(Press-News.org) Irvine, Calif., Jan. 7, 2025 – A study led by the University of California, Irvine has found cardiovascular conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes, which are known to contribute to brain blood vessel damage in younger populations, not to be associated with an increased risk of such harm in individuals 90 and older.
The work, published online today in the journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association, suggests that the relationship among blood pressure, vascular health and brain aging is more complex than previously thought.
“For decades, we’ve known that factors like high blood pressure and diabetes can injure blood vessels in the brain, increasing the risk for cognitive decline and dementia. However, our research found that these patterns may change as people age,” said corresponding author Dr. Ravi Rajmohan, UC Irvine clinical instructor of neurology. “Even more intriguing, the use of blood pressure-lowering medication in this 90-plus group was linked to a lower likelihood of specific types of brain damage.”
Team members analyzed the relationship between cardiovascular-related changes in the brain and self-reported vascular risk factors or use of heart-related medications by examining data from 267 participants in the National Institute on Aging’s 90+ Study, one of the largest and most comprehensive research projects on the oldest-old population. They applied statistical models that accounted for age, sex and education and found that the presence of brain changes was not linked to traditional risk factors like high blood pressure or diabetes.
In addition, they discovered that certain medications showed potential proactive effects. Diuretics were linked to a lower likelihood of atherosclerosis, commonly called “hardening of the arteries,” and beta blockers and vasodilators were associated with reduced odds of cerebral amyloid angiopathy, the buildup of a type of proteins in brain blood vessels.
“Our findings challenge the idea that traditional vascular risk factors are always harmful to brain health in the 90-plus population,” Rajmohan said. “Our findings may reflect the effectiveness of treatment for those conditions, or they could be influenced by survival bias, as individuals with untreated or severe risk factors may not live into their 90s. Further research is needed to explore whether blood pressure-lowering medications could directly reduce the risk of brain blood vessel damage and dementia under specific circumstances. Such knowledge could lead to more personalized advice for managing blood pressure and improving brain health outcomes.”
Team members also included Dr. Claudia Kawas, professor of neurology and neurobiology & behavior; Maria Corrada, professor in residence of neurology; Annlia Paganini Hill, project scientist in neurology; and biochemistry graduate student Joey Wong – all from UC Irvine – as well as Dr. Thomas Montine, chair pathology at Stanford University; Zeinah Al-Darsani, epidemiology and biostatistics graduate student at Temple University’s College of Public Health; and Chu-Ching Ho, computer science graduate student at the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign.
This work was supported by the National Institute on Aging under grant AG021055 and the Alzheimer’s Disease Research Consortium under grant P30AGO66519.
About the University of California, Irvine: Founded in 1965, UC Irvine is a member of the prestigious Association of American Universities and is ranked among the nation’s top 10 public universities by U.S. News & World Report. The campus has produced five Nobel laureates and is known for its academic achievement, premier research, innovation and anteater mascot. Led by Chancellor Howard Gillman, UC Irvine has more than 36,000 students and offers 224 degree programs. It’s located in one of the world’s safest and most economically vibrant communities and is Orange County’s second-largest employer, contributing $7 billion annually to the local economy and $8 billion statewide. For more on UC Irvine, visit www.uci.edu.
Media access: Radio programs/stations may, for a fee, use an on-campus studio with a Comrex IP audio codec to interview UC Irvine faculty and experts, subject to availability and university approval. For more UC Irvine news, visit news.uci.edu. Additional resources for journalists may be found at https://news.uci.edu/media-resources.
END
UC Irvine-led study challenges traditional risk factors for brain health in the oldest-old
Findings highlight potential significant role of certain medications in avoiding dementia
2025-01-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Study shows head trauma may activate latent viruses, leading to neurodegeneration
2025-01-07
Concussions and repetitive head trauma in sports like football and boxing, once accepted as an unpleasant consequence of intense athletic competition, are now recognized as serious health threats. Of particular concern is the connection between head injuries and neurodegenerative diseases such as chronic traumatic encephalopathy, Alzheimer’s disease, and Parkinson’s disease, prompting sports governing bodies to adjust protective equipment and rules of play to minimize the risk.
Researchers at Tufts University and Oxford University have now uncovered mechanisms that may ...
Advancements in neural implant research enhance durability
2025-01-07
Crucial research on brain diseases
Neural implants are crucial in order to study the brain and develop treatments for patients with diseases like Parkinson's or clinical depression. Neural implants electrically stimulate, block, or record signals from neurons or neural networks in the brain. For study and treatment, and specifically for chronic use, these neural implants must be durable.
"Miniaturized neural implants have enormous potential to transform healthcare, but their long-term stability in the body ...
SwRI models Pluto-Charon formation scenario that mimics Earth-Moon system
2025-01-07
SAN ANTONIO — January 7, 2025 —A NASA postdoctoral researcher at Southwest Research Institute has used advanced models that indicate that the formation of Pluto and Charon may parallel that of the Earth-Moon system. Both systems include a moon that is a large fraction of the size of the main body, unlike other moons in the solar system. The scenario also could support Pluto’s active geology and possible subsurface ocean, despite its location at the frozen edge of the solar system.
“We ...
Researchers identify public policies that work to prevent suicide
2025-01-07
An analysis led by New York University researchers determines which public policies effectively prevent suicide deaths in the United States. But it’s not just policies that limit firearms and expand access to health care—many economic and social policies that are not explicitly focused on mental health can also prevent suicide, according to their article published in the Annual Review of Public Health.
“Most of the policies that demonstrate evidence do not mention suicide and were not passed to prevent ...
Korea University College of Medicine and Yale Univeristy co-host forum on Advancing Healthcare through Data and AI Innovations
2025-01-07
Korea University College of Medicine and Yale Univeristy Co-Host Forum
on Advancing Healthcare through Data and AI Innovations
On October 2nd (Wednesday), Korea University College of Medicine (Dean: Pyun Sung-Bom) hosted a forum titled “Advancing Healthcare through Innovations in Data and AI in Clinical Informatics and Natural Language Processing” in the 6th-floor lecture hall of the First Medical Building.
As part of Korea University’s 120th-anniversary celebration, this annual joint forum with Yale University has been held since 2023. This year’s ...
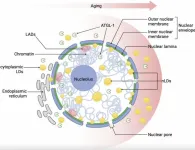
Nuclear lipid droplets: Key regulators of aging and nuclear homeostasis
2025-01-07
“A consistent feature of aging across diverse species is the progressive accumulation of lipid droplets (nLDs) within the nuclear compartment, which disrupts nuclear architecture and functionality.”
BUFFALO, NY- January 7, 2025 – A new research perspective was published in Aging (listed by MEDLINE/PubMed as “Aging (Albany NY)” and “Aging-US” by Web of Science) Volume 16, Issue 22 on December 9, 2024, entitled “Nuclear lipid droplets: a novel regulator of nuclear homeostasis ...
Driving autonomous vehicles to a more efficient future
2025-01-07
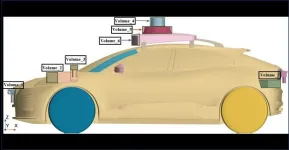
WASHINGTON, Jan. 7, 2025 – Thanks to the rapid progress of information technology and artificial intelligence, autonomous vehicles (AVs) have been taking off. In fact, AV technology is now advanced enough that the vehicles are being used for logistics delivery and low-speed public transportation.
While most research has focused on control algorithms to heighten safety, less attention has been directed at improving aerodynamic performance, which is essential for lowering energy consumption and extending driving range. As a result, aerodynamic drag issues have ...
Severe maternal morbidity among pregnant people with opioid use disorder enrolled in Medicaid
2025-01-07
About The Study: This cross-sectional study of pregnant people enrolled in Medicaid found that the rate of opioid use disorder among this group was more than twice as high as previous estimates. Pregnant people with opioid use disorder face a disproportionately high risk of severe maternal morbidity, particularly those who enroll in Medicaid later in pregnancy. Targeted interventions that facilitate early Medicaid enrollment and coverage continuity may be needed to reduce the burden of adverse outcomes in this group.
Corresponding ...
Macronutrients in human milk exposed to antidepressant and anti-inflammatory medications
2025-01-07
About The Study: In this cross-sectional study, some maternal medications were associated with lower levels of protein and fat in milk, which could impose health risks for breastfed infants. Other factors that could influence macronutrient levels need to be clarified before the clinical implications of these findings can be confirmed.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Essi Whaites Heinonen, MD, PhD, email essi.heinonen@ki.se.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2024.53332)
Editor’s Note: Please ...
Exploring the eco-friendly future of antibiotic particles
2025-01-07
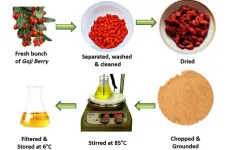
WASHINGTON, Jan. 7, 2025 – As the search for sustainability permeates all fields, researchers are turning to a unique organic source for creating antibacterial silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) – the humble goji berry.
Goji berries are a ubiquitous superfood known for a multitude of health benefits, including their antibiotic properties. In research published in AIP Advances, by AIP Publishing, researcher Kamran Alam from Sapienza University of Rome along with others from NED University of Engineering and Technology and King Saud University found an effective way to harvest ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
New knowledge on heritability paves the way for better treatment of people with chronic inflammatory bowel disease
Under the Lens: Microbiologists Nicola Holden and Gil Domingue weigh in on the raw milk debate
Science reveals why you can’t resist a snack – even when you’re full
Kidney cancer study finds belzutifan plus pembrolizumab post-surgery helps patients at high risk for relapse stay cancer-free longer
Alkali cation effects in electrochemical carbon dioxide reduction
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
[Press-News.org] UC Irvine-led study challenges traditional risk factors for brain health in the oldest-oldFindings highlight potential significant role of certain medications in avoiding dementia