(Press-News.org) LOS ANGELES, California, USA, 7 January 2025 - In a comprehensive Genomic Press Interview, Dr. Carrie E. Bearden, Professor of Psychiatry and Biobehavioral Sciences and Psychology at UCLA, shares transformative insights into the neurobiology of psychosis risk in young people. Her work represents a significant advance in understanding how genetic factors and brain development interact to influence mental health outcomes in adolescents.
Growing up in Hawaii, Dr. Bearden's early fascination with mysteries and marine biology evolved into a passionate pursuit of neuroscience's greatest puzzles. "What could be a better mystery to focus on than the human brain?" she reflects, describing her journey from literature student to leading neuroscientist.
Dr. Bearden's research uniquely combines two powerful approaches: studying clinically-defined high-risk cohorts and investigating highly penetrant genetic conditions. This dual strategy has yielded crucial insights into how psychosis develops, particularly during the critical adolescent period. Her work at UCLA's Center for Assessment and Prevention of Prodromal States (CAPPS) focuses on identifying early warning signs that could enable intervention before severe symptoms emerge.
The research has particularly exciting implications for personalized medicine. By connecting cellular and molecular phenotypes in neurons derived from individuals with genetic variants to their neurobehavioral characteristics, Dr. Bearden's team is opening new pathways for targeted preventive treatments.
Her recent work has expanded into studying sleep patterns in adolescents with neurodevelopmental disorders, leveraging new wearable technology to gather unprecedented data. "Sleep is still poorly understood, but it is essential for health and well-being, changing dramatically in adolescence," Dr. Bearden explains. "I think it holds much promise as a modifiable treatment target."
Dr. Bearden emphasizes the importance of making science accessible to all communities. Her research particularly focuses on understanding how social factors, including access to healthcare and cultural perspectives, influence treatment outcomes. This holistic approach reflects her commitment to bridging the gap between laboratory discoveries and real-world applications.
"I was very naïve when I started in this field, thinking that by focusing on a highly penetrant genetic variant with a well-understood genetic etiology, we would be able to 'solve' schizophrenia in short order," Dr. Bearden admits. "Of course, nothing is that simple, but it is astonishing when we look at how far we have come in psychiatric genetics in the past 20 years or so."
Dr. Carrie Bearden’s Genomic Press interview is part of a larger series that highlights the people behind today’s most influential scientific ideas. Each interview in the series offers a blend of cutting-edge research and personal reflections, providing readers with a comprehensive view of the scientists shaping the future. By combining a focus on professional achievements with personal insights, this interview style invites a richer narrative that both engages and educates readers. This format provides an ideal starting point for profiles that delve into the scientist’s impact on the field, while also touching on broader human themes. More information on the research leaders and research rising stars featured by Genomic Press can be found in our publication website: https://genomicpress.kglmeridian.com/.
The full Genomic Press Interview, titled “Carrie Bearden: What causes the onset of psychosis in adolescence, and how can we predict (and ultimately prevent) it?,” is available on 7 January 2025 in Genomic Psychiatry, offering readers an unparalleled opportunity to explore the thoughts and experiences of one of the most influential minds in neuroscience and neurobiology of brain disorders. The article is freely available online at https://doi.org/10.61373/gp025k.0002.
About Genomic Psychiatry – Genomic Psychiatry: Advancing Science from Genes to Society (ISSN: 2997-2388) represents a paradigm shift in genetics journals by interweaving advances in genomics and genetics with progress in all other areas of contemporary psychiatry. Genomic Psychiatry publishes peer-reviewed medical research articles of the highest quality from any area within the continuum that goes from genes and molecules to neuroscience, clinical psychiatry, and public health.
END
UCLA scientist unlocks early warning signs of adolescent psychosis through genetics
Dr. Carrie Bearden reveals groundbreaking neurodevelopment insights in exclusive Genomic Press Interview
2025-01-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Research reveals unique features of brain cells linked to neurodevelopmental conditions
2025-01-07
7 January 2025, Leuven – Specific brain cells known as layer 5 pyramidal neurons play a vital role in how our brains process information. Research by the team of Prof. Joris de Wit (VIB-KU Leuven) and colleagues highlights the differences between two types of these brain cells —intratelencephalic (IT) neurons and pyramidal tract (PT) neurons—and how these differences may affect their vulnerability to conditions like autism and schizophrenia.
Profiling synapses
Among the neural circuits that let our brain process information, brain cells known as layer 5 pyramidal neurons integrate information from various sources ...
Smarter memory: next-generation RAM with reduced energy consumption
2025-01-07
Osaka, Japan – Numerous memory types for computing devices have emerged in recent years, aiming to overcome the limitations imposed by traditional random access memory (RAM). Magnetoresistive RAM (MRAM) is one such memory type which offers several advantages over conventional RAM, including its non-volatility, high speed, increased storage capacity and enhanced endurance. Although remarkable improvements have been made to MRAM devices, reducing energy consumption during data writing remains a critical challenge.
A study recently published in Advanced Science by researchers from Osaka University proposes a new technology for MRAM ...
Core-membrane microstructured amine-modified mesoporous biochar templated via ZnCl2/KCl for CO2 capture
2025-01-07
In the ongoing battle against climate change, reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions remains a critical challenge. A recent study published in the journal Frontiers in Energy presents a significant breakthrough in CO2 capture technology through the development of a novel biochar material. This research, conducted by a team from Shanghai Jiao Tong University, introduces a core-membrane microstructured amine-modified mesoporous biochar, offering a promising solution for efficient CO2 capture.
The increasing concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere ...
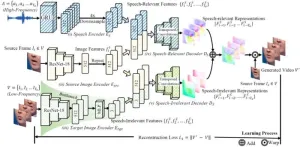
Audio-guided self-supervised learning for disentangled visual speech representations
2025-01-07
Learning visual speech representations from talking face videos is an important problem for several speech-related tasks, such as lip reading, talking face generation, audio-visual speech separation, and so on. The key difficulty lies in tackling speech-irrelevant factors presented in the videos, such as lighting, resolution, viewpoints, head motion, and so on.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Shuang YANG publishes their new research on 15 December 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education ...
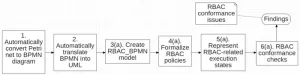
From logs to security: How process analysis is transforming access control
2025-01-07
Researchers at the University of Electro-Communications have developed a groundbreaking framework for improving system security by analyzing business process logs. This framework focuses on ensuring that role-based access control (RBAC) rules-critical to managing who can access specific system resources-are correctly implemented. Noncompliance with these rules, whether due to error or malicious activity, can result in unauthorized access and pose significant risks to organizations.
RBAC is a widely used access control model that relies on predefined roles assigned to users. However, as business processes become more complex, ensuring ...
Dronedarone inhibits the proliferation of esophageal squamous cell carcinoma through the CDK4/CDK6-RB1 axis in vitro and in vivo
2025-01-07
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is a severe health threat, being a predominant subtype of esophageal cancer and contributing significantly to cancer-related mortality globally. Despite advancements in combination therapies, patient prognosis remains poor, highlighting an urgent need for novel treatment strategies. In this context, a study explores the potential of dronedarone, an FDA-approved drug, in inhibiting ESCC proliferation through the CDK4/CDK6-RB1 axis, both in vitro and in vivo. The research reveals that dronedarone, ...
Photonic nanojet-regulated soft microalga-robot
2025-01-07
Micro/nanorobots hold exciting prospects for executing different tasks in complex microenvironments due to their small size, high flexibility, controllability, and environmental adaptability. However, traditional rigid micro/nanorobots are still difficult to perform different biomedical tasks in complex and unstructured narrow microenvironments due to their limited flexibility and insufficient deformability. To address this problem, in a new paper published in PhotoniX, a team of scientists led by Professor Hongbao Xin from Institute of Nanophotonics, Jinan University, China, has developed a new soft microalga robot (saBOT).
They innovatively used microalga, ...
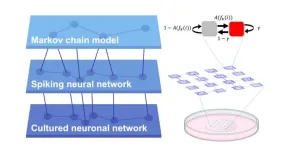
How do directional connections shape complex dynamics in neuronal networks?
2025-01-07
Uncovering the relationship between structure (connectivity) and function (neuronal activity) is a fundamental question across many areas of biology. However, investigating this directly in animal brains is challenging because of the immense complexity of their neural connections and the invasive surgeries that are typically needed. Lab-grown neurons with artificially-controlled connections have the possibility of becoming a useful alternative to animal testing, particularly as we learn how to accurately characterize their behaviour.
A research team at Tohoku University used microfluidic devices to reveal how directional connections shape the complex dynamics ...
Drug-resistant hookworms put pets and people at risk
2025-01-07
Canine hookworms are becoming increasingly resistant to drugs across Australia, according to new research.
Scientists at The University of Queensland and The University of Sydney have identified widespread resistance to benzimidazole-based dewormers which are commonly used to treat gastrointestinal parasites in dogs.
Dr Swaid Abdullah from UQ’s School of Veterinary Science said almost 70 per cent of the hookworm samples studied showed genetic mutations that can cause drug resistance.
“This is a big problem, as hookworm infections ...
New strontium isotope map of Sub-Saharan Africa is a powerful tool for archaeology, forensics, and wildlife conservation
2025-01-07
A team of researchers led by UC Santa Cruz recently released a sophisticated new map that reveals, for the first time, the unique “geologic fingerprints” for most of the African continent.
The map will help archaeologists, conservation scientists, and forensics experts match artifacts and plant, animal, and human remains found at locations around the world back to their most likely region of origin within Africa, offering new insights on issues ranging from the history of the transatlantic slave trade to modern wildlife trafficking and human migration patterns.
The research team’s ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
DGIST identifies “magic blueprint” for converting carbon dioxide into resources through atom-level catalyst design
COVID-19 vaccination during pregnancy may help prevent preeclampsia
Menopausal hormone therapy not linked to increased risk of death
Chronic shortage of family doctors in England, reveals BMJ analysis
Booster jabs reduce the risks of COVID-19 deaths, study finds
Screening increases survival rate for stage IV breast cancer by 60%
ACC announces inaugural fellow for the Thad and Gerry Waites Rural Cardiovascular Research Fellowship
University of Oklahoma researchers develop durable hybrid materials for faster radiation detection
Medicaid disenrollment spikes at age 19, study finds
Turning agricultural waste into advanced materials: Review highlights how torrefaction could power a sustainable carbon future
New study warns emerging pollutants in livestock and aquaculture waste may threaten ecosystems and public health
Integrated rice–aquatic farming systems may hold the key to smarter nitrogen use and lower agricultural emissions
Hope for global banana farming in genetic discovery
Mirror image pheromones help beetles swipe right
Prenatal lead exposure related to worse cognitive function in adults
Research alert: Understanding substance use across the full spectrum of sexual identity
Pekingese, Shih Tzu and Staffordshire Bull Terrier among twelve dog breeds at risk of serious breathing condition
Selected dog breeds with most breathing trouble identified in new study
Interplay of class and gender may influence social judgments differently between cultures
Pollen counts can be predicted by machine learning models using meteorological data with more than 80% accuracy even a week ahead, for both grass and birch tree pollen, which could be key in effective
Rewriting our understanding of early hominin dispersal to Eurasia
Rising simultaneous wildfire risk compromises international firefighting efforts
Honey bee "dance floors" can be accurately located with a new method, mapping where in the hive forager bees perform waggle dances to signal the location of pollen and nectar for their nestmates
Exercise and nutritional drinks can reduce the need for care in dementia
Michelson Medical Research Foundation awards $750,000 to rising immunology leaders
SfN announces Early Career Policy Ambassadors Class of 2026
Spiritual practices strongly associated with reduced risk for hazardous alcohol and drug use
Novel vaccine protects against C. diff disease and recurrence
An “electrical” circadian clock balances growth between shoots and roots
Largest study of rare skin cancer in Mexican patients shows its more complex than previously thought
[Press-News.org] UCLA scientist unlocks early warning signs of adolescent psychosis through geneticsDr. Carrie Bearden reveals groundbreaking neurodevelopment insights in exclusive Genomic Press Interview