(Press-News.org)
University of Iowa researchers are recommending all patients be surveyed about their physical activity levels, after a new study underscores the link between physical activity and chronic disease.
The study, led by Lucas Carr, associate professor in the Department of Health and Human Physiology, examined responses from more than 7,000 patients at University of Iowa Health Care Medical Center who noted their level of physical activity in a questionnaire.
From patients’ answers to the questionnaire, the researchers found that those who reported the highest level of physical activity — meaning they exercised moderately to vigorously at least 150 minutes per week — were at statistically significant lower risk of having 19 chronic conditions, including cardiovascular disease, cancer, respiratory disease, and diabetes.
The findings further suggest patients who are least active — meaning they reported little to no exercise in a given week — are at increased risk to develop a chronic disease.
Based on those results, the Iowa researchers also recommend health care systems provide information on health and wellness services for physically inactive patients who are at most risk.
“In our health care environment, there's no easy pathway for a doctor to be reimbursed for helping patients become more physically active,” says Carr, the study’s corresponding author. “And so, for these patients, many of whom report insufficient activity, we need options to easily connect them with supportive services like exercise prescriptions and/or community health specialists.”
Most hospitals in the United States do not ask patients about their physical activity, and no hospital system in the Midwest has done so, according to the researchers. In this study, Carr partnered with Britt Marcussen, a family medicine physician in UI Health Care, to offer the questionnaire to patients visiting for annual wellness exam appointments. The study period was from November 2017 to December 2022.
The Exercise Vital Sign survey, as the questionnaire is called, asked patients two questions that they answered on a tablet:
“On average, how many days per week do you engage in moderate to vigorous exercise (like a brisk walk)?” (0-7 days)
“On average, how many minutes do you engage in exercise at this level?”
Carr and his team propose making the survey available to all patients.
“This two-question survey typically takes fewer than 30 seconds for a patient to complete, so it doesn’t interfere with their visit. But it can tell us a whole lot about that patient’s overall health,” Carr says.
The researchers also compared results from patients who completed the surveys with more than 33,000 patients who weren’t offered the survey in other areas of the hospital. The researchers found patients who took the survey were younger and in better health than the patient population who weren’t given the questionnaire, based on analyzing all patients’ electronic medical records.
While the link between physical activity and reduced risk of chronic disease has been known, the researchers say the study underscores the value of surveying patients about their physical activity levels.
“We believe this finding is a result of those patients who take the time to come in for annual wellness exams also are taking more time to engage in healthy behaviors, such as being physically active,” Carr says.
In a related study, published this month in the Journal of Physical Activity and Health, Carr’s team found that when healthcare providers billed for providing exercise counseling to patients, those invoices were reimbursed by insurance providers nearly 95 percent of the time.
“Our findings suggest the recommended physical activity billing codes are reimbursed at a high rate when providers submit them for reimbursement, which reinforces the idea to make physical activity surveys and counseling services available,” Carr says.
Cole Chapman, assistant professor in the College of Pharmacy, is the first author on the study. Chapman, who joined the Pharmacy faculty in 2019 after earning bachelor’s and doctoral degrees at Iowa, collected and analyzed the data from the patients’ electronic medical records.
Marcussen and Mary Schroeder, associate professor in the Department of Pharmacy Practice and Science in the College of Pharmacy, are study co-authors.
The study, “Screening Patients for Physical Inactivity Helps Identify Patients at Risk for Cardiometabolic and Chronic Diseases,” was published online [INSERT ONLINE PUB DATE HERE] in Preventing Chronic Disease, a journal of the U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention.
UI Health Care Stead Family Children’s Hospital funded the research.
END
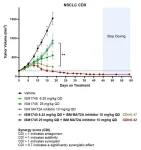
Since 2021, Insilico Medicine has successfully nominated 22 preclinical candidates (PCCs) with the help of its proprietary Pharma.AI platform, among which 5 were nominated just the year of 2024.
The novel scaffold of ISM1745 is based on de novo generation results of Insilico’s Chemistry42, the generative AI platform combining more than 40 generative models.
With in vivo anti-tumor activity validated in multiple cancer models, the candidate compound showed robust in vivo efficacy as monotherapy as well as combination potential with chemotherapies, targeted agents including MAT2A inhibitor, and immunotherapies.
CAMBRIDGE, ...
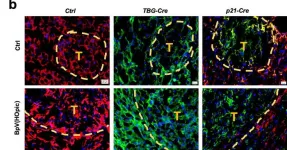
Scientists at University of California San Diego School of Medicine have shed new light on the development of liver cancer, the sixth most frequently diagnosed cancer and fourth leading cause of cancer deaths worldwide. The study, published in Nature, reveals a complex interplay between cellular metabolism and DNA damage that drives the progression of fatty liver disease to cancer. The findings suggest new paths forward for preventing and treating liver cancer and have significant implications on our understanding of cancer’s origin and the effects of diet on our DNA.
The incidence of the most common form of liver cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), has grown by 25-30% in the past ...
Inflammation is a crucial part of the body’s defense mechanism, playing a key role in fighting infections and repairing tissue damage. Basophils, a type of immune cell that makes up less than 1% of white blood cells, have recently emerged as critical players in triggering allergic responses by releasing pro-inflammatory cytokines like IL-4. Despite the established role of basophils in inflammation, the molecular mechanisms controlling their cytokine production have remained unclear.
To address this gap, a group of researchers from Institute of Science Tokyo, led by Professor Kensuke Miyake, conducted a study to explore the role of tristetraprolin ...
Researchers are aiming to bring the magic of playing music in person to the virtual world.
The Joint Active Music Sessions (JAMS) platform, created at the University of Birmingham, uses avatars created by individual musicians and shared with fellow musicians to create virtual concerts, practice sessions, or enhance music teaching.
Dr Massimiliano (Max) Di Luca from the University of Birmingham explains: “A musician records themselves and sends the video to another musician. The software creates a responsive avatar ...
One or two doses of psilocybin, a compound found in psychedelic mushrooms, may improve the mental health of cancer patients when accompanied by psychotherapy, a new report suggests. A second new study found that treatment with psilocybin resulted in lasting, positive personality changes in patients with alcohol use disorder.
The first report’s findings were published online Oct. 7 in the journal Nature Mental Health, and the second published online Jan. 1 in a special edition of The American Journal of Psychiatry focused on psilocybin research.
In the first study, a team of experts at NYU Langone Health found that psilocybin accompanied by psychotherapy significantly reduced anxiety, ...
To many, Vice President Kamala Harris’s loss in the 2024 presidential election was a sobering reminder of a larger and continuous gender gap across leadership positions in not only government, but also in business, higher education, and the military. A majority of Americans recognize the inadequacy of female representation in leadership, and the news media often portray women’s underrepresentation in these roles—but it nonetheless persists.
Recognizing that news coverage may have influence in forming attitudes and in driving ...
A new international study led by researchers at Karolinska Institutet in Sweden shows that AI-based models can outperform human experts at identifying ovarian cancer in ultrasound images. The study is published in Nature Medicine.
“Ovarian tumours are common and are often detected by chance,” says Professor Elisabeth Epstein at the Department of Clinical Science and Education, Södersjukhuset (Stockholm South General Hospital), at Karolinska Institutet and senior consultant at the hospital’s Department of Obstetrics and Gynecology. “There is a serious shortage of ultrasound experts in many parts of the world, which has ...
Researchers from the Bakkers group at the Hubrecht Institute have successfully repaired damaged mouse hearts using a protein from zebrafish. They discovered that the protein Hmga1 plays a key role in heart regeneration in zebrafish. In mice, this protein was able to restore the heart by activating dormant repair genes without causing side effects, such as heart enlargement. This study, supported by the Dutch Heart Foundation and Hartekind Foundation, marks an important step toward regenerative therapies to prevent heart failure. The findings were published in Nature Cardiovascular Research on January 2, 2025.
After a heart attack, the human heart loses millions of muscle cells that cannot ...
Artificial intelligence tools such as ChatGPT have been touted for their promise to alleviate clinician workload by triaging patients, taking medical histories and even providing preliminary diagnoses.
These tools, known as large-language models, are already being used by patients to make sense of their symptoms and medical tests results.
But while these AI models perform impressively on standardized medical tests, how well do they fare in situations that more closely mimic the real world?
Not that great, according to the findings of a new study led by researchers at Harvard Medical School and Stanford University.
For their analysis, published Jan. 2 in Nature ...
Fighting cancer can seem like a deadly game of chance. While some patients may respond well to certain treatments, others might not be as fortunate. Doctors and scientists have long struggled to explain why. Now, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory (CSHL) Assistant Professor Katherine Alexander and University of Pennsylvania Professor Shelley Berger have found a possible source of this variability in clear cell renal cell carcinoma (ccRCC)—the most common kidney cancer diagnosed in adults.
Alexander ...