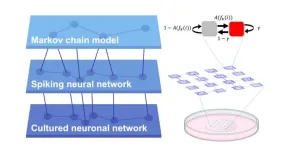
(Press-News.org) Uncovering the relationship between structure (connectivity) and function (neuronal activity) is a fundamental question across many areas of biology. However, investigating this directly in animal brains is challenging because of the immense complexity of their neural connections and the invasive surgeries that are typically needed. Lab-grown neurons with artificially-controlled connections have the possibility of becoming a useful alternative to animal testing, particularly as we learn how to accurately characterize their behaviour.
A research team at Tohoku University used microfluidic devices to reveal how directional connections shape the complex dynamics of neuronal networks. They also developed mathematical models based on experimental data to predict how connectivity influences activity across space and time.
The results were published in Neural Networks on November 28, 2024.
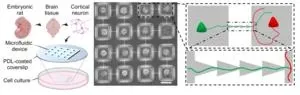
Like a river current, directional connections in neuronal networks propagate signals in a downstream flow from one area to another. A microfluid device has tiny channels that can precisely direct the flow, which can help fabricate neurons that react more similarly to in-vivo models. By studying in-vitro neurons in a lab environment, the research team was able to efficiently and constructively explore whether one-way connections play other fundamental roles in shaping brain dynamics.
"The brain is difficult to understand, in part, because it is dynamic - it can learn to respond differently to the same stimuli over time based on a number of factors," says lead author Nobuaki Monma.
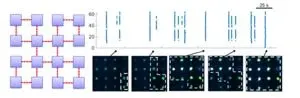
The research team fabricated neuronal networks bearing modular connectivity (as observed in animals' nervous systems) and embedded directional connections between modules using microchannels. The connections were embedded in a feedforward manner to minimize excessive excitatory reactions. Using calcium imaging to record spontaneous activity exhibited by the neuronal network, they found that networks incorporating directional connections exhibited more complex activity patterns compared to networks without directionality.
In addition, the researchers developed two mathematical models to clarify the underlying network mechanisms behind biological observations and to predict configurations that would yield greater dynamical complexity. The models determined that the interplay between modularity and connectivity fostered more complex activity patterns.
"The findings of this study are expected not only to deepen our fundamental understanding of neuronal networks in the brain, but also to find applications in fields such as medicine and machine learning," proposes Associate Professor Hideaki Yamamoto.
This may also offer an in-vitro model for developing biologically plausible artificial neural networks. Further theoretical advancements would also contribute to modeling large-scale networks, which may provide insights to future connectome analysis of the brain. The more thoroughly we understand these neuronal networks, the more it could be used as a trusty tool to unlock the many mysteries of the brain.
END
How do directional connections shape complex dynamics in neuronal networks?
2025-01-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Drug-resistant hookworms put pets and people at risk
2025-01-07
Canine hookworms are becoming increasingly resistant to drugs across Australia, according to new research.
Scientists at The University of Queensland and The University of Sydney have identified widespread resistance to benzimidazole-based dewormers which are commonly used to treat gastrointestinal parasites in dogs.
Dr Swaid Abdullah from UQ’s School of Veterinary Science said almost 70 per cent of the hookworm samples studied showed genetic mutations that can cause drug resistance.
“This is a big problem, as hookworm infections ...
New strontium isotope map of Sub-Saharan Africa is a powerful tool for archaeology, forensics, and wildlife conservation
2025-01-07
A team of researchers led by UC Santa Cruz recently released a sophisticated new map that reveals, for the first time, the unique “geologic fingerprints” for most of the African continent.
The map will help archaeologists, conservation scientists, and forensics experts match artifacts and plant, animal, and human remains found at locations around the world back to their most likely region of origin within Africa, offering new insights on issues ranging from the history of the transatlantic slave trade to modern wildlife trafficking and human migration patterns.
The research team’s ...
‘Sandwich carers’ experience decline in mental and physical health
2025-01-07
People who care for both their children and older family members – also known as ‘sandwich carers’ – suffer from deterioration in both their mental and physical health over time, finds a new study by UCL researchers.
The research, published in Public Health, analysed data from around 2,000 sandwich carers and 2,000 non-sandwich carers from the UK Household Longitudinal Study between 2009 and 2020.
Sandwich carers juggle the responsibilities of caring for ageing parents or older relatives while raising dependent children ...
A new way to determine whether a species will successfully invade an ecosystem
2025-01-06
CAMBRIDGE, MA -- When a new species is introduced into an ecosystem, it may succeed in establishing itself, or it may fail to gain a foothold and die out. Physicists at MIT have now devised a formula that can predict which of those outcomes is most likely.
The researchers created their formula based on analysis of hundreds of different scenarios that they modeled using populations of soil bacteria grown in their laboratory. They now plan to test their formula in larger-scale ecosystems, including forests. This approach could also be helpful in predicting whether probiotics or fecal microbiota treatments (FMT) would successfully combat infections of the human GI tract.
“People ...
A change in the weather in the U.S. Corn Belt
2025-01-06
A change in the weather in the U.S. Corn Belt
Intensive farming and shallow groundwater affect precipitation patterns
The sweeping land use changes and irrigation of the U.S. Corn Belt, along with the influence of the area’s shallow groundwater, have significantly altered precipitation patterns in that vital agricultural region, new research shows.
The study, published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, focuses on “precipitation recycling” — a process in which the moisture released to the atmosphere by plants, soils, lakes, and other features of the landscape returns to the same area in the form of rain.
By using advanced ...
How we classify flood risk may give developers, home buyers a false sense of security
2025-01-06
Common methods of communicating flood risk may create a false sense of security, leading to increased development in areas threatened by flooding.
This phenomenon, called the “safe development paradox,” is described in a new paper from North Carolina State University. Lead author Georgina Sanchez, a research scholar in NC State’s Center for Geospatial Analytics, said this may be an unintended byproduct of how the Federal Emergency Management Agency classifies areas based on their probability of dangerous flooding.
Known as flood mapping, this classification system describes areas in terms of their likelihood of being flooded each year. These ...
GLP-1 drugs may reduce surgery complications in patients with diabetes
2025-01-06
People with diabetes who were taking GLP-1 receptor agonist drugs such as tirzepatide and semaglutide had significantly lower rates of hospital readmission, wound re-opening and hematoma after surgery, according to a large study led by investigators at Weill Cornell Medicine, Columbia University Vagelos College of Physicians and Surgeons and NewYork-Presbyterian.
The study, published online in advance of print on Dec. 20 in the Annals of Surgery, analyzed de-identified hospital records covering 74,425 surgical procedures in 21,772 patients with diabetes over a three-and-a-half-year period ending in July 2023. The investigators found that patients taking GLP-1 receptor agonists, known informally ...
Physicists explain a stellar stream’s distinctive features
2025-01-06
RIVERSIDE, Calif. -- Physicists have proposed a solution to a long-standing puzzle surrounding the GD-1 stellar stream, one of the most well-studied streams within the galactic halo of the Milky Way, known for its long, thin structure, and unusual spur and gap features.
The team of researchers, led by Hai-Bo Yu at the University of California, Riverside, proposed that a core-collapsing self-interacting dark matter (SIDM) “subhalo” — a smaller, satellite halo within the galactic halo — is responsible for the peculiar spur and gap features observed in the GD-1 stellar stream.
Study ...
GLP-1 RA medications safe and very effective for treating obesity in adults without diabetes
2025-01-06
Embargoed for release until 5:00 p.m. ET on Monday 6 January 2025
@Annalsofim
Below please find summaries of new articles that will be published in the next issue of Annals of Internal Medicine. The summaries are not intended to substitute for the full articles as a source of information. This information is under strict embargo and by taking it into possession, media representatives are committing to the terms of the embargo not only on their own behalf, but also on behalf of the organization they represent.
----------------------------
1. ...
Efforts to reduce kids' screen time weakened by unequal access to green space
2025-01-06
When children have a place to play outside, programs aimed at reducing their screen time use are more successful, according to a University of Michigan study.
The study also found that such programs are less successful in neighborhoods where children have less access to green spaces, which include areas such as forests, shrubland, open spaces and grassland, according to lead author Ian-Marshall Lang, a researcher at U-M's School of Kinesiology and first author of the study.
"Because prior studies have shown differences in the effectiveness of community ...