(Press-News.org) A new guide aimed at helping aspiring science journalists in Albania to cover scientific topics has been published.
The guide has information about science journalism efforts in the country, and provides ideas for specific topics and how to approach them from a scientific and journalistic perspective. It also has links to relevant international sources for further study and advice.
The guide was written by Altin Raxhimi, an experienced journalist from Albania who has reported for print, digital media and television on topics ranging from war to food to academia. Raxhimi holds a degree in journalism from the University of Tirana. He was a Nieman Fellow at Harvard University.
Raxhimi said: "I hope the guide will be able to show how seducing, enlightening and useful the reporting about science is, and encourage more journalists writing in Albanian to explore it."
The guide was published by the Balkan Network of Science Journalists and the European Federation for Science Journalism and is available on the BNSJ and EFSJ websites.
Publication of the guide was made possible through the support of EurekAlert!, a science news release platform operated by the non-profit American Association for the Advancement of Science (AAAS).
"EurekAlert! is thrilled to support the latest in a series of science journalism guides from the Balkans and Eastern Europe," said Brian Lin, director of editorial content strategy at EurekAlert!. "The passion and dedication of journalists in this region in cultivating the next generation of talents is inspiring."
The initiative has previously brought science journalism guides to life in Croatian, Slovenian, Hungarian, and Romanian.
"We hope this latest guide will help future generations of science journalists in both Albania and Kosovo," said Mićo Tatalović, a board member of the European Federation for Science Journalism, who has been coordinating the project. “It is, to our knowledge, the only such guide in the Albanian language, and we hope that the advice it offers -- combining local knowledge and best international practices -- will be useful to science writers in the region."
END
Introduction to science journalism guide published in Albanian
2025-01-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Official launch of Global Heat Health Information Network Southeast Asia Hub at NUS Medicine
2025-01-07
The Heat Resilience & Performance Centre (HRPC) at the Yong Loo Lin School of Medicine, National University of Singapore (NUS Medicine) has been officially designated as the Global Heat Health Information Network (GHHIN) Southeast Asia Hub, a recognition that underscores its leading role in advancing heat resilience. This designation highlights the Centre's expertise in addressing the growing challenges of heat-related health risks in the region. With this appointment, the Centre is poised to play a pivotal role in working with the region to shape strategies, research, and policies aimed at mitigating ...
Childhood smoking increases a person’s risk of developing COPD
2025-01-07
Miami (January 7, 2025) – Childhood smoking before age 15 increases a person’s risk of developing chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), according to a new study. The study is published in the November 2024 issue of Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Diseases: Journal of the COPD Foundation, a peer-reviewed, open-access journal.
COPD is an inflammatory lung disease, comprising several conditions, including chronic bronchitis and emphysema, and can be caused by genetics and irritants like smoke or pollution. The disease affects more than 30 million Americans and is the ...
MD Anderson and Myriad Genetics form strategic alliance to evaluate clinical utility of Myriad’s molecular residual disease assay
2025-01-07
HOUSTON and SALT LAKE CITY ― The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center and Myriad Genetics, Inc. today announced a five-year strategic alliance to accelerate the clinical evaluation and development of Myriad’s molecular residual disease (MRD) assay.
This strategic alliance brings together the longstanding oncology diagnostic experience of Myriad Genetics and the clinical and translational research expertise of MD Anderson to create a portfolio of studies to evaluate the clinical validity and utility of Myriad’s Precise MRD.
“We look forward to working ...
Method can detect harmful salts forming in nuclear waste melters
2025-01-07
PULLMAN, Wash. – A new way to identify salts in nuclear waste melters could help improve clean-up technology, including at the Hanford Site, one of the largest, most complex nuclear waste clean-up sites in the world.
Reporting in the journal Measurement, Washington State University researchers used two detectors to find thin layers of sulfate, chloride and fluoride salts during vitrification, a nuclear waste storage process that involves converting the waste into glass. The formation of salts can be problematic for waste processing and storage.
“We were able to demonstrate a technique ...
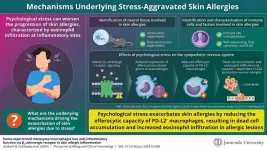
Researchers reveal how psychological stress may aggravate skin allergies
2025-01-07
Psychological stress is known to exacerbate skin allergies, but the underlying molecular mechanisms remain poorly understood. Recent studies using a mouse model of immunoglobulin E (IgE)-mediated cutaneous allergic inflammation (IgE-CAI) suggest that stress may disrupt immune functions, thereby worsening allergic symptoms by interfering with the body's inflammatory responses. IgE-CAI is characterized by swelling and infiltration of eosinophils, a type of immune cell involved in allergic inflammation, at the affected site.
In a recent study, a research group led by Associate Professor Soichiro Yoshikawa, Professor Kenji Takamori, and Professor Sachiko Miyake ...
International partnership aims to provide first-class osteopathy training
2025-01-07
The University of Plymouth and International Osteopathic Education (IOE) have formed a new partnership that will offer first-class training to aspiring osteopaths from across the world.
The organisations – both renowned internationally for quality healthcare training – have developed a rigorous and comprehensive Master of Osteopathic Medicine (MOstM) programme.
Those enrolling on the programme, which is being validated and awarded by the University of Plymouth, will engage in five years of flexible study.
They will benefit from clinical teaching in the IOE educational clinic in Bordeaux, ...
Reducing irrigation for livestock feed crops is needed to save Great Salt Lake, study argues
2025-01-07
CORVALLIS, Ore. – The Great Salt Lake has lost more than 15 billion cubic yards of water over the past three decades, is getting shallower at the rate of 4 inches a year, and an analysis of its water budget suggests reducing irrigation is necessary for saving it.
The study published today in Environmental Challenges shows that 62% of the river water bound for the lake is diverted for human uses, with agricultural activities responsible for nearly three-quarters of that percentage.
“The research highlights the alarming role of water consumption for feeding livestock in driving the lake’s rapid depletion,” said co-author ...
Clean energy tax credit safeguards could save taxpayers $1 trillion
2025-01-07
A new study published today in IOP Publishing’s journal Environmental Research: Energy shows why new safeguards adopted by the U.S. Treasury Department are necessary to avoid substantial climate impacts and wasted taxpayer resources from a generous hydrogen production tax credit.
The new study illustrates how, absent safeguards, hydrogen producers could potentially claim the highest level of tax credits ($3 per kilogram) for producing "gray" hydrogen from fossil natural gas, by blending in small amounts of biomethane or waste methane. ...
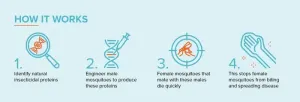
New genetic biocontrol breakthrough offers hope against disease-carrying mosquitoes and agricultural pests
2025-01-07
A revolutionary new biological pest control method that targets the lifespan of female insects could significantly reduce the threat of insect pests such as disease-carrying mosquitoes by offering faster and more effective results than current methods.
Described today in Nature Communications, the technique developed by researchers in Applied BioSciences and the ARC Centre of Excellence in Synthetic Biology at Macquarie University is a new approach called the Toxic Male Technique (TMT).
It works by genetically engineering male insects to produce insect-specific venom ...
Sex differences in brain structure present at birth
2025-01-07
Sex differences in brain structure are present from birth, research from the Autism Research Centre at the University of Cambridge has shown.
While male brains tended to be greater in volume than female brains, when adjusted for total brain volume, female infants on average had significantly more grey matter, while male infants on average had significantly more white matter in their brains.
Grey matter is made up of neuron cell bodies and dendrites and is responsible for processing and interpreting information, ...