(Press-News.org) KENNEDY SPACE CENTER (FL), January 7, 2025 – The International Space Station (ISSInternational Space Station) National Laboratory is soliciting flight concepts for technology advancement that utilizes the space-based environment of the orbiting laboratory. This solicitation, “Technology Advancement and Applied Research Leveraging the ISS National Lab,” is open to a broad range of technology areas, including chemical and material synthesis in space, translational medicine, in-space edge computing, and in-space servicing, assembly, and manufacturing. It also encompasses the application of space station remote sensing data to improve geospatial analytics for commercial use.
Space-based technology development and demonstration is a strategic priority for the ISS National Lab, as it provides an opportunity for accelerated technology maturation that may enable advancements to improve life for humanity and build commerce in low Earth orbit(Abbreviation: LEO) The orbit around the Earth that extends up to an altitude of 2,000 km (1,200 miles) from Earth’s surface. The International Space Station’s orbit is in LEO, at an altitude of approximately 250 miles. (LEO).
Through this research announcement, respondents may propose to use the unique environment of the orbiting platform to develop, test, or mature products and processes that have a demonstrated potential to produce near-term and positive direct or indirect economic impact. Flight concepts selected via this research announcement may be awarded funding to enable mission integration and operations support for projects that will be implemented on the space station.
Emphasis areas for this solicitation include but are not limited to:
Hardware prototype testing: Innovations addressing hardware product development gaps and emerging technology proliferation in the areas of electronics; semiconductors; nanotechnologies; robotics; sensors; and communications, remote sensing, computer, and satellite technology.
Process improvements: Use of the space station as a test bed to advance the development of facilities for high-throughput investigations or to demonstrate new methodologies for spaceflight research and development, or the use of space-based data to facilitate modeling of industrial systems.
Advanced materials: Current advanced materials research that addresses the development of next-generation production methods, testing of novel materials, and the exploitation of materials with unique properties.
Translational medicine: Validation of accelerated disease modeling, analyzing macromolecular structures for drug design, and demonstration of novel drug delivery and diagnostic services.
As an example, on SpaceX’s most recent Commercial Resupply Services mission for NASANational Aeronautics and Space Administration to the space station, Kall Morris Inc., launched a project funded through a prior ISS National Lab technology development solicitation. The project is testing the REACCH capture system for space debris removal using the Astrobees, free-flying autonomous robots on the space station, bringing the capture system closer to commercialization. The system could reduce risk to current space-based infrastructure and clear orbital slots for future infrastructure.
This research announcement will follow a two-step proposal submission process. Before being invited to submit a full proposal, all interested investigators must submit a Step 1: Concept Summary for review. The Center for the Advancement of Science in Space™, manager of the ISS National Lab, will host a webinar on Thursday, January 23, at 1 p.m. EST to discuss space station facilities and capabilities associated with this research announcement. Register in advance at the link.
Step 1: Concept Summaries must be submitted by the end of the day on March 3, 2025. Step 2: Full Proposals from those invited to submit will be due by the end of the day May 19, 2025. Multiple projects are expected to be awarded through this research announcement, with up to $650,000 in total funding available.
For more information about this opportunity, including how to submit a Step 1: Concept Summary, please visit the research announcement webpage. To learn more about the ISS National Lab and the science that it sponsors, please visit our website.
Download a high-resolution image for this release: NASA Astronaut Suni Williams
END
ISS National Lab announces up to $650,000 in funding for technology advancement in low Earth orbit
2025-01-08
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Scientists show how sleep deprived brain permits intrusive thoughts
2025-01-08
A new study has shown that sleep deprivation can inhibit the brain’s ability to suppress unwanted memories and intrusive thoughts.
Scientists at the University of York, in collaboration with the University of East Anglia, have shown that sleep deprivation interferes with the ability of the prefrontal area of the brain to restrict the retrieval of memories that would have otherwise been suppressed.
Dr Scott Cairney from the University of York said: “Memories of unpleasant experiences often intrude into our conscious ...
UC Irvine-led team discovers potential new therapeutic targets for Huntington’s disease
2025-01-08
Irvine, Calif., Jan. 8, 2025 — A University of California, Irvine-led research team has discovered intricate molecular mechanisms driving the RNA processing defects that lead to Huntington’s disease and link HD with other neurodegenerative disorders such as amyotrophic lateral sclerosis, frontotemporal lobar dementia and Alzheimer’s disease.
The findings may pave the way for neurodegenerative disorder researchers to collaborate and share therapeutic strategies across diseases, opening additional avenues for treatment.
While it’s known that HD is caused by an abnormal ...
Paul “Bear” Bryant Awards 2024 Coach of the Year finalists named
2025-01-08
HOUSTON, January 8, 2025 — Eight active college football coaches make up the American Heart Association’s 2024 Paul “Bear” Bryant Coach of the Year Award finalist list. The award is given each January to a college football coach for contributions that make the sport better for athletes and fans alike by demonstrating grit, integrity and a winning approach to coaching and life – both on and off the field. The Paul “Bear” Bryant Coach of the Year Award is the only college football coaching honor ...
Countering the next phase of antivaccine activism
2025-01-08
In a recent essay, pediatrician-scientist Peter Hotez proposes a focus on local data, improved benefit-risk communications, actively countering health disinformation, and state-level action to address antivaccine sentiment in the U.S.
Anti-vaccine sentiment isn’t going away any time soon. In a new opinion article published January 8 in the open-access journal PLOS Global Public Health, Prof. Peter Hotez from Baylor College of Medicine, outlines key actions to stem the momentum of anti-vaccine advocates in the U.S. over the next five years.
Anti-vaccine activities in the U.S. transformed to become a politically charged movement ...
Overcoming spasticity to help paraplegics walk again
2025-01-08
Electrical stimulation of the spinal cord is a promising strategy for reestablishing walking after spinal cord injury, recent studies show. But for patients suffering from muscle spasms, the stimulation protocols have a limited effect due to the unpredictable behaviour of involuntary muscle stiffness related to spasticity. Muscle spasticity affects almost 70% of spinal cord injured patients
Now, scientists at EPFL, Università San Raffaele and Scuola Sant’Anna have found a promising way to address and reduce muscle spasticity in patients with incomplete spinal cord injury. ...
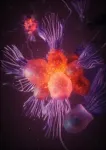
Tiny microbe colonies communicate to coordinate their behavior
2025-01-08
A new study published in Science Advances reveals evidence of electrical signaling and coordinated behavior in choanoflagellates, the closest living relatives of animals. This elaborate example of cell communication offers key insights into the early evolution of animal multicellularity and nervous systems.
Researchers from the Burkhardt group at the Michael Sars Centre, University of Bergen, uncovered a remarkable diversity of behaviors within the rosette-shaped colonies of the choanoflagellate Salpingoeca rosetta - and the small organisms held even more surprises. “We found communication among the cells of the colonies, which regulates shape and ciliary beating across the rosette,” ...
Researchers develop new technology for sustainable rare earth mining
2025-01-08
Ion-adsorption rare earth deposits (IADs) are primary sources of heavy rare earth elements (HREE), supplying over 90% of the global demand for HREE. However, the current ammonium-salt-based in-situ mining technique has led to severe environmental impacts.
To facilitate sustainable REE mining, Professors ZHU Jianxi and HE Hongping’s team from the Guangzhou Institute of Geochemistry of the Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS) has developed a green and efficient electrokinetic mining (EKM) technology.
Their work was published in Nature Sustainability on Jan. 6, 2025.
To address the challenges of sustainable and efficient REE extraction, ...
Words activate hidden brain processes shaping emotions, decisions, and behavior
2025-01-08
In an unprecedented new study in the journal Cell Reports, researchers have shown neurotransmitters in the human brain are released during the processing of the emotional content of language, providing new insights into how people interpret the significance of words.
The work, conducted by an international team led by Virginia Tech scientists, offers deeper understanding into how language influences human choices and mental health.
Spearheaded by computational neuroscientist Read Montague, a professor of the Fralin Biomedical Research Institute at VTC and ...
Understanding survival disparities in cancer care: A population-based study on mobility patterns
2025-01-08
A recent study published in Health Data Science, led by Dr. Fengyu Wen from the Institute of Medical Technology at Peking University Health Science Center and Professor Luxia Zhang from the National Institute of Health Data Science at Peking University, reveals significant survival disparities among cancer patients depending on their mobility patterns for medical care.
The study analyzed data from over 20,000 cancer patients in Shandong Province, China, to assess the impact of intra-city, local center, and national center mobility patterns on survival rates. Patients who traveled to local or national healthcare centers had higher five-year survival ...
Common sleep aid may leave behind a dirty brain
2025-01-08
Getting a good night’s sleep is a critical part of our daily biological cycle and is associated with improved brain function, a stronger immune system, and a healthier heart. Conversely, sleep disorders like insomnia and sleep apnea can significantly impact health and quality of life. Poor sleep often precedes the onset of neurodegenerative diseases and is a predictor of early dementia.
New research appearing in the journal Cell describes for the first time the tightly synchronized oscillations in the neurotransmitter norepinephrine, ...