(Press-News.org) Preschool wheeze is a common condition in children under six, affecting 30-40% of children
Aston University’s Dr Gemma Heath led a study into parents’ experiences of managing preschool wheeze, including confusion and psychological distress
They identified problems with inconsistent terminology and uncertainty around diagnosis and say a unified approach is needed.
A study led by Aston University’s Dr Gemma Heath and Dr Prasad Nagakumar from Birmingham Children’s Hospital, has shown that treatment and diagnosis for preschool wheeze needs more effective evidence-based guidelines.
Preschool wheeze is a condition affecting approximately 30–40% of children under six. The condition is characterised by episodes of wheezing or breathlessness, with younger children being particularly susceptible due to their narrower airways. Although it can resemble asthma, preschool wheeze is often triggered by viral infections or allergies and does not always mean a child will develop asthma.
The UK has the second highest prevalence of preschool wheeze in two-year-olds across Europe. It is a leading cause of emergency hospital visits and hospitalisations in the country. Repeated preschool wheeze attacks are frightening for parents, and result in significant morbidity, healthcare costs and impaired quality of life for both the child and parent.
There is currently no diagnostic pathway or definitive management guidelines for preschool wheeze. The research team interviewed affected parents and carers about their experiences, and found problems with diagnosis and treatment at multiple levels.
The first major issue identified by parents was inconsistent terminologies used by doctors, and confusing and conflicting diagnoses such as asthma, suspected asthma, viral wheeze and allergy. Some reported frustration at the lack of definitive diagnosis, an apparent lack of GP knowledge, sometimes false reassurance that the wheeze was viral rather than asthma, or that the cause was a “mystery”.
A common problem was that investigative tests did not occur until after multiple hospitalisations. Blood tests for particular markers have potential to identify whether asthma or an allergy is likely to have caused the wheeze, and therefore guide treatment. The parents in the study welcomed the idea of timely tests, but stressed that children should not be subjected to repeated testing.
Preschool wheeze is generally managed with steroid and salbutamol inhalers, as for asthma. While parents had concerns about the side-effects and long-term impacts of using the treatments, they deemed the medication “an acceptable cost”.
Parents reported being “terrified” while watching attacks of preschool wheeze, and significant psychological impacts when their child was admitted to hospital. Some had missed work or even given up work to care for their child, with high levels of anxiety, while others said they felt unable to go on holiday overseas due to concerns about healthcare access in the case of a wheeze attack.
Most parents preferred to access care at hospital rather that at doctors’ surgeries due to the perception of a lack of training for GPs and a lack of confidence. However, accessing necessary care can be difficult, including due to childcare difficulties, the cost of hospital parking and a lack of available ambulances.
The research team said that parents’ views highlight the problems and called for clinical trials to determine the efficacy of treatment decisions made according to the results of investigations.
Dr Heath said:
“This research demonstrates an urgent need for preschool wheeze management policies and treatment pathways that are evidence-based and co-developed with parents. We have shown that use of investigations such as blood or allergy tests would be acceptable to parents, if they were shown to be helpful in guiding more effective and timely treatments.”
Dr Nagakumar said:
“Preschool wheeze has significant impact on young children’s and their parents’ lives. Our research, involving parents with lived experience, will inform future studies to improve the care and reduce the impact of preschool wheeze on the already-stretched emergency health services in the UK.”
Archives of Disease in Childhood doi: 10.1136/archdischild-2024-327781
END
Aston University and Birmingham Children’s Hospital study shows diagnosis and treatment of preschool wheeze needs improvement
2025-01-13
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Manure management in China cuts river antibiotic pollution but raises groundwater contamination risks
2025-01-13
A recent study published in Environmental Science and Ecotechnology reveals significant changes in antibiotic pollution patterns in China’s water systems over the past decade, driven by evolving manure management practices. Conducted by researchers from China Agricultural University and Wageningen University, the study developed the MARINA-Antibiotics (China-1.0) model to track antibiotic flows from livestock manure into rivers and groundwater across 395 sub-basins between 2010 and 2020.
The study found a 59% decrease in antibiotic pollution in rivers, primarily due to improved manure recycling and reduced direct manure discharge into waterways. However, ...
New book provides big recommendations from the Advancing the Science of Cancer in Latinos Conference
2025-01-13
SAN ANTONIO, Jan. 13, 2025 – With cancer still rising in the U.S. Latino population, leaders at The University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio (UT Health San Antonio) and national cancer experts have published an online book with innovative recommendations to reduce Latino cancer.
The book, “Advancing the Science of Cancer in Latinos: 2024 Conference Proceedings,” highlights results of the same-named conference that brought 300 researchers, advocates and survivors to San Antonio in February 2024.
A follow-up conference is planned for Feb. 18-20, 2026, in San Antonio.
Included ...
Ash tree variability may offer restoration path post-beetle decimation
2025-01-13
UNIVERSITY PARK, Pa. — The invasive emerald ash borer, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture, was first found in the United States in southeast Michigan in 2002. In the decades since, the wood-boring beetle has spread east and west across the U.S. and Canada, killing tens of millions of ash trees, causing one of the costliest forest insect invasions to date. More than 90% of all ash infested by the insect native to Asia eventually die, threatening to make the tree species functionally extinct in North America. In response, researchers at Penn State are working with the U.S. Forest Service and other partners to identify and develop ...
Integrating CRISPR and biomaterials engineering: Paving the way for safer gene therapies
2025-01-13
CRISPR is a powerful gene-editing tool that holds enormous potential for treating genetic diseases by allowing scientists to cut, replace, or delete mutations in DNA. It can also modify gene expression, temporarily amplifying or diminishing its effects.
Yet, despite its promise, applying CRISPR (which is a reagent, or a substance that facilitates a reaction) in patients presents significant challenges.
“CRISPR is difficult to control when you want to do gene editing in vivo, or directly in the patient,” says Tomas Gonzalez-Fernandez, an assistant professor of bioengineering in Lehigh University’s P.C. Rossin College of Engineering ...
New tool for synthetic biology
2025-01-13
Scientists at the University of Stuttgart have succeeded in controlling the structure and function of biological membranes with the help of "DNA origami". The system they developed may facilitate the transportation of large therapeutic loads into cells. This opens up a new way for the targeted administration of medication and other therapeutic interventions. Thus, a very valuable instrument can be added to the toolbox of synthetic biology. Prof. Laura Na Liu and her team published their findings in the journal Nature Materials (DOI: 10.1038/s41563-024-02075-9).
The ...
Yu & Martin adapting mixed reality training programs to real-world scenes to enhance human-AI teaming in emergency responses
2025-01-13
Lap Fai (Craig) Yu, Associate Professor, Computer Science, College of Engineering and Computing, and Joel Martin, Associate Professor, Kinesiology, College of Education and Human Development, received funding for the project: “EAGER: TaskDCL: Adapting Mixed Reality Training Programs to Real-World Scenes to enhance Human-AI Teaming in Emergency Responses.”
This EArly-concept Grant for Exploratory Research (EAGER) project funds research that intends to speed up the development of mixed reality and artificial intelligence (AI) technologies to help ...
ExxonMobil donates $10 million to fund MD Anderson-led Be Well™ Beaumont initiative
2025-01-13
HOUSTON and BEAUMONT, TEXAS ― In an effort to improve public health and reduce cancer risk in East Texas, leaders in Beaumont are working with The University of Texas MD Anderson Cancer Center to launch Be Well™ Beaumont through a newly announced $10 million gift from ExxonMobil. Community members, collaborators and representatives from MD Anderson kicked off the 10-year initiative today in Beaumont.
Be Well Beaumont aims to promote wellness and to lower cancer risk among community members by providing them with cancer prevention education and tools. ...
Long reads successfully used to find genetic causes of rare diseases
2025-01-13
The cause of rare diseases is increasingly being detected through genome sequencing, which involves reading the entire human DNA by first breaking it into small pieces—short reads. Christian Gilissen, Lisenka Vissers, and colleagues found that a new technique using long reads is even more effective at detecting complex causes. They report that eighty to ninety percent of cases were detectable, as stated in the American Journal of Human Genetics.
Rare diseases are typically due to genetic causes. These causes are more and ...
X-ray flashes from a nearby supermassive black hole accelerate mysteriously
2025-01-13
One supermassive black hole has kept astronomers glued to their scopes for the last several years. First came a surprise disappearance, and now, a precarious spinning act.
The black hole in question is 1ES 1927+654, which is about as massive as a million suns and sits in a galaxy that is 100 million light-years away. In 2018, astronomers at MIT and elsewhere observed that the black hole’s corona — a cloud of whirling, white-hot plasma — suddenly disappeared, before reassembling months later. The brief though dramatic shut-off was a first in black hole astronomy.
Members of the MIT team have now caught the same black hole exhibiting ...
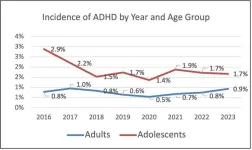
New research highlights trends in ADHD diagnoses
2025-01-13
New research identifies differing trends in attention-deficit/hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) diagnoses among adolescents and adults, including an increase among adults from 2020 to 2023. The study, published in the American Psychiatric Association Journal Psychiatric Research and Clinical Practice, found a significant downward trends in ADHD incidence among adults from 2016 to 2020 and adolescents from 2016 to 2018. The ADHD incidence rate remained stable for adolescents in subsequent years.
ADHD is a neurodevelopmental disorder involving inattention and/or hyperactivity and impulsivity that interferes with a person’s functioning and ability ...