(Press-News.org) Glass ceilings comprising gender norms and practices can prevent women from advancing in organizational hierarchies, but glass fences may also be limiting — especially to Japanese female faculty who must navigate strong cultural gender expectations, according to a new study by Megumi Watanabe, associate professor at Hiroshima University.
Watanabe, who teaches family sociology courses at HU’s Department of Integrated Global Studies, found that glass fences — a term coined by sociologist Kathrin Zippel to represent the invisible gendered barriers preventing female researchers from engaging in international research and collaboration — existed within Japan and were strengthened by cultural norms of the country. She published her findings in Gender, Work & Organization on December 11.
“Japanese female faculty experience similar glass fences as those observed in Western countries,” Watanabe said. “However, cultural factors influence the magnitude of these glass fences. In countries like Japan, where gender norms significantly shape women’s attitudes toward employment, family care-related glass fences can be particularly impactful and difficult to overcome, especially for faculty mothers. Japan in particular is a country with strong norms, where masculine work styles, such as working long hours, and a gendered division of household labor persist.”
Watanabe explained that women are severely underrepresented among faculty and in leadership positions at Japanese universities, and while federal organizations have increased research and support programs to correct the imbalance, the gender differences among Japanese academics participating in international research have received little attention.
“Globally, international research engagement is now an important and sometimes normative component for enhancing academic career opportunities,” Watanabe said. “Despite this trend, gender gaps have been reported worldwide. By analyzing the subjective experiences of international research among female faculty members at a Japanese university, this study extends knowledge on the mechanism of gender inequality reproduction.”
Watanabe interviewed 16 Japanese women in various faculty positions at a research-oriented national university in Japan selected for this case study because of its noted commitment to gender equality.
“Examining glass fences at universities such as this one, which has made various efforts for gender equality at the institutional level, offers valuable insights,” Watanabe said, noting the case study university has won several competitive government grants to promote gender equality, and has various policies and programs, such as on-site childcare and research grants targeted at women, in place.
“These insights may allow researchers and others to recognize the embedded influence of gender on female academics in Japan.”
From the interviews, Watanabe found two behavior mechanisms underpinned whether the faculty participated in international research. In the first, called the constrictive mechanism, women — most frequently mothers — distanced themselves from international research primarily due to family care-related glass fences. With the second, the emancipatory mechanism, women combined international research with child-rearing. She said the narratives of faculty members in the emancipatory group revealed a common thread of higher exposures to more diverse work and lifestyles and they were less likely to be confined to gender norms in their families.
“This paper suggests that unless the dominant gender norms influencing gender inequalities are transformed, it will be difficult to achieve gender equality in Japanese academia,” Watanabe said. “The next step should be to further explore how we can challenge and transform these slow-changing gender norms in Japan. Additionally, it is crucial to critically examine the masculine, work-centered, and increasingly globalized work styles of Japanese faculty, which are incompatible with family care responsibilities that are still primarily carried out by women.”
Next, Watanabe said she plans to expand the scope of her research to encompass a wider range of attributes, including foreign nationalities, and to seek ways to create more inclusive academic research environments.
###
About Hiroshima University
Since its foundation in 1949, Hiroshima University has striven to become one of the most prominent and comprehensive universities in Japan for the promotion and development of scholarship and education. Consisting of 12 schools for undergraduate level and 4 graduate schools, ranging from natural sciences to humanities and social sciences, the university has grown into one of the most distinguished comprehensive research universities in Japan. English website: https://www.hiroshima-u.ac.jp/en
END
'Glass fences' hinder Japanese female faculty in international research, study finds
2024-12-23
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
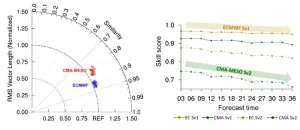
Vector winds forecast by numerical weather prediction models still in need of optimization
2024-12-23
Vector winds play a crucial role in triggering and maintaining convective weather, such as squall lines and typhoons, as well as the effective utilization of wind energy resources.
The mesoscale model of the China Meteorological Administration (CMA-MESO) and the highest-resolution model of the European Center for Medium Weather Forecasting (ECMWF) are widely used in weather forecasting. However, little attention has been paid to the ability of such models to simulate vector winds. Moreover, the modeled wind field is often divided ...
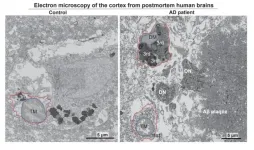
New research identifies key cellular mechanism driving Alzheimer’s disease
2024-12-23
NEW YORK, NY, December 23, 2024 — Researchers with the Advanced Science Research Center at the CUNY Graduate Center (CUNY ASRC) have unveiled a critical mechanism that links cellular stress in the brain to the progression of Alzheimer’s disease (AD). The study, published in the journal Neuron, highlights microglia, the brain's primary immune cells, as central players in both the protective and harmful responses associated with the disease.
Microglia, often dubbed the brain's first responders, are now recognized ...
Trends in buprenorphine dispensing among adolescents and young adults in the US
2024-12-23
About The Study: Between 2020 and 2023, buprenorphine dispensing increased among adolescents but decreased among young adults. The increases likely reflect successful outreach to pediatricians, enhanced prescribing through telehealth, and elimination of waiver requirements; these changes might differentially affect young adults, who might be less likely to access health care.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Andrew Terranella, MD, MPH, email aqt1@cdc.gov.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jama.2024.24121)
Editor’s ...
Emergency department physicians vary widely in their likelihood of hospitalizing a patient, even within the same facility
2024-12-23
Patients in emergency departments who are treated by physicians with a high propensity to admit those they see into the hospital are more likely to be discharged after only a short stay, suggesting a possible unnecessary admission, while they are no less likely to die, new research suggests.
The findings suggest that differences in physicians’ skill or risk aversion may come into play when they make admitting decisions, said Dr. Dan Ly, assistant professor of medicine in the division of general internal medicine and health ...
Firearm and motor vehicle pediatric deaths— intersections of age, sex, race, and ethnicity
2024-12-23
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, U.S. youths ages 0 to 19 years experienced important disparities in firearm and motor vehicle crash fatality rates and increases over time when considering the intersectionality by age group, sex, race, and ethnicity. These findings suggest that a multipronged strategy focused on individual, community, and policy level approaches for specific high-risk groups for each injury mechanism is necessary to address these leading causes of death in U.S. youths.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Lois K. Lee, MD, MPH, email lois.lee@childrens.harvard.edu.
To access the embargoed study: Visit ...
Association of state cannabis legalization with cannabis use disorder and cannabis poisoning
2024-12-23
About The Study: In this longitudinal cohort study, medical cannabis laws were associated with increased cannabis use disorder and cannabis poisoning diagnoses, and recreational cannabis laws were associated with increased cannabis poisoning in adults ages 18 to 64 with employer-sponsored health insurance. Communities with increased access to cannabis may experience increased health care use and costs due to increases in cannabis poisoning and cannabis use disorder, and new clinical and policy interventions are needed to curb these rising diagnoses.
Corresponding ...
Gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, and eclampsia and future neurological disorders
2024-12-23
About The Study: In this study, gestational hypertension, preeclampsia, and eclampsia were associated with an increased risk of new-onset migraine, headache, epilepsy, sleep disorder, or mental fatigue within months to years after giving birth. Guidelines recommend follow-up after delivery for women with gestational hypertension and preeclampsia for their increased risk of cardiovascular disease. At these visits, caregivers should also pay attention to persisting or new-onset of neurological symptoms, since this group of women ...
Adoption of “hospital-at-home” programs remains concentrated among larger, urban, not-for-profit and academic hospitals
2024-12-23
Hospitals that have adopted the Center for Medicare and Medicaid (CMS) “hospital-at-home” program, which serves as an alternative to admission to brick-and-mortar facilities, are concentrated in large, urban, not-for-profit, and academic hospitals, new research suggests.
The findings are among the first to portray the landscape of hospitals participating in this rapidly growing care model, said Dr. Hashem Zikry, a participant in the National Clinician Scholars Program at UCLA and lead author on the paper, which will be published in the peer-reviewed JAMA.
“If CMS’ goal is to continue to expand hospital-at-home, these findings suggest ...
Unlocking the mysteries of the human gut
2024-12-23
When making decisions about nutrition and diet, the focus is often on the potential impacts to the heart or brain; and gut health can frequently end up an afterthought despite a whole industry revolving around probiotics and digestive aids. With its direct link to those two important organs, should gut health be prioritized more?
Imagine an entire civilization of trillions of microorganisms living in harmony inside of your digestive system. This microbiome is unique to each individual and varies greatly based on many genetic and environmental factors. The complexity of gut health can often make diagnosis of maladies difficult, especially when new ...
High-quality nanodiamonds for bioimaging and quantum sensing applications
2024-12-23
Quantum sensing is a rapidly developing field that utilizes the quantum states of particles, such as superposition, entanglement, and spin states, to detect changes in physical, chemical, or biological systems. A promising type of quantum nanosensor is nanodiamonds (NDs) equipped with nitrogen-vacancy (NV) centers. These centers are created by replacing a carbon atom with nitrogen near a lattice vacancy in a diamond structure. When excited by light, the NV centers emit photons that maintain stable spin information ...