yet most people claim to be impatient,” Sweeny said. “That made me wonder if maybe patience is less about being a good person and more about how we deal with day-to-day frustrations.”
For purposes of her research, Sweeny sought to better define what constitutes patience, and impatience, and the factors that determine them.
Impatience, ...
The Lancet Psychiatry: Autism spectrum disorder ranks among the top 10 causes of non-fatal health burden in youth
2024-12-20
A new global analysis reveals that an estimated 61.8 million people in 2021 were autistic —equivalent to 1 in every 127 individuals. Conducted as part of the Global Burden of Diseases, Injuries, and Risk Factors Study (GBD) 2021, the research identifies autism spectrum disorder (ASD) as one of the top ten causes of non-fatal health burden for youth under 20 years old.
Key findings reveal stark disparities: the global prevalence of ASD is significantly higher among males, at 1,065 cases per 100,000 males, almost double of global prevalence among females (508 per 100,000 females). Regions like High-Income ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Evaluating the effects of hypnotics for insomnia in obstructive sleep apnea
A new reagent makes living brains transparent for deeper, non-invasive imaging
Smaller insects more likely to escape fish mouths
Failed experiment by Cambridge scientists leads to surprise drug development breakthrough
Salad packs a healthy punch to meet a growing Vitamin B12 need
Capsule technology opens new window into individual cells
We are not alone: Our Sun escaped together with stellar “twins” from galaxy center
Scientists find new way of measuring activity of cell editors that fuel cancer
Teens using AI meal plans could be eating too few calories — equivalent to skipping a meal
Inconsistent labeling and high doses found in delta-8 THC products: JSAD study
Bringing diabetes treatment into focus
Iowa-led research team names, describes new crocodile that hunted iconic Lucy’s species
One-third of Americans making financial trade-offs to pay for healthcare
Researchers clarify how ketogenic diets treat epilepsy, guiding future therapy development
PsyMetRiC – a new tool to predict physical health risks in young people with psychosis
Island birds reveal surprising link between immunity and gut bacteria
Research presented at international urology conference in London shows how far prostate cancer screening has come
Further evidence of developmental risks linked to epilepsy drugs in pregnancy
Cosmetic procedures need tighter regulation to reduce harm, argue experts
How chaos theory could turn every NHS scan into its own fortress
Vaccine gaps rooted in structural forces, not just personal choices: SFU study
Safer blood clot treatment with apixaban than with rivaroxaban, according to large venous thrombosis trial
Turning herbal waste into a powerful tool for cleaning heavy metal pollution
Immune ‘peacekeepers’ teach the body which foods are safe to eat
AAN issues guidance on the use of wearable devices
In former college athletes, more concussions associated with worse brain health
Racial/ethnic disparities among people fatally shot by U.S. police vary across state lines
US gender differences in poverty rates may be associated with the varying burden of childcare
3D-printed robotic rattlesnake triggers an avoidance response in zoo animals, especially species which share their distribution with rattlers in nature
Simple ‘cocktail’ of amino acids dramatically boosts power of mRNA therapies and CRISPR gene editing
[Press-News.org] Growing safer spuds: removing toxins from potatoesUsing genetics to reduce food waste