(Press-News.org) A revolutionary new biological pest control method that targets the lifespan of female insects could significantly reduce the threat of insect pests such as disease-carrying mosquitoes by offering faster and more effective results than current methods.
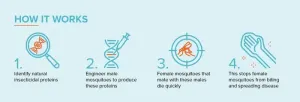
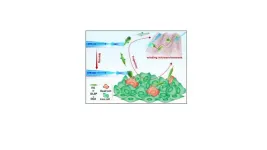
Described today in Nature Communications, the technique developed by researchers in Applied BioSciences and the ARC Centre of Excellence in Synthetic Biology at Macquarie University is a new approach called the Toxic Male Technique (TMT).
It works by genetically engineering male insects to produce insect-specific venom proteins in their semen. When these males mate with females, the proteins are transferred, significantly reducing female lifespan and their ability to spread disease.
Insect pests pose a growing threat to global health and agriculture, causing hundreds of thousands of deaths, millions of infections, and costing billions in healthcare and crop damage annually.
In mosquitoes like Aedes aegypti and Anopheles gambiae, only the females bite and transmit diseases such as malaria, dengue, Zika, chikungunya disease and yellow fever.
Pesticides face declining effectiveness due to resistance and have caused harm to non-target species and ecosystems. Genetic biocontrol has emerged as a promising alternative.
Current techniques like the Sterile Insect Technique (SIT) or insects carrying lethal genes (RIDL) work by releasing massive numbers of sterilised or genetically modified males to mate with the wild females.
While these mated females produce no offspring or only male offspring, they continue to blood feed and spread disease until they die naturally - meaning populations of biting females only decrease when the next generation emerges.
By immediately reducing the biting female population, TMT offers significant advantages over competing genetic biocontrol methods.
“As we’ve learned from COVID-19, reducing the spread of these diseases as quickly as possible is important to prevent epidemics,” says lead author Sam Beach.
“By targeting the female mosquitoes themselves rather than their offspring, TMT is the first biocontrol technology that could work as quickly as pesticides without also harming beneficial species.”
Laboratory tests using fruit flies (Drosophila melanogaster) demonstrated that females mated with TMT males had lifespans shortened by 37–64 per cent compared to those mated with unmodified males.
Computer models predict that applying TMT to Aedes aegypti, a highly aggressive mosquito species primarily responsible for transmitting Dengue and Zika, could reduce blood-feeding rates—a key factor in disease transmission—by 40 to 60 per cent compared to established methods.
Rigorous safety testing
Safety and environmental safety are central to the TMT approach. Venoms naturally contain a mixture of many proteins, and those used in TMT are very carefully selected.
Their targets are only present within invertebrates, so they aren’t toxic in any way to mammals, and they are not likely to cause harm when consumed by beneficial insects since their oral toxicity is very low.
The current study was performed in Associate Professor Maciej Maselko’s lab and provides the proof of concept for this breakthrough approach for suppressing the populations of pest species.
‘We still need to implement it in mosquitoes and conduct rigorous safety testing to ensure there are no risks to humans or other non-target species,” says Associate Professor Maselko.
“This innovative solution could transform how we manage pests, offering hope for healthier communities and a more sustainable future,” says Beach.
Competing interests: M.M. and S.J.B. have submitted a patent application (AU2023903662A0) to the Australian patent office pertaining to the enablement of the Toxic Male Technique.
END
New genetic biocontrol breakthrough offers hope against disease-carrying mosquitoes and agricultural pests
"Toxic Male Technique" genetically engineers male insects to produce insect-specific venom proteins in their semen
2025-01-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Sex differences in brain structure present at birth
2025-01-07
Sex differences in brain structure are present from birth, research from the Autism Research Centre at the University of Cambridge has shown.
While male brains tended to be greater in volume than female brains, when adjusted for total brain volume, female infants on average had significantly more grey matter, while male infants on average had significantly more white matter in their brains.
Grey matter is made up of neuron cell bodies and dendrites and is responsible for processing and interpreting information, ...
UCLA scientist unlocks early warning signs of adolescent psychosis through genetics
2025-01-07
LOS ANGELES, California, USA, 7 January 2025 - In a comprehensive Genomic Press Interview, Dr. Carrie E. Bearden, Professor of Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences and Psychology at UCLA, shares transformative insights into the neurobiology of psychosis risk in young people. Her work represents a significant advance in understanding how genetic factors and brain development interact to influence mental health outcomes in adolescents.
Growing up in Hawaii, Dr. Bearden's early fascination with mysteries and marine biology evolved into a passionate pursuit of neuroscience's greatest ...
Research reveals unique features of brain cells linked to neurodevelopmental conditions
2025-01-07
7 January 2025, Leuven – Specific brain cells known as layer 5 pyramidal neurons play a vital role in how our brains process information. Research by the team of Prof. Joris de Wit (VIB-KU Leuven) and colleagues highlights the differences between two types of these brain cells —intratelencephalic (IT) neurons and pyramidal tract (PT) neurons—and how these differences may affect their vulnerability to conditions like autism and schizophrenia.
Profiling synapses
Among the neural circuits that let our brain process information, brain cells known as layer 5 pyramidal neurons integrate information from various sources ...
Smarter memory: next-generation RAM with reduced energy consumption
2025-01-07
Osaka, Japan – Numerous memory types for computing devices have emerged in recent years, aiming to overcome the limitations imposed by traditional random access memory (RAM). Magnetoresistive RAM (MRAM) is one such memory type which offers several advantages over conventional RAM, including its non-volatility, high speed, increased storage capacity and enhanced endurance. Although remarkable improvements have been made to MRAM devices, reducing energy consumption during data writing remains a critical challenge.
A study recently published in Advanced Science by researchers from Osaka University proposes a new technology for MRAM ...
Core-membrane microstructured amine-modified mesoporous biochar templated via ZnCl2/KCl for CO2 capture
2025-01-07
In the ongoing battle against climate change, reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions remains a critical challenge. A recent study published in the journal Frontiers in Energy presents a significant breakthrough in CO2 capture technology through the development of a novel biochar material. This research, conducted by a team from Shanghai Jiao Tong University, introduces a core-membrane microstructured amine-modified mesoporous biochar, offering a promising solution for efficient CO2 capture.
The increasing concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere ...
Audio-guided self-supervised learning for disentangled visual speech representations
2025-01-07
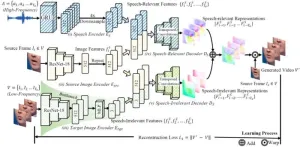
Learning visual speech representations from talking face videos is an important problem for several speech-related tasks, such as lip reading, talking face generation, audio-visual speech separation, and so on. The key difficulty lies in tackling speech-irrelevant factors presented in the videos, such as lighting, resolution, viewpoints, head motion, and so on.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Shuang YANG publishes their new research on 15 December 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education ...
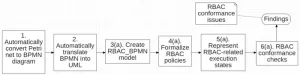
From logs to security: How process analysis is transforming access control
2025-01-07
Researchers at the University of Electro-Communications have developed a groundbreaking framework for improving system security by analyzing business process logs. This framework focuses on ensuring that role-based access control (RBAC) rules-critical to managing who can access specific system resources-are correctly implemented. Noncompliance with these rules, whether due to error or malicious activity, can result in unauthorized access and pose significant risks to organizations.
RBAC is a widely used access control model that relies on predefined roles assigned to users. However, as business processes become more complex, ensuring ...
Dronedarone inhibits the proliferation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through the CDK4/CDK6-RB1 axis in vitro and in vivo
2025-01-07
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is a severe health threat, being a predominant subtype of esophageal cancer and contributing significantly to cancer-related mortality globally. Despite advancements in combination therapies, patient prognosis remains poor, highlighting an urgent need for novel treatment strategies. In this context, a study explores the potential of dronedarone, an FDA-approved drug, in inhibiting ESCC proliferation through the CDK4/CDK6-RB1 axis, both in vitro and in vivo. The research reveals that dronedarone, ...
Photonic nanojet-regulated soft microalga-robot
2025-01-07
Micro/nanorobots hold exciting prospects for executing different tasks in complex microenvironments due to their small size, high flexibility, controllability, and environmental adaptability. However, traditional rigid micro/nanorobots are still difficult to perform different biomedical tasks in complex and unstructured narrow microenvironments due to their limited flexibility and insufficient deformability. To address this problem, in a new paper published in PhotoniX, a team of scientists led by Professor Hongbao Xin from Institute of Nanophotonics, Jinan University, China, has developed a new soft microalga robot (saBOT).
They innovatively used microalga, ...
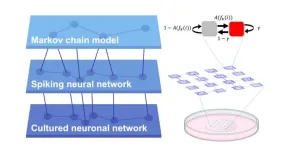
How do directional connections shape complex dynamics in neuronal networks?
2025-01-07
Uncovering the relationship between structure (connectivity) and function (neuronal activity) is a fundamental question across many areas of biology. However, investigating this directly in animal brains is challenging because of the immense complexity of their neural connections and the invasive surgeries that are typically needed. Lab-grown neurons with artificially-controlled connections have the possibility of becoming a useful alternative to animal testing, particularly as we learn how to accurately characterize their behaviour.
A research team at Tohoku University used microfluidic devices to reveal how directional connections shape the complex dynamics ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
Test platforms for charging wireless cars now fit on a bench
$3 million NIH grant funds national study of Medicare Advantage’s benefit expansion into social supports
Amplified Sciences achieves CAP accreditation for cutting-edge diagnostic lab
Fred Hutch announces 12 recipients of the annual Harold M. Weintraub Graduate Student Award
Native forest litter helps rebuild soil life in post-mining landscapes
Mountain soils in arid regions may emit more greenhouse gas as climate shifts, new study finds
Pairing biochar with other soil amendments could unlock stronger gains in soil health
Why do we get a skip in our step when we’re happy? Thank dopamine
UC Irvine scientists uncover cellular mechanism behind muscle repair
Platform to map living brain noninvasively takes next big step
Stress-testing the Cascadia Subduction Zone reveals variability that could impact how earthquakes spread
We may be underestimating the true carbon cost of northern wildfires
Blood test predicts which bladder cancer patients may safely skip surgery
Kennesaw State's Vijay Anand honored as National Academy of Inventors Senior Member
Recovery from whaling reveals the role of age in Humpback reproduction
Can the canny tick help prevent disease like MS and cancer?
Newcomer children show lower rates of emergency department use for non‑urgent conditions, study finds
Cognitive and neuropsychiatric function in former American football players
From trash to climate tech: rubber gloves find new life as carbon capturers materials
A step towards needed treatments for hantaviruses in new molecular map
Boys are more motivated, while girls are more compassionate?
Study identifies opposing roles for IL6 and IL6R in long-term mortality
AI accurately spots medical disorder from privacy-conscious hand images
Transient Pauli blocking for broadband ultrafast optical switching
Political polarization can spur CO2 emissions, stymie climate action
Researchers develop new strategy for improving inverted perovskite solar cells
Yes! The role of YAP and CTGF as potential therapeutic targets for preventing severe liver disease
Pancreatic cancer may begin hiding from the immune system earlier than we thought
Robotic wing inspired by nature delivers leap in underwater stability
A clinical reveals that aniridia causes a progressive loss of corneal sensitivity
[Press-News.org] New genetic biocontrol breakthrough offers hope against disease-carrying mosquitoes and agricultural pests"Toxic Male Technique" genetically engineers male insects to produce insect-specific venom proteins in their semen