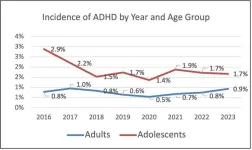
(Press-News.org) New research identifies differing trends in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) diagnoses among adolescents and adults, including an increase among adults from 2020 to 2023. The study, published in the American Psychiatric Association Journal Psychiatric Research and Clinical Practice, found a significant downward trends in ADHD incidence among adults from 2016 to 2020 and adolescents from 2016 to 2018. The ADHD incidence rate remained stable for adolescents in subsequent years.
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder involving inattention and/or hyperactivity and impulsivity that interferes with a person’s functioning and ability to perform daily activities, including at school or work. ADHD is often viewed as a condition primarily impacting childhood and adolescence; however, it can also affect adults. Research on the prevalence of ADHD in adults remains limited, with findings varying considerably.
The large retrospective cohort study, conducted by researchers at Saint Louis University and SSM Health, involved more than 140,000 adolescents and adult patients who used services with a large healthcare system located in four states. New ADHD diagnoses were identified using patient charts. Regression analysis was used to determine incidence rates and trends in ADHD diagnoses by age group.
They found a significant downward trend in ADHD incidence among adults from 2016 to 2020 and an upward trend from 2020 to 2023. Among adolescents, a significant downward trend was observed between 2016 and 2018, and the incidence rate remained stable between 2018 and 2023.
"Fluctuations in incidence rates are likely due to a complex interplay of various factors," the authors write. For example, increased awareness and destigmatization of ADHD can lead to more diagnoses. Changes in diagnostic criteria, such as the expansion of ADHD criteria in the DSM-5 compared to previous editions, may have contributed to an increase in diagnoses. Variations in diagnostic practices and assessment methods can contribute to differences in incidence rates. In addition, there are some indications, the authors note, that the COVID-19 pandemic may have contributed to new ADHD diagnoses and worsening symptoms.
The authors suggest that this research can support future efforts to identify modifiable risk factors, ensure sufficient treatment resources, develop targeted interventions, and address diagnostic disparities. The study authors include Margaret L. Paul, M.S., Poorva Sheth, B.S., Regan Davis, B.S., Timothy Chrusciel, M.P.H., Erick Messias, M.D., M.P.H., Ph.D.
More information
For a copy of full article, contact press@psych.org
More on ADHD
American Psychiatric Association
The American Psychiatric Association, founded in 1844, is the oldest medical association in the country. The APA is also the largest psychiatric association in the world with more than 38,900 physician members specializing in the diagnosis, treatment, prevention and research of mental illnesses. APA’s vision is to ensure access to quality psychiatric diagnosis and treatment. For more information, please visit www.psychiatry.org.
END
New research highlights trends in ADHD diagnoses
2025-01-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
United States dementia cases estimated to double by 2060
2025-01-13
A new study shows that the risk of developing dementia anytime after age 55 among Americans is 42%, more than double the risk reported by older studies.
That dementia risk translates into an estimated half-million cases this year, rising to 1 million new cases a year by 2060, according to the new work. Dementia involves progressive declines in memory, concentration, and judgment. The increasing number of cases is directly tied to the aging of the U.S. population. Beyond aging, a high risk of dementia is linked to genetic factors, as well as high rates of hypertension and diabetes, obesity, unhealthy diets, ...
“The biggest challenge is lacking public acceptance of wind turbines”
2025-01-13
In brief
In their overview study, the team of researchers led by Russell McKenna identified 14 key impact categories of wind energy.
They provide possible solutions for the identified impacts and suggest research priorities. More than 400 studies were included in the analysis.
The review paper, recently published in the journal Joule, provides guidance for future studies and policy decisions.
What is the study about, and what is its core message?
Russell McKenna: The study looks at the impacts of wind energy on the systems in which it is embedded; whether environmental and climate systems, socio-economic, ...
Six-month outcomes in the long-term outcomes after the multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children study
2025-01-13
About The Study: The results of this cohort study suggest that although children and young adults with multisystem inflammatory syndrome in children (MIS-C) can have severe disease during the acute phase, most recovered quickly and had a reassuring midterm prognosis.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Dongngan T. Truong, MD, email truongd@kidsheart.com.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2024.5466)
Editor’s Note: Please see the article for additional information, including other authors, author contributions and affiliations, ...
Global prevalence of sexual violence against children
2025-01-13
About The Study: The findings of this systematic review and meta-analysis highlight the burden of sexual violence against children worldwide based on current available evidence. There is a pressing need to enhance data collection efforts globally, especially in under-researched regions and for boys.
Corresponding Author: To contact the corresponding author, Antonio Piolanti, PhD, email antonio.piolanti@aau.at.
To access the embargoed study: Visit our For The Media website at this link https://media.jamanetwork.com/
(doi:10.1001/jamapediatrics.2024.5326)
Editor’s ...
Chances of quitting smoking improve with integrated care, including medication and counseling
2025-01-13
HOUSTON ― Smokers undergoing lung cancer screening may have the best chance of quitting if they receive integrated care, which includes medication and comprehensive counseling with tobacco treatment specialists, according to researchers at The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center.
The study results, published today in JAMA Internal Medicine, demonstrated that integrated care outperformed other cessation methods with a nearly two-fold improvement in the odds of quitting. In this randomized clinical trial of 630 current smokers who were eligible for lung cancer screening, over ...
From microplastics to macro-impact: KTU expert explains plastic recycling challenges
2025-01-13
“Microplastic particles are currently found almost everywhere – in water, food, fish, and even breast milk,” says Artūras Torkelis, a PhD student at Kaunas University of Technology (KTU). He emphasises that proper waste management is essential for reducing these risks.
The use of plastic in Europe has skyrocketed over the past decade. Recent statistics reveal that in 2021, each person in the European Union (EU) generated an average of 36 kg of plastic packaging waste. Of the more than 16 million tonnes of plastic packaging generated that year, only 6.5 million tonnes were recycled. Plastic recycling remains a serious problem. ...
How does the brain encode pain? Scientists uncover neuronal mechanisms of pain intensity encoding
2025-01-13
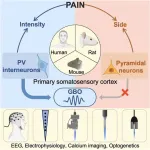
A research team led by Prof. HU Li at the Institute of Psychology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences, has revealed that parvalbumin (PV) interneurons in the primary somatosensory cortex (S1) preferentially encode pain intensity and drive nociceptive-evoked gamma oscillations (GBOs).
Published online in Neuron on January 13, the study fills a longstanding gap in understanding the origins of nociceptive-evoked GBOs and their selective relationship with pain processing across different species.
The findings suggest the potential for using these oscillations as a promising target for therapeutic interventions.
Pain is a ...
Study finds opioid pain medications very infrequently prescribed to NFL players
2025-01-13
INDIANAPOLIS – Due to the physical contact nature of their occupation, the elite athletes of the National Football League (NFL) often experience pain. However, an analysis of 2021 and 2022 data from the National Football League Prescription Drug Monitoring Program shows that team members in those two years were even less likely than both the general U.S. population and males of similar age living in the U.S., to have a prescription for an opioid pain medication.
The study found that less than 3 percent of pain medications prescribed to the athletes who played in one or both of the two seasons were for opioids. Slightly more than 86 percent of the ...
Wrong place, wrong time: Why Zika virus hijacks a protein needed for brain growth
2025-01-13
The mosquito-borne Zika virus is known for causing microcephaly, a birth defect in which abnormal brain development results in a smaller-than-expected head. A new study published Jan. 13 in mBio shows that the Zika virus hijacks a host protein called ANKLE2, which happens to be important for brain development, to assist its own reproduction. Because Zika, unlike most related viruses, can cross the placenta, this can have disastrous consequences in pregnancy.
“It’s a case of Zika being in the wrong place at the wrong time,” said Priya Shah, associate professor in the departments of Microbiology and Molecular ...
The new age of infrastructure maintenance using data from space
2025-01-13
The concentration of the population in cities is accelerating, and difficulties in maintaining various infrastructures are arising due to extreme weather. Extensive infrastructures like waste landfill facilities face significant challenges due to the difficulty for managers to stay on-site or access them. These maintenance issues are resulting in various problems, including environmental pollution.
To solve these issues, Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Building Technology (KICT, President Sun Kyu, Park) has developed a cost-effective and high-efficiency maintenance technology using satellite ...