(Press-News.org) URBANA, Ill.– Food drying is a common process for preserving many types of food, including fruits and meat; however, drying can alter the food’s quality and nutritional value. In recent years, researchers have developed precision techniques that use optical sensors and AI to facilitate more efficient drying. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign discusses three emerging smart drying techniques, providing practical information for the food industry.
“With traditional drying systems, you need to remove samples to monitor the process. But with smart drying, or precision drying, you can continuously monitor the process in real time, enhancing accuracy and efficiency,” said corresponding author Mohammed Kamruzzaman, assistant professor in the Department of Agricultural and Biological Engineering (ABE), part of the College of Agricultural, Consumer and Environmental Sciences and The Grainger College of Engineering at Illinois.
In the paper, the researchers review academic literature about different types of equipment that apply precision techniques to enhance smart drying capabilities in the food industry.
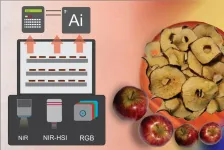
They focus on three optical sensing systems – RGB imaging with computer vision, near-infrared (NIR) spectroscopy, and near-infrared hyperspectral imaging (NIR-HSI) – discussing the mechanisms, applications, advantages, and limitations of each. They also provide an overview of standard industrial drying methods, such as freeze drying, spray, microwave, or hot-air oven drying, which can be combined with the precision monitoring techniques.
“You can use each of the three sensors separately or in combination. What you choose will depend on the particular drying system, your needs, and cost-effectiveness,” said lead author Marcus Vinicius da Silva Ferreira, a postdoctoral fellow in ABE.
RGB with computer vision uses a regular camera that captures visible light with a RGB color spectrum. It can provide information about surface-level features, such as size, shape, color, and defects, but it is not capable of measuring moisture content.
NIR spectroscopy uses near-infrared light to measure the absorbance of different wavelengths, which can be correlated to unique chemical and physical product characteristics, and it can measure internal qualities such as moisture content. However, NIR scans one point at a time.
This can work for a single product, like an apple slice, at least initially, Kamruzzaman said.
“But as the drying progresses, the material will shrink and become heterogeneous, because of cracking and bending. If you use NIR at that stage, and if you only scan a single point, you cannot measure the drying rate,” he noted.
NIR-HSI is the most comprehensive of the three techniques. It scans the whole surface of the product, so it provides much more precise information about the drying rate and other features than NIR alone, since it extracts three-dimensional spatial and spectral information. However, NIR-HSI is also much more expensive than the two other sensors. The equipment costs 10 to 20 times more than NIR sensors, and 100 times or more than RGB cameras. Additionally, maintenance and computing requirements for HSI are substantially higher, further increasing the total cost.
All three methodologies must be combined with AI and machine learning to process the information, and the models must be trained for each specific application. Again, HSI requires more computational power than the other two systems because of the large amount of data it collects.
The researchers also developed their own drying system to test the various methods. They built a convective heat oven and tested the techniques on the drying of apple slices. They first combined the system with RGB and NIR; later they also tested the NIR-HSI system, the findings of which they plan to discuss in a forthcoming paper.
“For real-time monitoring, the convergence of RGB imaging, NIR spectroscopic sensors, and NIR-HSI with AI represents a transformative future for food drying. Integrating these technologies overcomes conventional drying process monitoring limitations and propels real-time monitoring capabilities,” they concluded in the paper.
Future development of portable, hand-held NIR-HSI devices will further enable continuous monitoring of drying systems, providing real-time quality control in a variety of operating environments, they noted.
The paper, “AI-Enabled Optical Sensing for Smart and Precision Food Drying: Techniques, Applications and Future Directions,” is published in Food Engineering Reviews [DOI: 10.1007/s12393-024-09388-0]. This study was financially supported by the Center for Advanced Research in Drying (CARD), a U.S. National Science Foundation Industry University Cooperative Research Center. CARD is located at Worcester Polytechnic Institute and the University of Illinois at Urbana-Champaign.
END
Smart food drying techniques with AI enhance product quality and efficiency
2025-01-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Typical cost of developing new pharmaceuticals is skewed by high-cost outliers
2025-01-07
The typical cost of developing new medications may not be as high as generally believed, with a few ultra-costly medications skewing public discussions about the cost of pharmaceutical research and development, according to a new RAND study.
Using a novel method to assess spending on research and development for 38 drugs that were recently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, researchers found that the mean, or average, cost of developing a new drug was much higher than the mid-point (median) cost of development.
Researchers estimated a median direct research and development cost of $150 million compared to a mean of $369 million.
Costs ...
Predicting the progression of autoimmune disease with AI
2025-01-07
HERSHEY, Pa. — Autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own healthy cells and tissues, often have a preclinical stage before diagnosis that’s characterized by mild symptoms or certain antibodies in the blood. However, in some people, these symptoms may resolve before culminating in the full disease stage.
Knowing who may progress along the disease pathway is critical for early diagnosis and intervention, improved treatment and better disease management, according to a team led by researchers from the ...
Unlocking Romance: UCLA offers dating program for autistic adults
2025-01-07
Love doesn’t come with an instruction manual, but for autistic adults seeking to navigate the complexities of romance, a UCLA Health program offers a roadmap to finding and sustaining meaningful relationships through the launch of a new research study, called PEERS for Dating.
Led by the UCLA Program for the Education and Enrichment of Relationship Skills (PEERS) Clinic, the new 20-week program aims to demystify the often complex social rules surrounding dating and help participants gain a deeper understanding of relationship dynamics
“Romantic relationships can be transformative, but for many autistic adults, the path to connection can feel uncertain,” ...
Research Spotlight: Researchers reveal the influences behind timing of sleep spindle production
2025-01-07
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
Our research focuses on sleep spindles—short bursts of brain activity during sleep that are crucial for stabilizing sleep and supporting memory.
Sleep spindles are of great interest because changes in spindle activity have been linked to many neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and autism.
While many factors influence when and how these spindles occur, such as sleep stages or brain rhythms, we discovered that short-term patterns, like a musical rhythm spanning just a few seconds, play the most ...
New research reveals groundwater pathways across continent
2025-01-07
Researchers from Princeton University and the University of Arizona have created a simulation that maps underground water on a continental scale. The result of three years’ work studying groundwater from coast to coast, the findings plot the unseen path that each raindrop or melted snowflake takes before reemerging in freshwater streams, following water from land surface to depths far below and back up again, emerging up to 100 miles away, after spending from 10 to 100,000 years underground.
The simulation, published Jan. 6 in the journal Nature Water, shows that rainfall and snowmelt ...
Students and faculty to join research teams this spring at Department of Energy National Laboratories and a fusion facility
2025-01-07
WASHINGTON, D.C. - A diverse group of 164 undergraduate students and six faculty will participate in unique workforce development programs at 11 of the nation’s national laboratories and a fusion facility during Spring 2025.
This opportunity is part of a continuing effort by the Department of Energy (DOE) to ensure the nation has a strong, sustained workforce trained in the skills needed to address the energy, environment, and national security challenges of today and tomorrow.
“The ...
SETI Forward recognizes tomorrow’s cosmic pioneers
2025-01-07
January 7, 2025, Mountain View, CA -- The SETI Institute announces the 2024 SETI Forward Award recipients: Gabriella Rizzo and Pritvik Sinhadc. This year's recipients worked on research projects to understand extremophiles in deep-sea hydrothermal vents and to analyze gravitational wave signals for potential extraterrestrial technosignatures. Established by Lew Levy, SETI Forward committee founder and member of the SETI Institute’s Council of Advisors, this award is a beacon for promising young scientists. The goal is to connect students with opportunities that foster their ...
Top mental health research achievements of 2024 from the Brain & Behavior Research Foundation
2025-01-07
The Brain & Behavior Research Foundation (BBRF) has announced the 2024 Leading Research Achievements by BBRF grantees, prizewinners, and scientific council members. It includes important studies of suicide, childhood anxiety, depression, eating disorders, cocaine addiction, and other aspects of brain and behavior illness.
The 2024 Leading Research Achievements are:
Suicide Risk Fluctuates Across the Menstrual Cycle, Affecting Different Women Differently
Tory Anne Eisenlohr-Moul, Ph.D., University of Illinois, Chicago
Preliminary Trial of Psychoactive ...
FAU names Lewis S. Nelson, M.D., Dean of the Schmidt College of Medicine
2025-01-07
Florida Atlantic University has named Lewis S. Nelson, M.D., as the new dean of the Charles E. Schmidt College of Medicine. Nelson previously served as professor and inaugural chair of the Department of Emergency Medicine and chief of the Division of Medical Toxicology and Addiction Medicine at Rutgers New Jersey Medical School in Newark, and chief of the Emergency Department at University Hospital of Newark, a public safety net hospital. He assumed his role as dean on Jan. 6.
Nelson has more than 30 years of academic and clinical leadership experience with a proven record of fostering innovation, research, and clinical excellence. During his eight-year tenure ...
UC Irvine-led study challenges traditional risk factors for brain health in the oldest-old
2025-01-07
Irvine, Calif., Jan. 7, 2025 – A study led by the University of California, Irvine has found cardiovascular conditions such as high blood pressure and diabetes, which are known to contribute to brain blood vessel damage in younger populations, not to be associated with an increased risk of such harm in individuals 90 and older.
The work, published online today in the journal Alzheimer’s & Dementia: The Journal of the Alzheimer’s Association, suggests that the relationship among blood pressure, vascular health and brain aging is more complex than previously thought.
“For decades, we’ve known that factors like high blood ...