(Press-News.org) A recent study analyzing data from the National Survey on Drug Use and Health (NSDUH) found that past-year recreational ketamine use among adults has increased dramatically since 2015, including significant shifts in associations with depression and sociodemographic characteristics such as race, age and education status. Ketamine use has shown promise in clinical trials therapy for several mental illnesses, including treatment-resistant depression, and the new research suggests that ongoing monitoring of recreational use trends is crucial to balancing these clinical benefits against the risk of unmonitored recreational use.
Key findings include:
Overall past-year recreational ketamine use increased by 81.8% from 2015 to 2019 and by 40% from 2021 to 2022.
Adults with depression were 80% more likely to have used ketamine in the past year in 2015-2019, but this association weakened in later years. In 2021-2022, ketamine use increased only among those without depression.
In 2021-2022, adults aged 26-34 were 66% more likely to have used ketamine in the past year compared to adults aged 18-25. Those with college degrees were more than twice as likely to have used ketamine compared to people with a high school education or less.
People were more likely to use ketamine if they used other substances, such as ecstasy/MDMA, GHB, and cocaine.
The researchers recommend expanding prevention outreach to settings like colleges, where younger adults may be at heightened risk, as well as providing education on the harms of polydrug use, particularly in combination with opioids. As medical ketamine becomes more widely available, they also emphasize the need for continued surveillance of recreational ketamine use patterns and further research to understand the factors that contribute to ketamine use.
The study, published online in the Journal of Affective Disorders, was led by Kevin Yang, M.D., a third-year resident physician in the Department of Psychiatry at UC San Diego School of Medicine. The research was supported by the National Institute on Drug Abuse of the National Institutes of Health.
# # #
END
Research alert: Ketamine use on the rise in U.S. adults; new trends emerge
2025-01-07
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
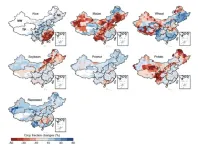
Crop switching for climate change in China
2025-01-07
A study of Chinese agriculture recommends planting areas currently growing maize and rapeseed with alternative crops to reduce environmental costs while maximizing food production as the climate changes.
Chinese food production has nearly doubled since the 1980s, mainly thanks to intensified nutrient usage and irrigation. Given that China’s demand for food is forecast to increase further, Qi Guan and colleagues modeled the country’s agricultural system under varying climate change scenarios in the 21st century, using a dynamic global vegetation model. The authors created scenarios ...
Cell-based therapy improves outcomes in a pig model of heart attacks
2025-01-07
BIRMINGHAM, Ala. – In a large-animal model study, researchers have found that heart attack recovery is aided by injection of heart muscle cell spheroids derived from human induced pluripotent stem cells, or hiPSCs, that overexpress cyclin D2 and are knocked out for human leukocyte antigen classes I and II. This research, published in the journal Circulation Research, used a pig model of heart attacks. Pig hearts more closely resemble the human heart in size and physiology, and thus have a higher clinical relevance to human disease, compared to studies in mice.
University of Alabama at Birmingham researchers, led by Jianyi “Jay” ...
Researchers have a better understanding of how our cells dispose of waste while developing ways to control it
2025-01-07
Recycling takes place in our cells at all times: in a process called autophagy, cell components that are no longer needed are enclosed by membranes and broken down into their basic building blocks. This vital process prevents the formation of harmful aggregates and makes nutrients available again. A research team co-led by Prof. Dr. Claudine Kraft from the CIBSS Cluster of Excellence at the University of Freiburg and Dr. Florian Wilfling from the Max Planck Institute of Biophysics in Frankfurt has now discovered the conditions necessary for autophagy to start. They were also able ...
Earth’s air war: Explaining the delayed rise of plants, animals on land
2025-01-07
New Haven, Conn. — If you like the smell of spring roses, the sounds of summer birdsong, and the colors of fall foliage, you have the stabilization of the ozone layer to thank for it. Located in the stratosphere, where it shields the Earth from harmful ultraviolet radiation, the ozone layer plays a key role in preserving the planet’s biodiversity.
And now we may have a better idea of why that took so long — more than 2 billion years — to happen.
According to a new, Yale-led study, ...
More than half of college students report alcohol-related harms from others
2025-01-07
FOR IMMEDIATE RELEASE
Tuesday, January 7, 2025
Contact:
Jillian McKoy, jpmckoy@bu.edu
Michael Saunders, msaunder@bu.edu
##
More than half of US college students experienced alcohol-related harms caused by others, according to the first national probability-based survey of such harms conducted in 20 years. The findings, published in the journal Drug and Alcohol Review in December, shed light on how others’ drinking affects students’ health, academics, and safety.
“Our research ...
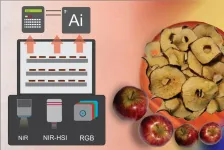
Smart food drying techniques with AI enhance product quality and efficiency
2025-01-07
URBANA, Ill.– Food drying is a common process for preserving many types of food, including fruits and meat; however, drying can alter the food’s quality and nutritional value. In recent years, researchers have developed precision techniques that use optical sensors and AI to facilitate more efficient drying. A new study from the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign discusses three emerging smart drying techniques, providing practical information for the food industry.
“With traditional drying systems, you need to remove samples to monitor the process. But with smart drying, or precision drying, you can continuously ...
Typical cost of developing new pharmaceuticals is skewed by high-cost outliers
2025-01-07
The typical cost of developing new medications may not be as high as generally believed, with a few ultra-costly medications skewing public discussions about the cost of pharmaceutical research and development, according to a new RAND study.
Using a novel method to assess spending on research and development for 38 drugs that were recently approved by the U.S. Food and Drug Administration, researchers found that the mean, or average, cost of developing a new drug was much higher than the mid-point (median) cost of development.
Researchers estimated a median direct research and development cost of $150 million compared to a mean of $369 million.
Costs ...
Predicting the progression of autoimmune disease with AI
2025-01-07
HERSHEY, Pa. — Autoimmune diseases, where the immune system mistakenly attacks the body’s own healthy cells and tissues, often have a preclinical stage before diagnosis that’s characterized by mild symptoms or certain antibodies in the blood. However, in some people, these symptoms may resolve before culminating in the full disease stage.
Knowing who may progress along the disease pathway is critical for early diagnosis and intervention, improved treatment and better disease management, according to a team led by researchers from the ...
Unlocking Romance: UCLA offers dating program for autistic adults
2025-01-07
Love doesn’t come with an instruction manual, but for autistic adults seeking to navigate the complexities of romance, a UCLA Health program offers a roadmap to finding and sustaining meaningful relationships through the launch of a new research study, called PEERS for Dating.
Led by the UCLA Program for the Education and Enrichment of Relationship Skills (PEERS) Clinic, the new 20-week program aims to demystify the often complex social rules surrounding dating and help participants gain a deeper understanding of relationship dynamics
“Romantic relationships can be transformative, but for many autistic adults, the path to connection can feel uncertain,” ...
Research Spotlight: Researchers reveal the influences behind timing of sleep spindle production
2025-01-07
How would you summarize your study for a lay audience?
Our research focuses on sleep spindles—short bursts of brain activity during sleep that are crucial for stabilizing sleep and supporting memory.
Sleep spindles are of great interest because changes in spindle activity have been linked to many neurodevelopmental and neurodegenerative disorders, such as Alzheimer’s disease and autism.
While many factors influence when and how these spindles occur, such as sleep stages or brain rhythms, we discovered that short-term patterns, like a musical rhythm spanning just a few seconds, play the most ...