(Press-News.org) ANN ARBOR—Bright, twisted light can be produced with technology similar to an Edison light bulb, researchers at the University of Michigan have shown. The finding adds nuance to fundamental physics while offering a new avenue for robotic vision systems and other applications for light that traces out a helix in space.
"It's hard to generate enough brightness when producing twisted light with traditional ways like electron or photon luminescence," said Jun Lu, an adjunct research investigator in chemical engineering at U-M and first author of the study on the cover of this week's Science.
"We gradually noticed that we actually have a very old way to generate these photons—not relying on photon and electron excitations, but like the bulb Edison developed."
Every object with any heat to it, including yourself, is constantly sending out photons (particles of light) in a spectrum tied to its temperature. When the object is the same temperature as its surroundings, it is also absorbing an equivalent amount of photons—this is idealized as "blackbody radiation" because the color black absorbs all photon frequencies.
While a tungsten lightbulb's filament is much warmer than its surroundings, the law defining blackbody radiation—Planck's law—offers a good approximation of the spectrum of photons it sends out. All together, the visible photons look like white light, but when you pass the light through a prism, you can see the rainbow of different photons within it.
This radiation is also why you show up brightly in a thermal image, but even room-temperature objects are constantly emitting and receiving blackbody photons, making them dimly visible as well.
Typically, the shape of the object emitting the radiation doesn't get much consideration—for most purposes (as so often in physics), the object can be imagined as a sphere. But while shape doesn't affect the spectrum of wavelengths of the different photons, it can affect a different property: their polarization.
Usually photons from a blackbody source are randomly polarized—their waves may oscillate along any axis. The new study revealed that if the emitter was twisted at the micro or nanoscale, with the length of each twist similar to the wavelength of the emitted light, the blackbody radiation would be twisted too. The strength of the twisting in the light, or its elliptical polarization, depended on two main factors: how close the wavelength of the photon was to the length of each twist and the electronic properties of the material—nanocarbon or metal, in this case.
Twisted light is also called "chiral" because the clockwise and counterclockwise rotations are mirror images of one another. The study was undertaken to demonstrate the premise of a more applied project that the Michigan team would like to pursue: using chiral blackbody radiation to identify objects. They envision robots and self-driving cars that can see like mantis shrimp, differentiating among light waves with different directions of twirl and degrees of twistedness.
"The advancements in physics of blackbody radiation by chiral nanostructures is central to this study. Such emitters are everywhere around us," said Nicholas Kotov, the Irving Langmuir Distinguished Professor of Chemical Sciences and Engineering, director of NSF Center of Complex Particles and Particle Systems (COMPASS) and corresponding author of the study.
"These findings, for example, could be important for an autonomous vehicle to tell the difference between a deer and a human, which emit light with similar wavelengths but different helicity because deer fur has a different curl from our fabric."
While brightness is the main advantage of this method for producing twisted light—up to 100 times brighter than other approaches—the light includes a broad spectrum of both wavelengths and twists. The team has ideas about how to address this, including exploring the possibility of building a laser that relies on twisted light-emitting structures.
Kotov also wants to explore further into the infrared spectrum. The peak wavelength of blackbody radiation at room temperature is roughly 10,000 nanometers or 0.01 millimeters.
"This is an area of the spectrum with a lot of noise, but it may be possible to enhance contrast through their elliptical polarization," Kotov said.
The study was supported by the National Science Foundation via COMPASS, and the Office of Naval Research.
Kotov is also the Joseph B. and Florence V. Cejka Professor of Engineering, a professor of macromolecular science and engineering and a member of U-M’s Biointerfaces Institute. Lu is an incoming assistant professor of chemistry and physics at the National University of Singapore.
The device was built in the COMPASS Lab located at the North Campus Research Complex of U-M and studied at the Michigan Center for Materials Characterization.
Study: Bright, circularly-polarized black-body radiation from twisted nanocarbon
Filaments (DOI: 10.1126/science.adq4068)
Images
END
Twisted Edison: Bright, elliptically polarized incandescent light
Filaments curling at the micro and nanoscale produce light waves that twirl as they travel
2024-12-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Structural cell protein also directly regulates gene transcription
2024-12-23
ITHACA, N.Y. -- A cell protein previously believed only to provide a scaffolding for DNA has also been shown to directly influence DNA transcription into RNA – the first step of the process by which an organism’s genetic code expresses itself. The fundamental breakthrough was discovered in apple cells but is relevant to all living organisms made of nucleus-containing cells, including humans.
The finding, published Dec. 20 in Plant Cell, was co-authored by Cornell researchers and colleagues from the University of California, Davis, and Shandong Agricultural University in Shandong, China.
Every cell in an organism ...
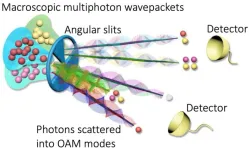
Breaking boundaries: Researchers isolate quantum coherence in classical light systems
2024-12-23
Understanding the boundary between classical and quantum physics has long been a central question in science. While thermal light fields have traditionally been viewed as classical, the team fragmented these fields into smaller multiphoton subsystems. Surprisingly, they uncovered quantum coherence—features such as particle interference previously thought unique to quantum systems—within a classical light source.
By using a sophisticated technique involving photon-number-resolving detection and orbital angular momentum (OAM) measurements, the researchers projected a classical pseudothermal light field into isolated multiphoton ...
Brain map clarifies neuronal connectivity behind motor function
2024-12-23
(MEMPHIS, Tenn. – December 23, 2024) Signals relayed to motor neurons from the brain enable muscle movement, but these signals typically pass through spinal interneurons before they reach their destination. How the brain and this highly diverse group of “switchboard operator” cells are connected is poorly understood. To address this, scientists at St. Jude Children’s Research Hospital created a whole-brain atlas visualizing regions of the brain that send direct inputs to V1 interneurons, a group of cells necessary for movement. The resulting atlas and accompanying three-dimensional interactive website provide a framework to further understand ...
Researchers find compromised indoor air in homes following Marshall Fire
2024-12-23
2021’s Marshall Fire became the most destructive fire in Colorado history, burning nearly 1,000 homes and forcing more than 37,000 residents of Boulder County to evacuate.
New research by scientists at the Cooperative Institute for Research in Environmental Sciences (CIRES) at the University of Colorado Boulder found compromised indoor air quality in homes near the burnt area for weeks after the fire, similar to pollution levels recorded in urban Los Angeles in the 1990s. According to the researchers, the findings can help individuals weigh their options when returning ...
Months after Colorado's Marshall Fire, residents of surviving homes reported health symptoms, poor air quality
2024-12-23
Six months after the Marshall Fire destroyed more than 1,000 houses in Boulder County, Colo., more than half of residents of surviving homes in the area reported physical symptoms— including headaches, sore throats or a strange taste in their mouth— that they attributed to poor air quality, a new CU Boulder study has found.
A companion study showed that the air quality inside one home post-fire equaled that of downtown Los Angeles in the 1990s on a high pollution day, with hazardous gases lingering for weeks.
“Our research suggests that there could be important health impacts for people returning ...
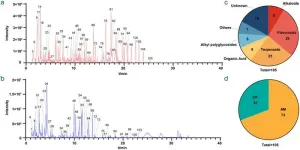
Identification of chemical constituents and blood-absorbed components of Shenqi Fuzheng extract based on UPLC-triple-TOF/MS technology
2024-12-23
Background and objectives
Shenqi Fuzheng (SQ) is a widely used Chinese medicine formula known for its immune-enhancing and Qi-supplementing properties. However, the blood-absorbed components of SQ and their pharmacokinetics remain underexplored. This study aimed to comprehensively analyze the chemical constituents of SQ and investigate their absorption and pharmacokinetic behavior in rat plasma.
Methods
Ultra-performance liquid chromatography-triple quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry (hereinafter referred to as UPLC-Triple-TOF/MS) ...
'Glass fences' hinder Japanese female faculty in international research, study finds
2024-12-23
Glass ceilings comprising gender norms and practices can prevent women from advancing in organizational hierarchies, but glass fences may also be limiting — especially to Japanese female faculty who must navigate strong cultural gender expectations, according to a new study by Megumi Watanabe, associate professor at Hiroshima University.
Watanabe, who teaches family sociology courses at HU’s Department of Integrated Global Studies, found that glass fences — a term coined by sociologist Kathrin Zippel to represent the invisible gendered barriers preventing female researchers ...
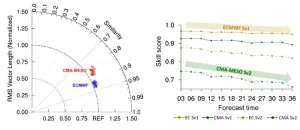
Vector winds forecast by numerical weather prediction models still in need of optimization
2024-12-23
Vector winds play a crucial role in triggering and maintaining convective weather, such as squall lines and typhoons, as well as the effective utilization of wind energy resources.
The mesoscale model of the China Meteorological Administration (CMA-MESO) and the highest-resolution model of the European Center for Medium Weather Forecasting (ECMWF) are widely used in weather forecasting. However, little attention has been paid to the ability of such models to simulate vector winds. Moreover, the modeled wind field is often divided ...
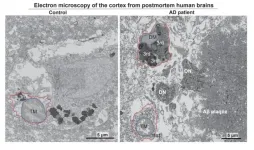
New research identifies key cellular mechanism driving Alzheimer’s disease
2024-12-23
NEW YORK, NY, December 23, 2024 — Researchers with the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) have unveiled a critical mechanism that links cellular stress in the brain to the progression of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The study, published in the journal Neuron, highlights microglia, the brain's primary immune cells, as central players in both the protective and harmful responses associated with the disease.
Microglia, often dubbed the brain's first responders, are now recognized ...
Trends in buprenorphine dispensing among adolescents and young adults in the US
2024-12-23
About The Study: Between 2020 and 2023, buprenorphine dispensing increased among adolescents but decreased among young adults. The increases likely reflect successful outreach to pediatricians, enhanced prescribing through telehealth, and elimination of waiver requirements; these changes might differentially affect young adults, who might be less likely to access health care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Andrew Terranella, MD, MPH, email aqt1@cdc.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.24121)
Editor’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Towards tailor-made heat expansion-free materials for precision technology
New research delves into the potential for AI to improve radiology workflows and healthcare delivery
Rice selected to lead US Space Force Strategic Technology Institute 4
A new clue to how the body detects physical force
Climate projections warn 20% of Colombia’s cocoa-growing areas could be lost by 2050, but adaptation options remain
New poll: American Heart Association most trusted public health source after personal physician
New ethanol-assisted catalyst design dramatically improves low-temperature nitrogen oxide removal
New review highlights overlooked role of soil erosion in the global nitrogen cycle
Biochar type shapes how water moves through phosphorus rich vegetable soils
Why does the body deem some foods safe and others unsafe?
Report examines cancer care access for Native patients
New book examines how COVID-19 crisis entrenched inequality for women around the world
Evolved robots are born to run and refuse to die
Study finds shared genetic roots of MS across diverse ancestries
Endocrine Society elects Wu as 2027-2028 President
Broad pay ranges in job postings linked to fewer female applicants
How to make magnets act like graphene
The hidden cost of ‘bullshit’ corporate speak
Greaux Healthy Day declared in Lake Charles: Pennington Biomedical’s Greaux Healthy Initiative highlights childhood obesity challenge in SWLA
Into the heart of a dynamical neutron star
The weight of stress: Helping parents may protect children from obesity
Cost of physical therapy varies widely from state-to-state
Material previously thought to be quantum is actually new, nonquantum state of matter
Employment of people with disabilities declines in february
Peter WT Pisters, MD, honored with Charles M. Balch, MD, Distinguished Service Award from Society of Surgical Oncology
Rare pancreatic tumor case suggests distinctive calcification patterns in solid pseudopapillary neoplasms
Tubulin prevents toxic protein clumps in the brain, fighting back neurodegeneration
Less trippy, more therapeutic ‘magic mushrooms’
Concrete as a carbon sink
RESPIN launches new online course to bridge the gap between science and global environmental policy
[Press-News.org] Twisted Edison: Bright, elliptically polarized incandescent lightFilaments curling at the micro and nanoscale produce light waves that twirl as they travel