Core-membrane microstructured amine-modified mesoporous biochar templated via ZnCl2/KCl for CO2 capture
2025-01-07
(Press-News.org)
In the ongoing battle against climate change, reducing carbon dioxide (CO2) emissions remains a critical challenge. A recent study published in the journal Frontiers in Energy presents a significant breakthrough in CO2 capture technology through the development of a novel biochar material. This research, conducted by a team from Shanghai Jiao Tong University, introduces a core-membrane microstructured amine-modified mesoporous biochar, offering a promising solution for efficient CO2 capture.
The increasing concentration of CO2 in the atmosphere is a major driver of global warming. Industries, particularly those involving fossil fuel combustion, are significant contributors to these emissions. Traditional methods of CO2 capture, such as amine scrubbing, have limitations in terms of efficiency and cost. Therefore, there is a pressing need for innovative materials that can effectively capture CO2 with enhanced performance and reduced environmental impact.
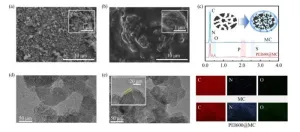
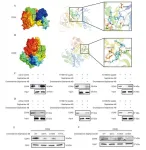
The study focuses on the synthesis of mesoporous biochar (MC) derived from biomass, using a dual-salt template method involving ZnCl2 and KCl. This process is followed by the impregnation of polyethyleneimine (PEI) with varying average molecular weights to create a core-membrane structure. The researchers systematically characterized the resulting materials, examining their surface properties, porous morphology, thermal stability, phase composition, and functional groups. The CO2 sorption performance of these materials was then evaluated under various conditions.
The results showed that the PEI-modified biochar, specifically PEI-600@MC, demonstrated exceptional CO2 sorption capacity, reaching approximately 3.35 mmol/g at 0.1 MPa and 70 °C. This performance is significantly higher than that of the unmodified biochar and comparable or superior to other reported amine-modified materials. The study also found that the sorption capacity and thermal stability of the materials varied with the molecular weight of PEI, providing insights into the optimal design of such materials.
This research highlights the potential of dual-salt templated biomass-derived MC as an effective, widely available, and cost-efficient material for CO2 capture. The innovative core-membrane structure and the use of PEI offer enhanced performance in terms of both sorption capacity and selectivity. This development could pave the way for more sustainable and economically viable CO2 capture technologies, contributing to global efforts to mitigate climate change and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.
The findings of this study not only advance the field of carbon capture and storage but also provide a foundation for further research and development in creating materials that can effectively address environmental challenges associated with industrial emissions.
END
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
2025-01-07
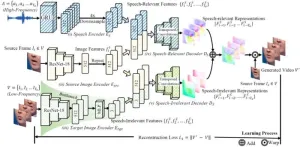
Learning visual speech representations from talking face videos is an important problem for several speech-related tasks, such as lip reading, talking face generation, audio-visual speech separation, and so on. The key difficulty lies in tackling speech-irrelevant factors presented in the videos, such as lighting, resolution, viewpoints, head motion, and so on.
To solve the problems, a research team led by Shuang YANG publishes their new research on 15 December 2024 in Frontiers of Computer Science co-published by Higher Education ...
2025-01-07
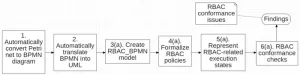
Researchers at the University of Electro-Communications have developed a groundbreaking framework for improving system security by analyzing business process logs. This framework focuses on ensuring that role-based access control (RBAC) rules-critical to managing who can access specific system resources-are correctly implemented. Noncompliance with these rules, whether due to error or malicious activity, can result in unauthorized access and pose significant risks to organizations.
RBAC is a widely used access control model that relies on predefined roles assigned to users. However, as business processes become more complex, ensuring ...
2025-01-07
Esophageal squamous cell carcinoma (ESCC) is a severe health threat, being a predominant subtype of esophageal cancer and contributing significantly to cancer-related mortality globally. Despite advancements in combination therapies, patient prognosis remains poor, highlighting an urgent need for novel treatment strategies. In this context, a study explores the potential of dronedarone, an FDA-approved drug, in inhibiting ESCC proliferation through the CDK4/CDK6-RB1 axis, both in vitro and in vivo. The research reveals that dronedarone, ...
2025-01-07
Micro/nanorobots hold exciting prospects for executing different tasks in complex microenvironments due to their small size, high flexibility, controllability, and environmental adaptability. However, traditional rigid micro/nanorobots are still difficult to perform different biomedical tasks in complex and unstructured narrow microenvironments due to their limited flexibility and insufficient deformability. To address this problem, in a new paper published in PhotoniX, a team of scientists led by Professor Hongbao Xin from Institute of Nanophotonics, Jinan University, China, has developed a new soft microalga robot (saBOT).
They innovatively used microalga, ...
2025-01-07
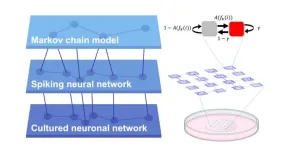
Uncovering the relationship between structure (connectivity) and function (neuronal activity) is a fundamental question across many areas of biology. However, investigating this directly in animal brains is challenging because of the immense complexity of their neural connections and the invasive surgeries that are typically needed. Lab-grown neurons with artificially-controlled connections have the possibility of becoming a useful alternative to animal testing, particularly as we learn how to accurately characterize their behaviour.
A research team at Tohoku University used microfluidic devices to reveal how directional connections shape the complex dynamics ...
2025-01-07
Canine hookworms are becoming increasingly resistant to drugs across Australia, according to new research.
Scientists at The University of Queensland and The University of Sydney have identified widespread resistance to benzimidazole-based dewormers which are commonly used to treat gastrointestinal parasites in dogs.
Dr Swaid Abdullah from UQ’s School of Veterinary Science said almost 70 per cent of the hookworm samples studied showed genetic mutations that can cause drug resistance.
“This is a big problem, as hookworm infections ...
2025-01-07
A team of researchers led by UC Santa Cruz recently released a sophisticated new map that reveals, for the first time, the unique “geologic fingerprints” for most of the African continent.
The map will help archaeologists, conservation scientists, and forensics experts match artifacts and plant, animal, and human remains found at locations around the world back to their most likely region of origin within Africa, offering new insights on issues ranging from the history of the transatlantic slave trade to modern wildlife trafficking and human migration patterns.
The research team’s ...
2025-01-07
People who care for both their children and older family members – also known as ‘sandwich carers’ – suffer from deterioration in both their mental and physical health over time, finds a new study by UCL researchers.
The research, published in Public Health, analysed data from around 2,000 sandwich carers and 2,000 non-sandwich carers from the UK Household Longitudinal Study between 2009 and 2020.
Sandwich carers juggle the responsibilities of caring for ageing parents or older relatives while raising dependent children ...
2025-01-06
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- When a new species is introduced into an ecosystem, it may succeed in establishing itself, or it may fail to gain a foothold and die out. Physicists at MIT have now devised a formula that can predict which of those outcomes is most likely.
The researchers created their formula based on analysis of hundreds of different scenarios that they modeled using populations of soil bacteria grown in their laboratory. They now plan to test their formula in larger-scale ecosystems, including forests. This approach could also be helpful in predicting whether probiotics or fecal microbiota treatments (FMT) would successfully combat infections of the human GI tract.
“People ...
2025-01-06
A change in the weather in the U.S. Corn Belt
Intensive farming and shallow groundwater affect precipitation patterns
The sweeping land use changes and irrigation of the U.S. Corn Belt, along with the influence of the area’s shallow groundwater, have significantly altered precipitation patterns in that vital agricultural region, new research shows.
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, focuses on “precipitation recycling” — a process in which the moisture released to the atmosphere by plants, soils, lakes, and other features of the landscape returns to the same area in the form of rain.
By using advanced ...
LAST 30 PRESS RELEASES:
[Press-News.org] Core-membrane microstructured amine-modified mesoporous biochar templated via ZnCl2/KCl for CO2 capture