(Press-News.org) The near future could see AI assistants that forecast and influence our decision-making at an early stage, and sell these developing “intentions” in real-time to companies that can meet the need – before we even realise we have made up our minds.
This is according to AI ethicists from the University of Cambridge, who say we are at the dawn of a “lucrative yet troubling new marketplace for digital signals of intent”, from buying movie tickets to voting for candidates. They call this the "Intention Economy".
Researchers from Cambridge’s Leverhulme Centre for the Future of Intelligence (LCFI) argue that the explosion in generative AI, and our increasing familiarity with chatbots, opens a new frontier of “persuasive technologies” – one hinted at in recent corporate announcements by tech giants.
“Anthropomorphic” AI agents, from chatbot assistants to digital tutors and girlfriends, will have access to vast quantities of intimate psychological and behavioural data, often gleaned via informal, conversational spoken dialogue.
This AI will combine knowledge of our online habits with an uncanny ability to attune to us in ways we find comforting – mimicking personalities and anticipating desired responses – to build levels of trust and understanding that allow for social manipulation on an industrial scale, say researchers.
“Tremendous resources are being expended to position AI assistants in every area of life, which should raise the question of whose interests and purposes these so-called assistants are designed to serve”, said LCFI Visiting Scholar Dr Yaqub Chaudhary.
“What people say when conversing, how they say it, and the type of inferences that can be made in real-time as a result, are far more intimate than just records of online interactions”
“We caution that AI tools are already being developed to elicit, infer, collect, record, understand, forecast, and ultimately manipulate and commodify human plans and purposes.”
Dr Jonnie Penn, an historian of technology from Cambridge’s LCFI, said: “For decades, attention has been the currency of the internet. Sharing your attention with social media platforms such as Facebook and Instagram drove the online economy.”
“Unless regulated, the intention economy will treat your motivations as the new currency. It will be a gold rush for those who target, steer, and sell human intentions.”
“We should start to consider the likely impact such a marketplace would have on human aspirations, including free and fair elections, a free press, and fair market competition, before we become victims of its unintended consequences.”
In a new Harvard Data Science Review paper, Penn and Chaudhary write that the intention economy will be the attention economy “plotted in time”: profiling how user attention and communicative style connects to patterns of behaviour and the choices we end up making.
“While some intentions are fleeting, classifying and targeting the intentions that persist will be extremely profitable for advertisers,” said Chaudhary.
In an intention economy, Large Language Models or LLMs could be used to target, at low cost, a user’s cadence, politics, vocabulary, age, gender, online history, and even preferences for flattery and ingratiation, write the researchers.
This information-gathering would be linked with brokered bidding networks to maximize the likelihood of achieving a given aim, such as selling a cinema trip (“You mentioned feeling overworked, shall I book you that movie ticket we’d talked about?”).
This could include steering conversations in the service of particular platforms, advertisers, businesses, and even political organisations, argue Penn and Chaudhary.
While researchers say the intention economy is currently an “aspiration” for the tech industry, they track early signs of this trend through published research and the hints dropped by several major tech players.
These include an open call for “data that expresses human intention… across any language, topic, and format” in a 2023 OpenAI blogpost, while the director of product at Shopify – an OpenAI partner – spoke of chatbots coming in “to explicitly get the user’s intent” at a conference the same year.
Nvidia’s CEO has spoken publicly of using LLMs to figure out intention and desire, while Meta released “Intentonomy” research, a dataset for human intent understanding, back in 2021.
In 2024, Apple’s new “App Intents” developer framework for connecting apps to Siri (Apple’s voice-controlled personal assistant), includes protocols to “predict actions someone might take in future” and “to suggest the app intent to someone in the future using predictions you [the developer] provide”.
“AI agents such as Meta’s CICERO are said to achieve human level play in the game Diplomacy, which is dependent on inferring and predicting intent, and using persuasive dialogue to advance one’s position,” said Chaudhary.
“These companies already sell our attention. To get the commercial edge, the logical next step is to use the technology they are clearly developing to forecast our intentions, and sell our desires before we have even fully comprehended what they are.”
Penn points out that these developments are not necessarily bad, but have the potential to be destructive. “Public awareness of what is coming is the key to ensuring we don’t go down the wrong path,” he said.
END
Coming AI economy will sell your decisions before you take them, researchers warn
2024-12-30
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe makes history with closest pass to Sun
2024-12-27
Operations teams have confirmed NASA’s mission to “touch” the Sun survived its record-breaking closest approach to the solar surface on Dec. 24, 2024.
Breaking its previous record by flying just 3.8 million miles above the surface of the Sun, NASA’s Parker Solar Probe hurtled through the solar atmosphere at a blazing 430,000 miles per hour — faster than any human-made object has ever moved. A beacon tone received late on Dec. 26 confirmed the spacecraft had made it through the encounter safely and is operating normally.
This pass, the ...
Are we ready for the ethical challenges of AI and robots?
2024-12-27
Fukuoka, Japan―Artificial intelligence (AI) and AI-enabled robots are becoming a bigger part of our daily lives. Real-time, flexible interactions between humans and robots are no longer just science fiction. As robots become smarter and more human-like in both behavior and appearance, they are transforming from mere tools to potential partners and social entities.
This rapid evolution presents significant challenges to our legal and ethical frameworks, including concerns about privacy, safety, and regulation in the context of AI and robots. The Cambridge Handbook of the Law, Policy, ...
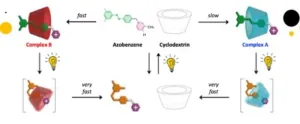
Nanotechnology: Light enables an "impossibile" molecular fit
2024-12-27
Exploiting an ingenious combination of photochemical (i.e., light-induced) reactions and self-assembly processes, a team led by Prof. Alberto Credi of the University of Bologna has succeeded in inserting a filiform molecule into the cavity of a ring-shaped molecule, according to a high-energy geometry that is not possible at thermodynamic equilibrium. In other words, light makes it possible to create a molecular “fit” that would otherwise be inaccessible.
“We have shown that by administering ...
Estimated vaccine effectiveness for pediatric patients with severe influenza
2024-12-27
About The Study: The findings from this case-control study suggest that children should receive influenza vaccination to protect against all levels of severe influenza illness.
Corresponding Authors: To contact the corresponding authors, email Kelsey M. Sumner, PhD, MSPH (rhq3@cdc.gov) and Samantha M. Olson, MPH (ylz8@cdc.gov).
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.52512)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, conflict of interest and financial disclosures, ...
Changes to the US preventive services task force screening guidelines and incidence of breast cancer
2024-12-27
About The Study: In this cohort study, in situ breast cancer decreased since 2009, consistent with decreasing use of screening mammography since the 2009 U.S. Preventive Services Task Force guideline changes, but this decrease did not appear to have translated to more advanced breast cancer stages at diagnosis or decreases in the proportion of cases treated with partial mastectomy. Further research is needed to understand the long-standing increase in localized invasive breast cancer and the decrease in regional invasive breast cancer observed during the past 20 years in the context of decreased breast ...
Urgent action needed to protect the Parma wallaby
2024-12-27
The creation of more fox-free safe havens and greater collaboration between government and landowners is needed to ensure the survival of a species of wallaby, an expert from The Australian National University (ANU) argues.
The Parma wallaby, also known as the white-throated wallaby, is listed as a vulnerable species in Australia, while the International Union for Conservation of Nature (IUCN) classifies it as Near Threatened. The marsupial is found along the Great Dividing Range in northern New South Wales.
According to ANU Professor George Wilson, who is a co-author of a new ...
Societal inequality linked to reduced brain health in aging and dementia
2024-12-27
Researchers from Trinity College Dublin have collaborated with international partners to explore if societal inequality affects our brain. Their research paper is published in Nature Aging today, [Friday, December 27th] by an international team of researchers from the Multipartner Consortium to expand dementia research in Latin America (ReDLat), the Latin American Brain Health Institute (BrainLat), the GIobal Brain Health Institute (GBHI) at Trinity College Dublin, and other centres across the globe. The study reveals a direct link between structural inequality—such as socioeconomic disparities measured by a country-level index ...
Singles differ in personality traits and life satisfaction compared to partnered people
2024-12-26
Although being married or in a long-term relationship is often seen as the norm, more people are staying single for life. But singlehood can bring economic and medical disadvantages, especially as people get older and may become more reliant on others.
New research in Psychological Science reveals that lifelong singles have lower scores on life satisfaction measures and different personality traits compared to partnered people, findings that point to the need for both helpful networks and ways to create such networks that are better catered to single people.
“When there are ...
President Biden signs bipartisan HEARTS Act into law
2024-12-26
WASHINGTON, D.C., December 26, 2024 — President Biden earlier this week signed into law the bipartisan Cardiomyopathy Health Education, Awareness, Research and Training in Schools (HEARTS) Act, which will help ensure students and staff in schools nationwide are prepared to respond to a cardiac emergency. The bipartisan legislation unanimously passed the U.S. House of Representatives in September and the U.S. Senate earlier this month.
The American Heart Association, which is celebrating 100 years of lifesaving service as the world’s leading voluntary organization focused on heart and brain health, strongly supports this legislation as part of its goal to double the survival ...
Advanced DNA storage: Cheng Zhang and Long Qian’s team introduce epi-bit method in Nature
2024-12-26
Why it matters:
In the era of big data, global mass data flow has presented data storage systems with a looming challenge. As DNA has incredibly high storage density – a single gram of DNA can store 215,000 terabytes, the same size as 10 million hours of high-definition video (Imburgia & Nivala, 2024)– and long-term stability, it is an attractive medium for data storage. However, conventional DNA storage relies on de novo synthesis, where nucleotides are added one by one in a fixed order, ...