(Press-News.org) Giant isopods of the genus Bathynomus, which can reach more than 30 cm in length, are known as bọ biển or “sea bugs” in Vietnam. For the first time, one such species was described from Vietnamese waters and named Bathynomus vaderi. The name “vaderi” is inspired by the appearance of its head, which closely resembles the distinctive and iconic helmet of Darth Vader, the most famous Sith Lord of Star Wars.
Bathynomus vaderi belongs to a group known as “supergiants,” reaching lengths of 32.5 cm and weighing over a kilogram. So far, this new species has only been found near the Spratly Islands in Vietnam, but further research will probably confirm its presence in other parts of the South China Sea.
Giant isopods like Bathynomus vaderi have become an expensive delicacy in Vietnam. Until 2017, local fishermen only sold them as a bycatch product for low prices, but in recent years the media has drawn public attention to this unusual seafood. Some go as far as claiming it’s more delicious than lobster, the “king of seafood”.
These animals have been commercially fished by trawlers operating in various deep-water parts of Biển Đông ( East Sea, Vietnamese part of the South China Sea) and offshore of provinces in south-central coastal of Vietnam. Over the last five years, it has become common to see them sold alive in some seafood markets in Hanoi, Hồ Chí Minh City, and Đà Nẵng City. Some outlets and restaurants even advertise the sale of these “sea bugs” online on various social media platforms, including how best to cook them!
In March 2022, staff from Hanoi University purchased four giant isopod individuals from Quy Nhơn City and sent two of them to Peter Ng from the Lee Kong Chian Natural History Museum in the National University of Singapore for identification. Peter Ng has a very active crustacean laboratory in Singapore and has worked on the deep-sea fauna from many parts of Asia. He subsequently co-opted Conni M. Sidabalok from the National Research and Innovation Agency Indonesia, who had described Bathynomus from southern Java with him. Together with Nguyen Thanh Son from the Vietnam National University, who is the resident crustacean researcher there, they studied the specimens. In early 2023, they realised they had specimens of a so far undescribed species. Now, they have published their findings in the open-access journal ZooKeys.
The discovery of a species as strange as Bathynomus vaderi in Vietnam highlights just how poorly we understand the deep-sea environment. That a species as large as this could have stayed hidden for so long reminds us just how much work we still need to do to find out what lives in Southeast Asian waters.
There is an urgent need to better understand our deep-sea biodiversity as humans increasingly endeavour to exploit this habitat for fisheries, oil and gas, and even minerals. The sustainable fishery of giant isopods just adds to the many challenges we face. And the first step is to know what lives there.
Original source:
Ng PKL, Sidabalok CM, Nguyen TS (2025) A new species of supergiant Bathynomus A. Milne-Edwards, 1879 (Crustacea, Isopoda, Cirolanidae) from Vietnam, with notes on the taxonomy of Bathynomus jamesi Kou, Chen & Li, 2017. ZooKeys 1223: 289–310. https://doi.org/10.3897/zookeys.1223.139335
END
The Dark Side of the ocean: New giant sea bug species named after Darth Vader
2025-01-14
ELSE PRESS RELEASES FROM THIS DATE:
Roman urbanites followed medical recommendations for weaning babies
2025-01-14
Babies were weaned earlier in cities in the Roman Empire than in smaller and more rural communities, according to a study of ancient teeth. Urban weaning patterns more closely hewed to guidelines from ancient Roman physicians, mirroring contemporary patterns of adherence to medical experts in urban and rural communities.
Roman health authorities recommended breastfeeding babies for two years. Carlo Cocozza and colleagues were interested in how ancient Romans actually fed their babies in varying settlement types. Carbon and nitrogen isotope ratios in dentine from the first permanent molars record ...
Strength connected to sexual behavior of women as well as men
2025-01-14
VANCOUVER, Wash. – While many studies have looked at possible evolutionary links between men’s strength and sexual behavior, a Washington State University study included data on women with a surprising result. Women, as well as men, who had greater upper body strength tended to have more lifetime sexual partners compared to their peers.
The study, published in the journal Evolution and Human Behavior, was designed to test evolutionary theories for human sexual dimorphism—namely that in early human history there was likely a reproductive advantage selecting for men’s greater upper body strength.
Another ...
Eating pork linked with better handgrip strength, vegetable intake in Korean older adults
2025-01-14
New research1 underscores the potential role of pork consumption in supporting dietary and muscle health in Korean older adults. Older adults are a nutritionally vulnerable population who often face unique challenges, including meeting daily protein and micronutrient requirements.
The study,* conducted through a collaborative partnership between researchers from Gachon University in South Korea, Tufts University, Think Healthy Group, LLC, and other leading institutions, suggests that pork consumption may be positively linked to nutrient intake, diet quality and handgrip strength—an indicator of overall muscle strength in older adults.
Using data from more than 2,000 ...
Direct discharge electrical pulses for carbon fiber recycling
2025-01-14
The world is hurtling rapidly towards a developed future, and carbon fiber-reinforced polymers (CFRPs) play a key role in enabling technological and industrial progress. These composite materials are lightweight and highly strong, making them desirable for applications in various fields, including aviation, aerospace, automotive, wind power generation, and sports equipment.
However, recycling CFRPs presents a significant challenge, with waste management being a pressing issue. Conventional recycling methods ...
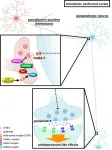
Scientists uncover rapid-acting, low-side-effect antidepressant target
2025-01-14
The global burden of anxiety- and depression-related disorders is on the rise. While multiple drugs have been developed to treat these conditions, current medications have several limitations, including slow action and adverse effects with long-term use. This underscores the urgent need for novel, rapidly-acting therapeutic agents with minimal side effects.
The delta opioid receptor (DOP) plays a key role in mood regulation, making it a promising target for therapeutic intervention. Studies have shown that selective DOP agonists (compounds that activate DOP), such as SNC80 ...
Diamond continues to shine: new properties discovered in diamond semiconductors
2025-01-14
CLEVELAND and CHAMPAIGN-URBANA, ILL.—Diamond, often celebrated for its unmatched hardness and transparency, has emerged as an exceptional material for high-power electronics and next-generation quantum optics. Diamond can be engineered to be as electrically conductive as a metal, by introducing impurities such as the element boron.
Researchers from Case Western Reserve University and the University of Illinois Urbana-Champaign have now discovered another interesting property in diamonds with added boron, known as boron-doped diamonds. Their findings could pave the way for new types ...
Researchers find the key to Artificial Intelligence’s learning power – an inbuilt, special kind of Occam’s razor
2025-01-14
A new study from Oxford University has uncovered why the deep neural networks (DNNs) that power modern artificial intelligence are so effective at learning from data. The new findings demonstrate that DNNs have an inbuilt ‘Occam's razor,’ meaning that when presented with multiple solutions that fit training data, they tend to favour those that are simpler. What is special about this version of Occam’s razor is that the bias exactly cancels the exponential growth of the number of possible solutions with complexity. The study has been published ...
Genetic tweak optimizes drug-making cells by blocking buildup of toxic byproduct
2025-01-14
An international team of researchers led by the University of California San Diego has developed a new strategy to enhance pharmaceutical production in Chinese hamster ovary (CHO) cells, which are commonly used to manufacture protein-based drugs for treating cancer, autoimmune diseases and much more. By knocking out a gene circuit responsible for producing lactic acid—a metabolite that makes the cells’ environment toxic—researchers eliminate a primary hurdle in developing cells that can produce higher amounts of pharmaceuticals like Herceptin and Rituximab, without compromising their growth or energy production.
The research, published on Jan. 14 in Nature Metabolism, ...
University of Birmingham researchers awarded grant to tackle early-stage heart disease in chronic kidney disease
2025-01-14
New research funding will investigate the early stages of heart disease associated with chronic kidney disease led by the University of Birmingham.
Dr Davor Pavlovic will lead an international research team after receiving almost £300,000 from the British Heart Foundation to understand the mechanisms driving the early stages of CKD-associated cardiomyopathy.
The research approach will allow detailed investigation of cellular and electrophysiological changes before irreversible damage to the heart occurs. Researchers will also test whether in the setting of CKD, early treatment can reverse or prevent heart disease.
The research will be ...
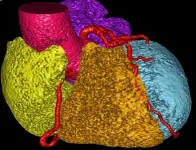
Researchers harness AI to predict cardiovascular risk from CT scans
2025-01-14
CLEVELAND—Researchers at Case Western Reserve University, University Hospitals and Houston Methodist will harness the power of artificial intelligence (AI) to more accurately predict risk of heart failure and other cardiovascular events, including estimating when an adverse event might occur, by developing an AI model that “learns” from patient scans.
Cardiovascular disease is the leading cause of death worldwide, claiming over 17 million lives every year, according to the American Heart Association. Accurately ...