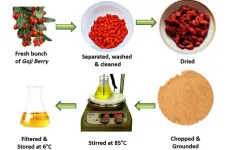
(Press-News.org) WASHINGTON, Jan. 7, 2025 – As the search for sustainability permeates all fields, researchers are turning to a unique organic source for creating antibacterial silver nanoparticles (Ag-NPs) – the humble goji berry.
Goji berries are a ubiquitous superfood known for a multitude of health benefits, including their antibiotic properties. In research published in AIP Advances, by AIP Publishing, researcher Kamran Alam from Sapienza University of Rome along with others from NED University of Engineering and Technology and King Saud University found an effective way to harvest silver nanoparticles from these berries.
“Silver nanoparticles are responsible for disrupting the cell membrane structure, which can generate reactive oxygen species used for inhibiting bacterial growth,” explained Alam.
Silver nanoparticles can be generated using a number of chemical techniques, but green solutions that use biological sources like fruit or leaf extracts are preferred because they save on energy and are nontoxic, nonhazardous, and biologically compatible with humans.
In this interdisciplinary undertaking, Alam and researchers demonstrated a technique for the synthesis of silver nanoparticles using store-bought goji berries.
“Goji berries are easily and locally available in the botanic garden and are rich in bioactive compounds that have natural reducing and stabilizing agents, eliminating the need for additional capping agents during processing,” Alam said.
Alam and the team created silver nanoparticles by drying, grinding, and then filtering the goji berries to create an extract. Then, they added chemical silver nitrate (AgNO3) and reduced the solution.
Using visualization techniques such as X-ray diffraction, Ultraviolet-Visible (UV-Vis) Spectroscopy, and Fourier Transform Infrared (FT-IR) Spectroscopy, the team confirmed the presence of silver nanoparticles. The nanoparticles were also viewed under a microscope and tested for their antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus, a gram-positive bacterium that causes staph infections among other diseases.
In the future, Alam plans to study the cellular toxicity and biocompatibility of the nanoparticles synthesized from these berries, which could positively contribute to biomedical research.
“This is a simple and straightforward synthesis method which does not need additional chemicals or complex equipment and can be scaled up for industrial applications,” he said.
###
The article “Ecofriendly synthesis of silver nanoparticles using metallic solution-based goji berry extract for their antibacterial properties” is authored by Abdul Rauf Jamali, Waseem Khan, Salahuddin Khan, Ahmed Ahmed Ibrahim, and Kamran Alam. It will appear in AIP Advances on Jan. 7, 2025 (DOI: 10.1063/5.0237276). After that date, it can be accessed at https://doi.org/10.1063/5.0237276.
ABOUT THE JOURNAL
AIP Advances is an open access journal publishing in all areas of physical sciences—applied, theoretical, and experimental. The inclusive scope of AIP Advances makes it an essential outlet for scientists across the physical sciences. See https://pubs.aip.org/aip/adv.
###
END
Exploring the eco-friendly future of antibiotic particles
How goji berries can be used to create silver nanoparticles
2025-01-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Can you steam away prostate cancer?
2025-01-07
LOS ANGELES — Steam eliminates wrinkles and germs, but can it destroy cancer cells too?
Keck Medicine of USC is participating in a national, multisite clinical trial examining if a water vapor system that uses small, targeted amounts of steam to kill cancer cells is a safe and effective treatment for prostate cancer.
Researchers hope that steam may offer patients a less invasive way of controlling or curing cancer than currently exists.
“The most common therapies for prostate cancer often cause life-altering side effects, and we are investigating if this new treatment may not only treat the cancer, ...
The CTAO becomes a European Research Infrastructure Consortium
2025-01-07
Bologna, Italy, 7 January 2025 – On January 7, 2025, the European Commission established the Cherenkov Telescope Array Observatory (CTAO) as a European Research Infrastructure Consortium (ERIC), furthering its mission to become the world’s largest and most powerful observatory for gamma-ray astronomy. The creation of the CTAO ERIC will enable the Observatory's construction to advance rapidly and provide a framework for distributing its data worldwide, significantly accelerating its progress toward scientific discovery.
“The ERIC will streamline the construction and operation ...
Introduction to science journalism guide published in Albanian
2025-01-07
A new guide aimed at helping aspiring science journalists in Albania to cover scientific topics has been published.
The guide has information about science journalism efforts in the country, and provides ideas for specific topics and how to approach them from a scientific and journalistic perspective. It also has links to relevant international sources for further study and advice.
The guide was written by Altin Raxhimi, an experienced journalist from Albania who has reported for print, digital media and television on topics ranging from war to food ...
Official launch of Global Heat Health Information Network Southeast Asia Hub at NUS Medicine
2025-01-07
The Heat Resilience & Performance Centre (HRPC) at the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore (NUS Medicine) has been officially designated as the Global Heat Health Information Network (GHHIN) Southeast Asia Hub, a recognition that underscores its leading role in advancing heat resilience. This designation highlights the Centre's expertise in addressing the growing challenges of heat-related health risks in the region. With this appointment, the Centre is poised to play a pivotal role in working with the region to shape strategies, research, and policies aimed at mitigating ...
Childhood smoking increases a person’s risk of developing COPD
2025-01-07
Miami (January 7, 2025) – Childhood smoking before age 15 increases a person’s risk of developing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), according to a new study. The study is published in the November 2024 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
COPD is an inflammatory lung disease, comprising several conditions, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, and can be caused by genetics and irritants like smoke or pollution. The disease affects more than 30 million Americans and is the ...
MD Anderson and Myriad Genetics form strategic alliance to evaluate clinical utility of Myriad’s molecular residual disease assay
2025-01-07
HOUSTON and SALT LAKE CITY ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and Myriad Genetics, Inc. today announced a five-year strategic alliance to accelerate the clinical evaluation and development of Myriad’s molecular residual disease (MRD) assay.
This strategic alliance brings together the longstanding oncology diagnostic experience of Myriad Genetics and the clinical and translational research expertise of MD Anderson to create a portfolio of studies to evaluate the clinical validity and utility of Myriad’s Precise MRD.
“We look forward to working ...
Method can detect harmful salts forming in nuclear waste melters
2025-01-07
PULLMAN, Wash. – A new way to identify salts in nuclear waste melters could help improve clean-up technology, including at the Hanford Site, one of the largest, most complex nuclear waste clean-up sites in the world.
Reporting in the journal Measurement, Washington State University researchers used two detectors to find thin layers of sulfate, chloride and fluoride salts during vitrification, a nuclear waste storage process that involves converting the waste into glass. The formation of salts can be problematic for waste processing and storage.
“We were able to demonstrate a technique ...
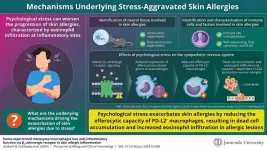
Researchers reveal how psychological stress may aggravate skin allergies
2025-01-07
Psychological stress is known to exacerbate skin allergies, but the underlying molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood. Recent studies using a mouse model of immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated cutaneous allergic inflammation (IgE-CAI) suggest that stress may disrupt immune functions, thereby worsening allergic symptoms by interfering with the body's inflammatory responses. IgE-CAI is characterized by swelling and infiltration of eosinophils, a type of immune cell involved in allergic inflammation, at the affected site.
In a recent study, a research group led by Associate Professor Soichiro Yoshikawa, Professor Kenji Takamori, and Professor Sachiko Miyake ...
International partnership aims to provide first-class osteopathy training
2025-01-07
The University of Plymouth and International Osteopathic Education (IOE) have formed a new partnership that will offer first-class training to aspiring osteopaths from across the world.
The organisations – both renowned internationally for quality healthcare training – have developed a rigorous and comprehensive Master of Osteopathic Medicine (MOstM) programme.
Those enrolling on the programme, which is being validated and awarded by the University of Plymouth, will engage in five years of flexible study.
They will benefit from clinical teaching in the IOE educational clinic in Bordeaux, ...
Reducing irrigation for livestock feed crops is needed to save Great Salt Lake, study argues
2025-01-07
CORVALLIS, Ore. – The Great Salt Lake has lost more than 15 billion cubic yards of water over the past three decades, is getting shallower at the rate of 4 inches a year, and an analysis of its water budget suggests reducing irrigation is necessary for saving it.
The study published today in Environmental Challenges shows that 62% of the river water bound for the lake is diverted for human uses, with agricultural activities responsible for nearly three-quarters of that percentage.
“The research highlights the alarming role of water consumption for feeding livestock in driving the lake’s rapid depletion,” said co-author ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
A comprehensive review charts how psychiatry could finally diagnose what it actually treats
Thousands of genetic variants shape epilepsy risk, and most remain hidden
First comprehensive sex-specific atlas of GLP-1 in the mouse brain reveals why blockbuster weight-loss drugs may work differently in females and males
When rats run, their gut bacteria rewrite the chemical conversation with the brain
Movies reconstructed from mouse brain activity
Subglacial weathering may have slowed Earth's escape from snowball Earth
Simple test could transform time to endometriosis diagnosis
Why ‘being squeezed’ helps breast cancer cells to thrive
Mpox immune test validated during Rwandan outbreak
Scientists pinpoint protein shapes that track Alzheimer’s progression
Researchers achieve efficient bicarbonate-mediated integrated capture and electrolysis of carbon dioxide
Study reveals ancient needles and awls served many purposes
Key protein SYFO2 enables 'self-fertilization’ of leguminous plants
AI tool streamlines drug synthesis
Turning orchard waste into climate solutions: A simple method boosts biochar carbon storage
New ACP papers say health care must be more accessible and inclusive for patients and physicians with disabilities
Moisture powered materials could make cleaning CO₂ from air more efficient
Scientists identify the gatekeeper of retinal progenitor cell identity
American Indian and Alaska native peoples experience higher rates of fatal police violence in and around reservations
Research alert: Long-read genome sequencing uncovers new autism gene variants
Genetic mapping of Baltic Sea herring important for sustainable fishing
In the ocean’s marine ‘snow,’ a scientist seeks clues to future climate
Understanding how “marine snow” acts as a carbon sink
In search of the room temperature superconductor: international team formulates research agenda
Index provides flu risk for each state
Altered brain networks in newborns with congenital heart disease
Can people distinguish between AI-generated and human speech?
New robotic microfluidic platform brings ai to lipid nanoparticle design
COSMOS trial results show daily multivitamin use may slow biological aging
Immune cells play key role in regulating eye pressure linked to glaucoma
[Press-News.org] Exploring the eco-friendly future of antibiotic particlesHow goji berries can be used to create silver nanoparticles